NCEA L1 Science: Punnett Squares And Pedigree Chart Explained
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the fundamentals of genetics, focusing on key concepts like DNA, genes, alleles, and base sequences. It explains how different versions of genes, or alleles, lead to variations in physical traits, using examples like hairline patterns. The video also teaches how to use Punnett squares and pedigree charts to predict genetic outcomes in offspring, with practical examples like albinism in rats. It emphasizes the importance of understanding dominant and recessive alleles, and how they manifest in different genotypes, providing a comprehensive guide for students navigating genetics.
Takeaways
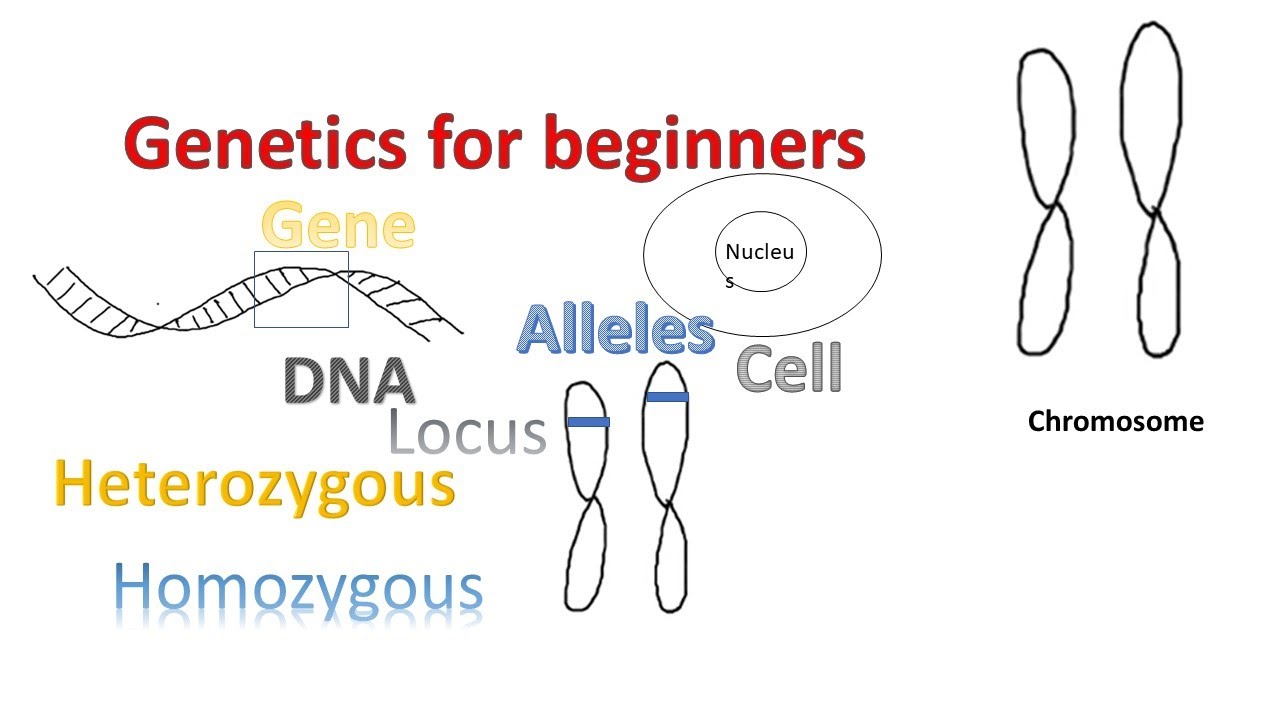
- 🧬 DNA is the double helix structure that contains all genetic information, with specific sections called genes that represent individual traits.
- 🔑 Genes have different versions known as alleles, which are responsible for variations of the same trait due to different base sequences (A, T, C, G).
- 🔠 Dominant alleles are represented by capital letters and are more likely to be expressed, while recessive alleles are in lowercase and only appear when no dominant allele is present.
- 🌟 Understanding the difference between heterozygous (one dominant, one recessive allele) and homozygous (two dominant or two recessive alleles) genotypes is crucial for predicting genetic outcomes.
- 📊 Punnett squares are used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring by combining the alleles of two parents.
- 🐀 The example of rat coloration, where albinism is caused by a recessive allele (small a), illustrates how genetic traits can be analyzed.
- 👨👩👧👦 Pedigree charts help visualize the inheritance of traits within a family tree and are essential for predicting genetic outcomes across generations.
- 🔄 The importance of understanding both forward (from parents to offspring) and backward (from offspring to parents) inheritance to solve genetic problems.
- 📚 The video emphasizes the value of practice with past exam papers for mastering genetics and related statistical analysis.
- 🌐 The instructor encourages students to utilize available resources, like past exams on the instructor's YouTube channel, for better understanding and preparation.
Q & A
What is DNA and what is its significance?
-DNA stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, and it is the double helix structure that contains all the genetic information. It is crucial as it carries the instructions for the development, functioning, growth, and reproduction of all known living organisms and many viruses.
What is a gene and how does it relate to physical traits?
-A gene is a segment of DNA that represents one particular trait or physical characteristic. It is responsible for determining specific features such as eye color or hair type.
What are alleles and how do they contribute to genetic variation?
-Alleles are different versions of the same gene, which can result in different expressions of the same trait. They arise due to variations in the base sequence of DNA, leading to genetic diversity.
What is the difference between a dominant and a recessive allele?
-A dominant allele is a version of a gene that is expressed when present, even in a single copy. A recessive allele, on the other hand, is only expressed when two copies are inherited. Dominant alleles are usually represented by uppercase letters, while recessive alleles are represented by lowercase letters.
What is meant by the term 'heterozygous' in genetics?
-Heterozygous refers to an individual having two different alleles for a particular gene. This means they have one dominant and one recessive allele, resulting in a mix of traits.
How is a Punnett square used in genetics?
-A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the genotypes of offspring based on the genotypes of the parents. It is a simple way to visualize the possible genetic combinations that can occur in a cross.
What is a pedigree chart and how is it used to study genetics?
-A pedigree chart is a graphical representation of the inheritance of a particular trait through successive generations of a family. It helps in understanding the pattern of inheritance and predicting the likelihood of a trait appearing in future generations.
Why is it important to understand the difference between genotype and phenotype in genetics?
-Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an individual, including the alleles they carry for specific traits. Phenotype is the observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an individual, which results from the interaction of their genotype and the environment. Understanding this difference is important for predicting how traits will be expressed and inherited.
What is the significance of the term 'homozygous' in the context of genetics?
-Homozygous refers to an individual having two identical alleles for a particular gene. This can be either homozygous dominant, where both alleles are dominant, or homozygous recessive, where both alleles are recessive. It is significant because it indicates a higher likelihood of the trait being expressed consistently.
How can one determine the likelihood of an offspring inheriting a specific trait?
-The likelihood of an offspring inheriting a specific trait can be determined by analyzing the genotypes of the parents and using tools like Punnett squares or pedigree charts. This allows for the prediction of the probability of different genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

Introduction to Cytogenetics (Filipino) Genes Alleles Chromosomes

RESUMO - Conceitos básicos de Genética - 3 ano
Genetics for beginners | Genes Alleles Loci on Chromosomes |

EASY TO UNDERSTAND | INTRO TO GENETICS
Inheritance Explained || How do we inherit features from our parents?

MATERI GENETIKA: BIOLOGI KELAS 12 SMA
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
