Overview of Cell Boundaries
Summary
TLDRThis video delves into the outer boundaries of cells, highlighting the cell wall's role in providing support, shape, and protection for plant cells, bacteria, and fungi. It contrasts this with animal cells, which possess only a cell membrane, crucial for maintaining homeostasis by selectively regulating the passage of substances. The cell membrane's selective permeability ensures a stable internal environment, essential for cellular survival and function.
Takeaways
- 🌿 Every cell has a boundary: Plant cells have a rigid cell wall, while animal cells do not.
- 🛡️ Cell walls in bacteria and fungi provide support, shape, and protection, differing in structure and composition.
- 🐠 Animal cells are unique in that they possess a cell membrane but never a cell wall.
- 🏞️ The cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane, acts as a barrier for animal cells, maintaining a stable internal environment.
- ⚖️ Homeostasis is crucial for cell survival, growth, and reproduction, and the cell membrane plays a key role in achieving this equilibrium.
- 🚪 The cell membrane is selectively permeable, acting as a gatekeeper to regulate the passage of substances into and out of the cell.
- 🔬 The mechanisms of how cells control substance passage will be explored in more detail in future discussions.
- 🌀 All cells have a flexible cell membrane, which is essential for maintaining intracellular homeostasis.
- 🔗 The rigid cell wall and flexible cell membrane work in tandem to support cell structure and function.
- 🎓 It's important to remember these distinctions, especially that animal cells lack a cell wall, for understanding cellular biology.
Q & A
What is the outer boundary of cells called?
-The outer boundary of cells is called a cell membrane, also known as the plasma membrane.
Do all cells have a cell wall?
-No, not all cells have a cell wall. Animal cells never have a cell wall, while plant cells, bacteria, and fungi do.
What is the primary function of the cell wall in cells that have one?
-The cell wall provides support, shape, and protection to the cell.
What is the main role of the cell membrane in maintaining cell stability?
-The cell membrane helps maintain a stable internal environment by being selectively permeable, allowing it to control what enters and exits the cell.
What is homeostasis, and how does the cell membrane contribute to it?
-Homeostasis is a state of equilibrium where the cell maintains a relatively constant and stable internal environment. The cell membrane contributes to homeostasis by selectively allowing substances to pass through, thus helping to maintain this balance.
Why is it essential for cells to maintain stable internal conditions?
-Stable internal conditions are necessary for cells to survive, grow, and reproduce.
How does the cell membrane act as a gatekeeper for the cell?
-The cell membrane acts as a gatekeeper by selectively permeable, which means it allows certain substances to pass through while blocking others, thus controlling the movement of materials in and out of the cell.
What is the difference between the cell walls of plants, bacteria, and fungi?
-While all provide support, shape, and protection, the structure and composition of the cell walls in plants, bacteria, and fungi differ.
Can you provide an example of how the cell membrane maintains homeostasis?
-The cell membrane maintains homeostasis by regulating the movement of ions and molecules, such as allowing water to move in and out of the cell through osmosis to maintain the correct balance of solutes and water.
What are some other functions of the cell membrane besides maintaining homeostasis?
-The cell membrane also plays a role in cell signaling, cell adhesion, and acts as a site for various enzymatic reactions.
How does the cell membrane differ in structure between animal cells and plant cells?
-Animal cells have a flexible cell membrane without a cell wall, whereas plant cells have a cell membrane plus a rigid cell wall made of cellulose.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

GCSE Biology: Revision Guide | Plant, Animal, Bacteria Cells & Orders of Magnitude

CELL WALL
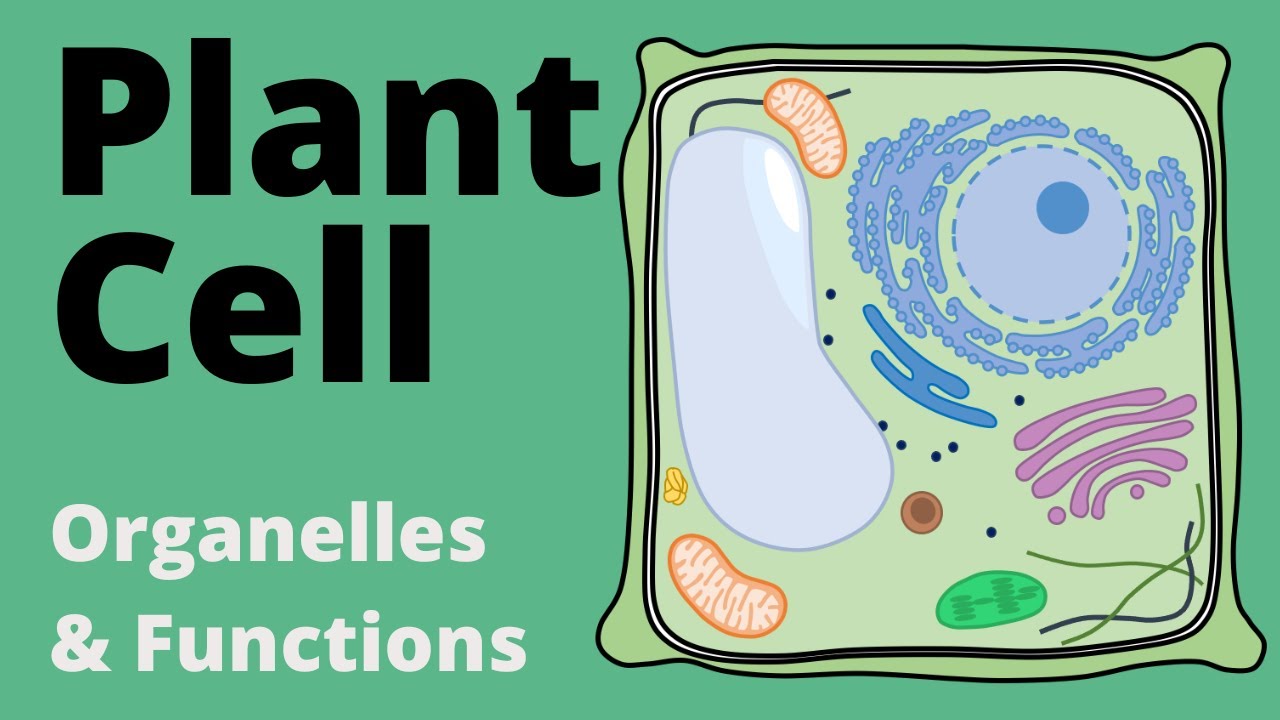
Structure and Function of the PLANT CELL explained (Organelles)
BIOLOGIA - Lezione 3 - La Cellula Eucariota

Cell Wall | iKen | iKen App | iKen Edu

Cell Wall structure, composition and function Lecture 7 in Urdu Hindi by dr A.Hadi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
