Chapter 1
Summary
TLDRThe transcript introduces quantitative business analysis, highlighting its evolution from the scientific management revolution to the modern era of computing power. It emphasizes the importance of blending qualitative and quantitative methods for effective decision-making, especially in complex, critical, new, and repetitive problems. The process involves identifying and defining problems, evaluating alternatives, and selecting the best solution using mathematical models, which are crucial for understanding and optimizing business operations.
Takeaways
- 📊 Quantitative Business Analysis encompasses various fields like management science, operations research, decision science, and business analytics.
- 🏭 It originated from the scientific management revolution (Taylorism) in the early 20th century, aiming to improve workplace efficiency.
- 💡 Post-WWII developments in methodological understanding and computing power significantly advanced quantitative analysis.
- 🔍 The process of quantitative business analysis involves seven steps, with the first five focusing on decision-making through problem identification, alternative selection, criteria determination, evaluation, and choice.
- 📈 Both qualitative and quantitative analyses are essential for decision-making, with qualitative aspects like experience and intuition being valuable for simpler problems.
- 🔢 Quantitative methods are particularly useful for complex, critical, new, and repetitive problems, providing more structured and data-driven decision-making.
- 🛠️ Model development is a key component, requiring the definition of objective functions and constraints, as well as understanding controllable and uncontrollable inputs.
- 📊 The course will focus on mathematical models, including cost, revenue, and profit models, which need to accurately represent real-world situations.
- 💧 Data preparation is often the most time-consuming part of quantitative analysis, requiring careful formatting and ensuring all necessary variables are accounted for.
- 📝 Interpreting the results of quantitative methods is crucial, with an emphasis on understanding when and how to use these methods effectively.
- 🚀 Modern computing power has reduced the need for manual calculations, shifting the focus to setting up the models and interpreting their outcomes.
Q & A
What is quantitative business analysis?
-Quantitative business analysis is the use of mathematical and statistical methods to support decision-making and problem-solving in business. It may also be referred to as management science, operations research, decision science, or business analytics.
How did quantitative business analysis originate?
-Quantitative business analysis originated with the scientific management revolution in the early 20th century, also known as Taylorism, which introduced more efficient ways of working in factories and workplaces, contributing to economic growth.
What developments made quantitative business analysis more prevalent?
-Two significant developments contributed to the prevalence of quantitative business analysis: methodological advancements in probability, regression analysis, forecasting, and linear programming, and the explosion in computing power that allows for quick data processing and decision-making.
What are the steps of problem-solving in quantitative business analysis?
-The steps of problem-solving in quantitative business analysis include identifying and defining the problem, determining the set of alternatives, establishing evaluation criteria, evaluating the alternatives, and choosing an alternative.
How does quantitative analysis complement qualitative analysis in decision-making?
-Quantitative analysis complements qualitative analysis by providing numerical data and mathematical models to support decision-making, especially for complex, critical, new, or repetitive problems. It allows for a more objective assessment alongside the subjective insights and experiences from qualitative analysis.
What types of models are discussed in the context of quantitative business analysis?
-Three types of models are discussed: iconic models, analog models, and mathematical models. The focus of the course is on developing and understanding mathematical models.
What are the components of a mathematical model in quantitative business analysis?
-A mathematical model in quantitative business analysis includes objective functions, which can be minimizing or maximizing something, and constraints, which define what is feasible and not feasible.
What are controllable and uncontrollable inputs in a mathematical model?
-Controllable inputs are the decision variables that can be manipulated, while uncontrollable inputs are factors outside of the decision-maker's control that are taken as given.
What is the importance of data preparation in quantitative analysis?
-Data preparation is crucial in quantitative analysis as it ensures the data is in the correct format and shape for analysis. It involves identifying all necessary variables, handling missing observations, and preparing the data for the model solution.
What is the role of a report or summary in quantitative analysis?
-A report or summary is used to communicate the results of quantitative analysis. It helps interpret the data and present the findings in a way that is understandable to stakeholders who may not be familiar with the technical aspects of the analysis.
What simple mathematical models are introduced in the script?
-The script introduces models of cost, revenue, and profit. These models help in understanding how to minimize costs, maximize profits, and perform break-even analysis based on given volumes and costs.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

PENGGUNAAN SOFTWARE, DATA dan MANAJEMEN DATA | PENGANTAR SAINS DAN DATA

matematica pra que

Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind | By Yuval Noah Harari | Book Summary

Sejarah Perkembangan Manajemen dan Teori Teori Manajemen | Topik 2 Pengantar Manajemen

#1.2 Sejarah Perkembangan Manajemen dari Masa ke Masa
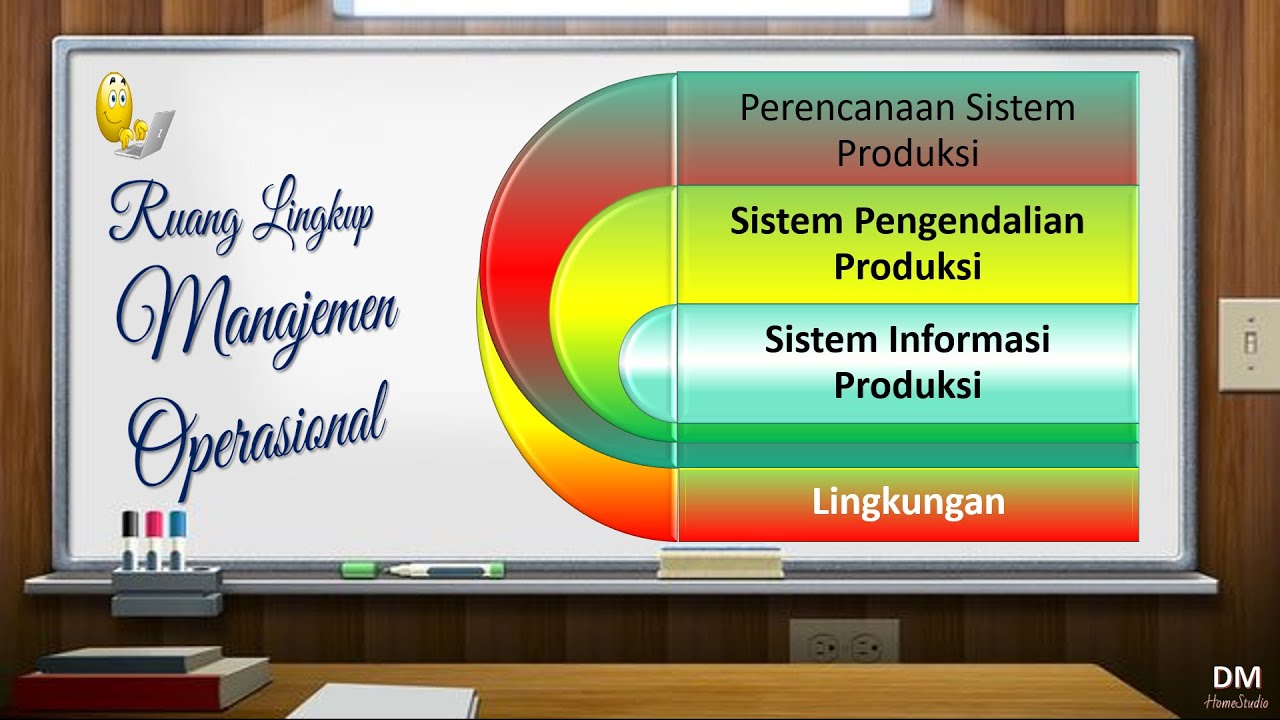
Pengantar Manajemen Operasional
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
