How Boost Converters Work (DC-DC Step-Up) - Electronics Intermediate 1
Summary
TLDRIn this 'Simply Electronics' episode, the host explores a boost converter, a switch mode power supply that efficiently steps up a 9-volt input to over 68 volts. The demonstration highlights the importance of safety when handling high voltages and explains the role of inductors and MOSFET transistors in the conversion process. The video provides a simplified view of the rapid voltage increase, emphasizing the inductor's magnetic field collapse and the voltage spike it induces, which is then stored in a capacitor to achieve the higher output voltage. Viewers are encouraged to subscribe for more in-depth content and interactive learning opportunities.
Takeaways
- 🔌 The video discusses a circuit that can step up a lower voltage to a higher voltage using a simple setup.
- ⚠️ Safety is emphasized due to the high voltages involved, which can be dangerous if not handled properly.
- 🔋 The example given starts with a 9-volt power supply and demonstrates stepping up to 68 volts.
- ⚡ The circuit is a type of switch mode power supply known as a boost converter or step-up converter.
- 🕒 The video script mentions that the circuit operates much faster in real life than what is shown in the slowed-down demonstration.
- 🧲 The operation of the circuit relies on the properties of an inductor, which is a key component in the boost converter.
- 🔄 The circuit uses a MOSFET transistor as a switch to control the flow of current, which is turned on and off rapidly.
- 📈 The voltage is stepped up as the collapsing magnetic field of the inductor induces a current that adds to the capacitor's voltage.
- 🔄 The polarity of the inductor changes when the switch is turned off, allowing current to flow through the rest of the circuit.
- 🔗 The video provides a link for viewers to interact with a simulation of the circuit for a better understanding.
- 🎥 The host plans to create a video on making a boost converter and encourages viewers to subscribe for updates.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the circuit discussed in the video?
-The circuit discussed is a boost converter, also known as a step-up converter, which is designed to step up a lower voltage to a higher voltage using simple circuitry.
What safety precautions should be taken when working with high voltage circuits?
-When working with high voltage circuits, it is crucial to stay safe by not touching any high voltage contacts and ensuring that less than 20 milliamps of current doesn't pass through the body, as it can be harmful or even stop the human heart.
What is a switch mode power supply and how is it related to the discussed circuit?
-A switch mode power supply is a type of power supply that uses a switch, such as a transistor, to turn a part of the circuit on and off at a very high speed. The discussed circuit is a type of switch mode power supply because it uses a transistor to step up the voltage.
How does the boost converter circuit step up the voltage from a 9V power supply?
-The boost converter circuit steps up the voltage by taking advantage of the properties of an inductor. When the transistor switch is turned on and off rapidly, it causes the inductor's magnetic field to collapse, inducing a high voltage spike that is stored in a capacitor, thus stepping up the voltage.
What is the role of the inductor in the boost converter circuit?
-The inductor in the boost converter circuit builds up a magnetic field when current flows through it. When the current flow is interrupted by turning off the transistor switch, the collapsing magnetic field induces a high voltage spike that contributes to stepping up the voltage.
What is the purpose of the diode in the boost converter circuit?
-The diode in the circuit allows the high voltage spike created by the collapsing magnetic field of the inductor to be pushed through and stored in the capacitor, while preventing current from flowing back from the capacitor to the switch and power supply.
What happens to the polarity of the inductor when the transistor switch is turned off?
-When the transistor switch is turned off, the polarity of the inductor changes, with the negative side becoming positive and vice versa, allowing the current to flow through the rest of the circuit.
What is the expected final voltage output of the boost converter circuit?
-The video suggests that the boost converter circuit would eventually settle at around 100 volts, although the exact voltage may vary depending on the specific components and settings used.
How can viewers interact with and learn more about the boost converter circuit?
-Viewers can interact with and learn more about the boost converter circuit by following the link provided in the video description, which allows them to view and even modify the circuit in a browser, provided they are using Google Chrome.
Is there a plan to create a video on making a boost converter?
-Yes, the video creator plans to make a video on actually making a boost converter and encourages viewers to subscribe to the channel for updates.
What is the significance of the capacitor in the boost converter circuit?
-The capacitor in the boost converter circuit stores the high voltage spikes generated by the collapsing magnetic field of the inductor. Each spike adds to the capacitor's voltage, effectively stepping up the overall voltage output of the circuit.
Outlines

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードMindmap

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードKeywords

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードHighlights

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレードTranscripts

このセクションは有料ユーザー限定です。 アクセスするには、アップグレードをお願いします。
今すぐアップグレード関連動画をさらに表示

⚡ DC-DC Buck-Boost Converter Design 🔋 Power Electronics Calculations & MATLAB/Simulink

PLC OMRON CP1E | CARA PASANG INPUT OUTPUT

Beginner Electronics - 10 - Bread Boards
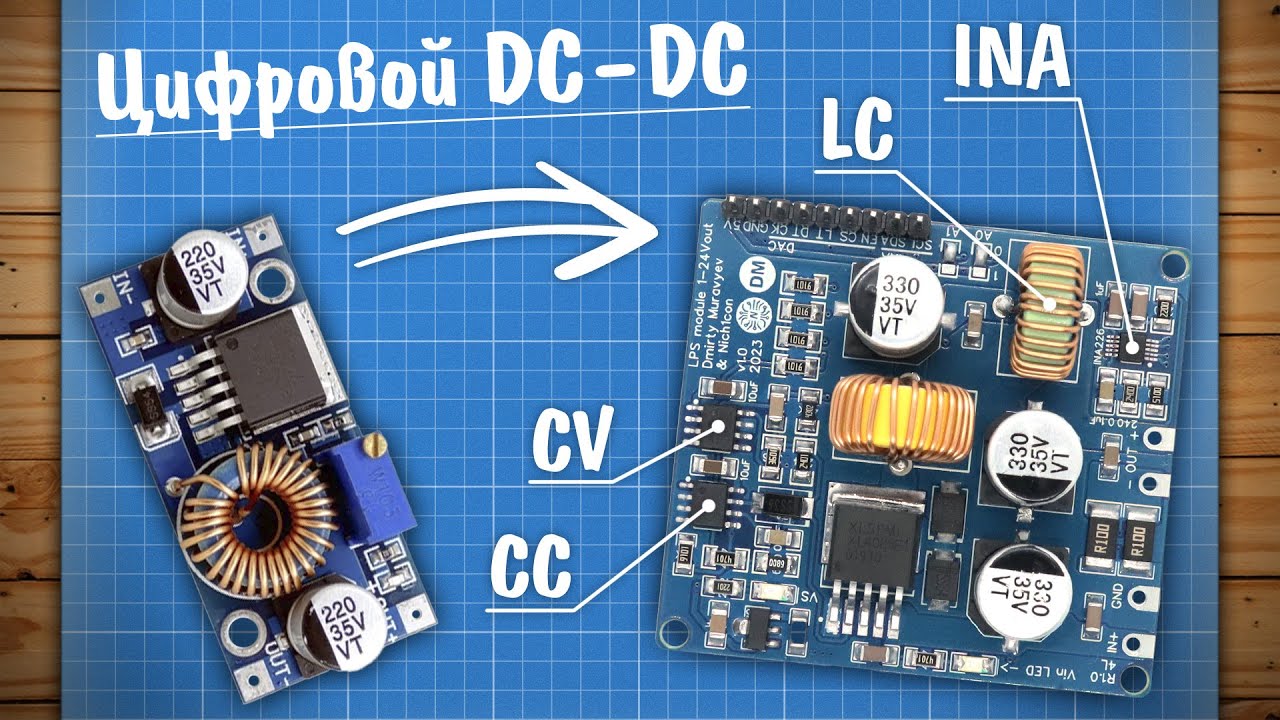
Проектируем цифровой DC-DC с контролем тока и напряжения!

DABBSSON DBS1300 | Expansion & Parallel Capable Solar Generator - 1330Wh | 1200W
entrance into the DC DC Converter Basic Topologies
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
