Chloroplasts - Structure
Summary
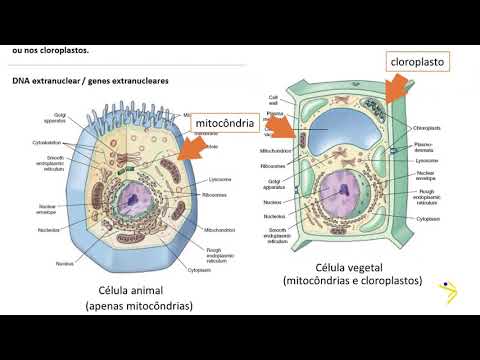
TLDRThis module explains the structure and function of chloroplasts, the organelles responsible for photosynthesis. It highlights how the number, size, and shape of chloroplasts vary among different plants and conditions. Chloroplasts consist of a bilayer membrane, with an inner selectively permeable layer enclosing a stroma filled with enzymes, DNA, and ribosomes. Within the stroma, thylakoid membranes form structures called grana, essential for photosynthesis. These thylakoids house photosystems, which capture solar energy. The internal organization of chloroplasts is more complex than other organelles due to their multiple membrane systems.
Takeaways
- 🌱 Chloroplasts are membrane-bound organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plants.
- 🍃 The number of chloroplasts per cell varies, with green algae having a constant number, while higher plants have between 30 and 200 chloroplasts per cell.
- 📏 Chloroplasts vary in size, typically 4-5 micrometers, and are larger in plants growing in shade compared to those in intense light.
- 🔵 Chloroplast shapes differ by species: plate-shaped in Chlorella, cup-shaped in Chlamydomonas, ribbon-shaped in Spirogyra, and star-shaped in Zygnema.
- 🔬 Chloroplasts are surrounded by a double membrane called the chloroplast envelope, with the inner membrane being selectively permeable and containing transporters.
- 🧬 Inside the chloroplast is a protein-rich substance called stroma, which contains enzymes, DNA, RNA, and ribosomes.
- 🌞 The thylakoid membrane system divides the chloroplast into three compartments: the intermembrane space, the stroma, and the thylakoid lumen.
- 🌾 Thylakoids are flattened discs arranged in stacks called grana, connected by intergranal lamellae, and are involved in photosynthesis.
- 💡 Thylakoid membranes are made of 20-30% lipids and 70-80% proteins, with embedded structures called quantasomes responsible for capturing solar energy.
- 🌿 Photosystems in the thylakoids include Photosystem II (PS2) and Photosystem I (PS1), which contain chlorophyll and carotenoids, essential for photosynthesis.
Q & A
What is the primary function of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are membrane-bound organelles that serve as the main centers for photosynthesis in plant cells.
How does the number of chloroplasts vary among different plants and plant cells?
-The number of chloroplasts varies widely. In green algae, like *Chlamydomonas* and *Spirogyra*, the number is constant, while in higher plants, the number ranges from 30 to 200 per cell.
What factors influence the size of chloroplasts in plants?
-The size of chloroplasts varies by plant species, with general dimensions of 4 to 5 micrometers. Plants growing in shade have larger chloroplasts compared to those growing in intense light.
How does the shape of chloroplasts vary across different species?
-Chloroplast shape differs by species: plate-shaped in *Chlorella*, cup-shaped in *Chlamydomonas*, ribbon-shaped in *Spirogyra*, star-shaped in *Zygnema*, and spherical or ovoidal in higher plants.
What is the chloroplast envelope and how does it function?
-The chloroplast envelope is a bilayer membrane surrounding the chloroplast. The outer membrane is permeable to molecules, while the inner membrane is selectively permeable, containing transporters that regulate the passage of molecules like sugars.
What is the stroma and what does it contain?
-The stroma is a protein-rich fluid inside the chloroplast, containing enzymes, DNA, RNA, and ribosomes, playing a role in the synthesis of organic molecules during photosynthesis.
What are thylakoids, and how are they arranged inside the chloroplast?
-Thylakoids are membrane-bound flattened discs within the chloroplast, arranged in stacks called grana. The thylakoid membranes are interconnected by tubular membranes called intergrana lamellae.
What are quantasomes, and what role do they play in chloroplasts?
-Quantasomes are granular structures embedded in the thylakoid membranes, responsible for capturing photons of solar energy and acting as photosynthetic units. They include photosystem II (PS2) and photosystem I (PS1).
What pigments are found in thylakoid membranes, and what is their function?
-Thylakoid membranes contain chlorophyll a and b, which are green pigments, and carotenoids, which range from yellow to red. These pigments absorb light energy for photosynthesis.
How does the three-membrane structure of chloroplasts contribute to its complexity?
-The three-membrane structure, consisting of the outer and inner membranes and the thylakoid membranes, creates distinct internal compartments, making the organization of chloroplasts more complex than that of other organelles.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード5.0 / 5 (0 votes)