Similar Triangles - GCSE Maths
Summary
TLDRThis educational video explores the concept of similar triangles, focusing on two types of problems: connected triangles and overlapping ones. It explains that similar triangles have a constant scale factor, and this is used to solve problems involving unknown side lengths. The video demonstrates how to find missing values by setting up equations based on the properties of similar triangles, including corresponding angles and proportional sides. It also covers how to handle more complex scenarios with given ratios and multiple triangles, providing a step-by-step approach to solving such geometric problems.
Takeaways
- 🔍 The video discusses the concept of similar triangles, focusing on two types of problems: triangles that are connected and triangles that overlap.
- 📏 It explains that for two triangles to be similar, there must be a constant scale factor when comparing their corresponding sides.
- 📐 The script demonstrates how to find the scale factor by dividing pairs of corresponding sides and shows that the reciprocal of these fractions also yield the same value.
- 📝 It highlights that the scale factor can be determined by comparing sides within the same triangle, emphasizing the consistency in the method used for comparison.
- 🔄 The video uses the concept of alternate angles to show that triangles connected by parallel lines are similar, as these angles are equal.
- 📈 It provides a method to solve for missing side lengths in similar triangles by setting up equations based on the proportionality of corresponding sides.
- 📚 The script introduces the technique of using fractions to solve problems involving similar triangles, which is particularly useful for more complex questions.
- 📋 The video gives examples of worded problems involving similar triangles and demonstrates step-by-step solutions, emphasizing the importance of consistency in setting up fractions.
- 🔢 It tackles a more challenging problem involving the calculation of side lengths in overlapping triangles, showing how to handle different scenarios where some side lengths are known and others are not.
- 📘 Lastly, the video includes a problem with a given ratio of sides, illustrating how to use this ratio along with the properties of similar triangles to find unknown lengths.
Q & A
What is the definition of similar triangles?
-Similar triangles are defined as two triangles that have the same shape but not necessarily the same size, meaning their corresponding angles are equal and their corresponding sides are in proportion.
How do you determine the scale factor between two similar triangles?
-The scale factor between two similar triangles is determined by dividing the corresponding sides of the triangles. If the sides of one triangle are all twice as long as the corresponding sides of another, the scale factor is 2.
What is the relationship between the sides of similar triangles?
-The sides of similar triangles are in proportion. This means that if you take any two corresponding sides from each triangle, the ratios of those sides will be equal.
How can you use the concept of similar triangles to solve for missing side lengths?
-You can set up a proportion using the known sides of the triangles and the unknown side you're trying to find. By solving the proportion, you can determine the length of the missing side.
What is the significance of alternate angles when dealing with similar triangles?
-Alternate angles are equal when the lines forming the angles are parallel. This is significant in similar triangles because it helps establish that the triangles are similar when the corresponding angles are the same.
How does the presence of parallel lines affect the similarity of triangles?
-The presence of parallel lines indicates that certain angles are alternate and therefore equal, which is a key factor in determining that two triangles are similar.
What is the reciprocal of the scale factor and how does it relate to similar triangles?
-The reciprocal of the scale factor is the scale factor inverted. For similar triangles, if the scale factor is 2 (meaning one triangle is twice as large as the other), the reciprocal would be 1/2, indicating the scaling down from the larger to the smaller triangle.
Can you find the scale factor by dividing sides within the same triangle?
-Yes, you can find the scale factor by dividing sides within the same triangle, as long as you are consistent with the sides you choose for comparison.
What is the importance of being consistent when setting up fractions to solve for unknowns in similar triangles?
-Consistency is crucial when setting up fractions to ensure that the smaller triangle's side is always on top or always on the bottom, relative to the larger triangle's side, to avoid errors in solving for unknowns.
How can you use the concept of similar triangles to solve problems with overlapping triangles?
-Even with overlapping triangles, you can still identify corresponding sides and angles, and use these to set up proportions to solve for unknown side lengths, taking into account the overlapping parts as part of the triangle sides.
What additional information might be provided in a problem involving similar triangles, and how does it help?
-Problems might provide ratios of certain sides, like a 5:4 ratio in the script, which helps establish the relationship between unknown sides by assuming arbitrary lengths that maintain the given ratio.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示
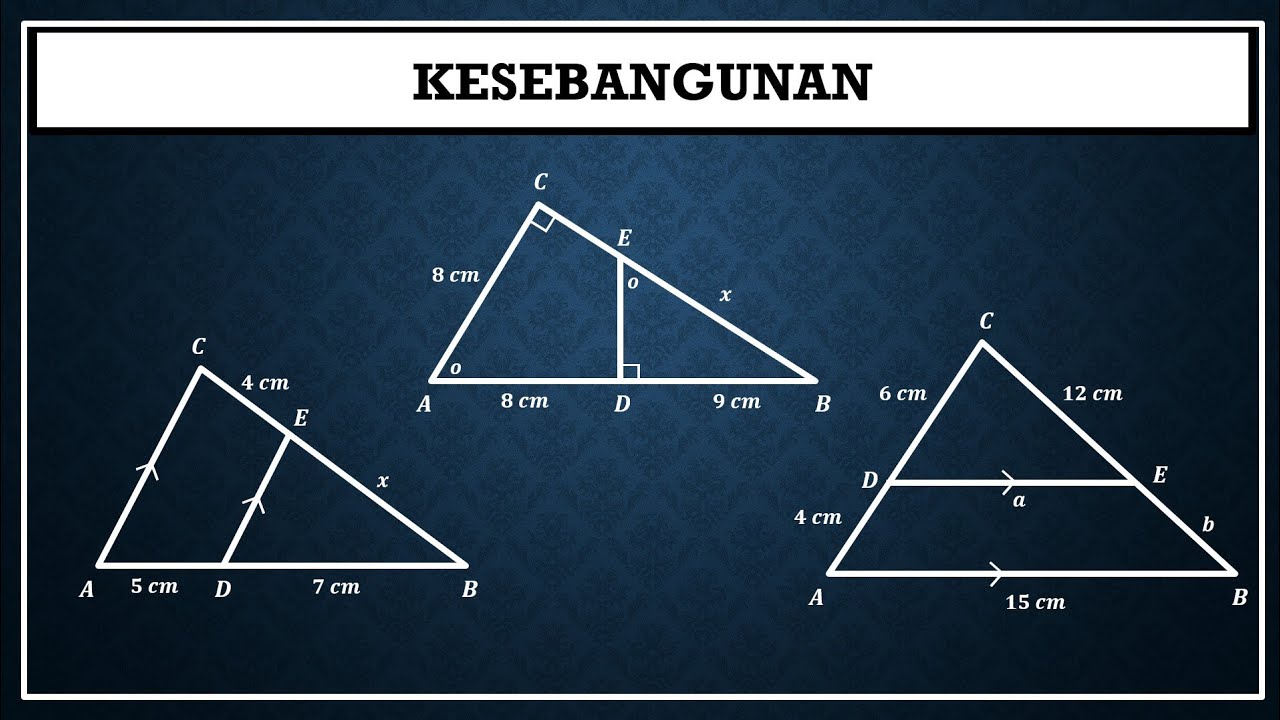
Kesebangunan pada segitiga

Kesebangunan Segitiga: Kesebangunan Segitiga Siku-siku (Belajar Matematika Kelas 7) - Kak Hasan
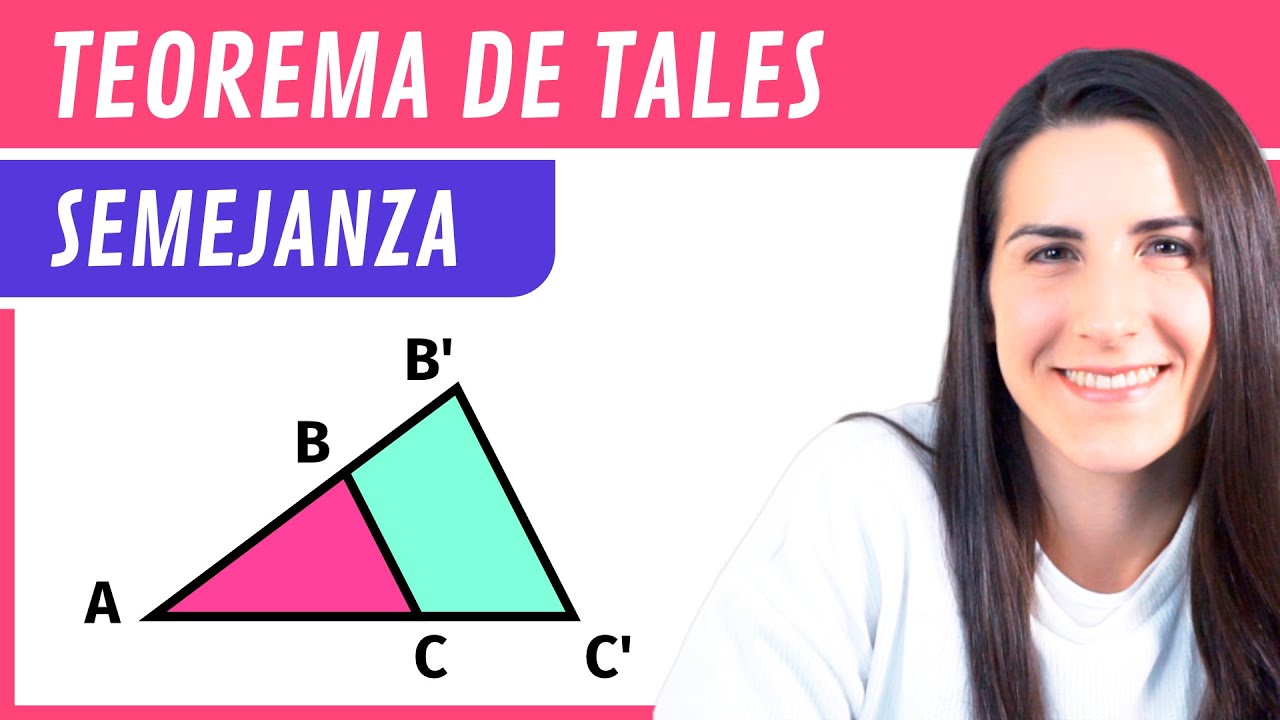
Teorema de TALES 📐 SEMEJANZA de Triángulos

Kekongruenan dan Kesebangunan [Part 4] - Kesebangunan Dua Segitiga
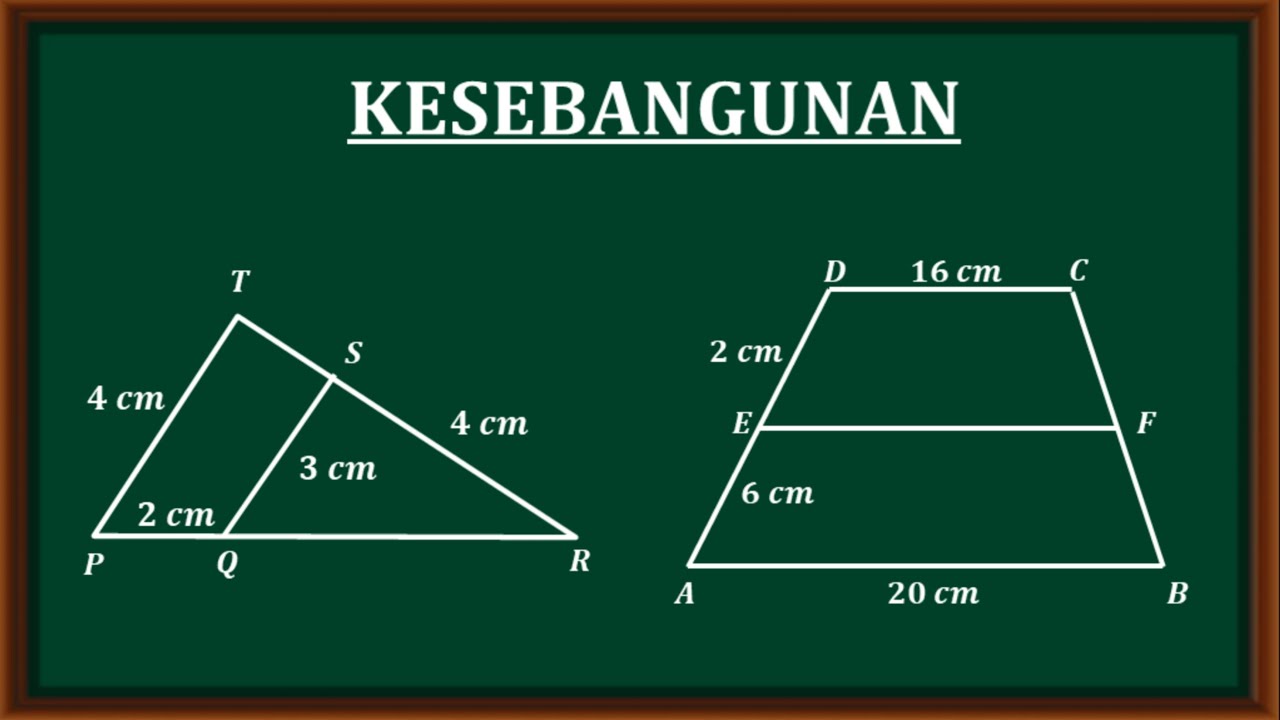
Kesebangunan - soal dan pembahasan materi kesebangunan matematika tingkat SMP kelas ix

Kurikulum Merdeka Materi Matematika Kelas 7 Bab 5 Kesebangunan
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
