CARBON CYCLE
Summary
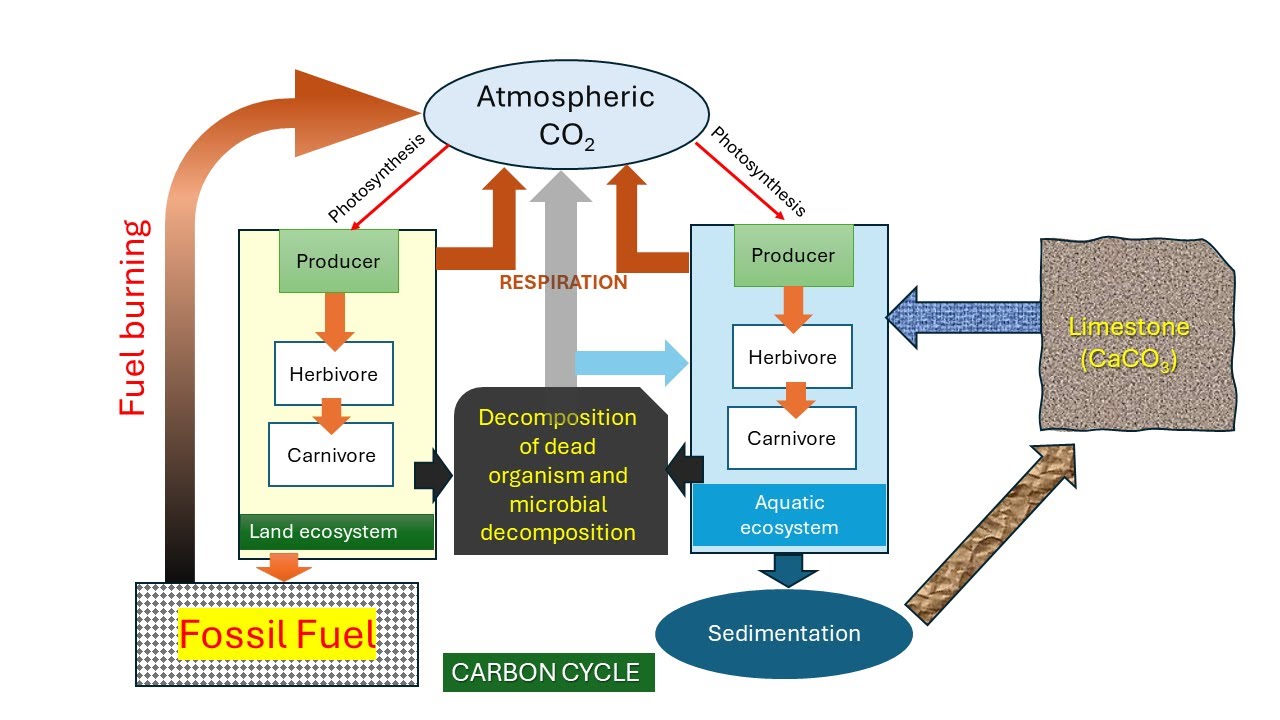
TLDRThe carbon cycle is a vital process where carbon circulates from the atmosphere to the biosphere and hydrosphere, with plants absorbing CO2 through photosynthesis and releasing it back through respiration and decomposition. CO2 also enters water as carbonates, aiding aquatic plant life. However, human activities such as burning fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes disrupt this balance, increasing atmospheric CO2 levels and contributing to global warming. The release of chlorofluorocarbons from appliances further depletes the ozone layer. Maintaining the natural 0.03% carbon concentration is crucial for environmental stability.
Takeaways
- 🌱 The carbon cycle is the circulation of carbon between the atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere.
- 🌿 CO2 from the atmosphere enters plants through photosynthesis to synthesize food particles.
- 🐛 When plants are consumed by terrestrial organisms, CO2 is transferred to them and eventually returns to the soil upon their death.
- 🌊 CO2 enters water as carbonates, aiding aquatic plants in photosynthesis and forming limestone in the process.
- 🔥 CO2 returns to the atmosphere through various processes, including respiration, burning of wood, and industrial activities.
- 🚗 Emissions from motor vehicles and industries, as well as the extraction and burning of fossil fuels, contribute to increased atmospheric CO2 levels.
- 🌲 Deforestation disrupts the carbon cycle by reducing the number of trees available to absorb CO2.
- ⚠️ An increase in atmospheric CO2 can disturb the natural carbon cycle and lead to global warming.
- 🌡️ The release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) from air conditioners and refrigerators depletes the ozone layer and contributes to global warming.
- 📉 Maintaining the natural carbon concentration of 0.03 percent in the atmosphere is crucial for environmental balance.
- 🌳 Efforts should be made to preserve and enhance the carbon cycle to mitigate the impacts of human activities on the environment.
Q & A
What is the carbon cycle?
-The carbon cycle is the process by which carbon is circulated between the atmosphere, biosphere, and hydrosphere. It involves the exchange of carbon dioxide (CO2) between these spheres through various natural processes.
What percentage of carbon concentration is found in the atmosphere?
-The carbon concentration in the atmosphere is approximately 0.03 percent.
How does carbon dioxide enter the biosphere?
-Carbon dioxide enters the biosphere through the process of photosynthesis, where plants absorb CO2 and convert it into organic compounds.
What happens to carbon when plants are consumed by animals?
-When plants are eaten by animals, the carbon stored in the plants becomes part of the animals' bodies. Upon the animals' death, this carbon is returned to the soil.
How does carbon dioxide enter the hydrosphere?
-Carbon dioxide enters the hydrosphere as carbonates, which can be beneficial for aquatic plants to perform photosynthesis.
What is the role of carbonates in the hydrosphere?
-Carbonates in the hydrosphere provide a source of carbon for aquatic plants, enabling them to carry out photosynthesis.
How does carbon dioxide return to the atmosphere from the hydrosphere?
-Carbon dioxide can return to the atmosphere through the decomposition of organic matter in the water or through the respiration of aquatic organisms.
What are some human activities that contribute to the release of CO2 into the atmosphere?
-Human activities such as burning fossil fuels, respiration of animals, deforestation, cement manufacturing, and the extraction of fuels contribute to the release of CO2 into the atmosphere.
What is the impact of increased CO2 levels in the atmosphere?
-An increase in atmospheric CO2 levels can lead to the disturbance of the natural carbon cycle and contribute to global warming.
How do chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) affect the environment?
-The release of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) from air coolers and refrigerators leads to the depletion of the ozone layer and contributes to global warming.
Why is it important to maintain the carbon concentration at 0.03 percent?
-Maintaining the carbon concentration at 0.03 percent is important to prevent the disruption of the natural carbon cycle and to mitigate the effects of global warming.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Daur Karbon dan Oksigen - Daur Biogeokimia - Ekologi - Biologi X

#CASEETWOSTUDY BIOLOGI || DAUR OKSIGEN [KELOMPOK 5/X-2]

Siklus Biogeokimia (Daur Karbon dan Oksigen)
Carbon cycle | gaseous cycle | CARBON FIXATION | RESPIRATION| COMBUSTION | Decomposition

Siklus Oksigen dan Karbon

SIKLUS DAUR KARBON / BIOLOGI XE-6
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
