What Is Volcanic Smog?
Summary
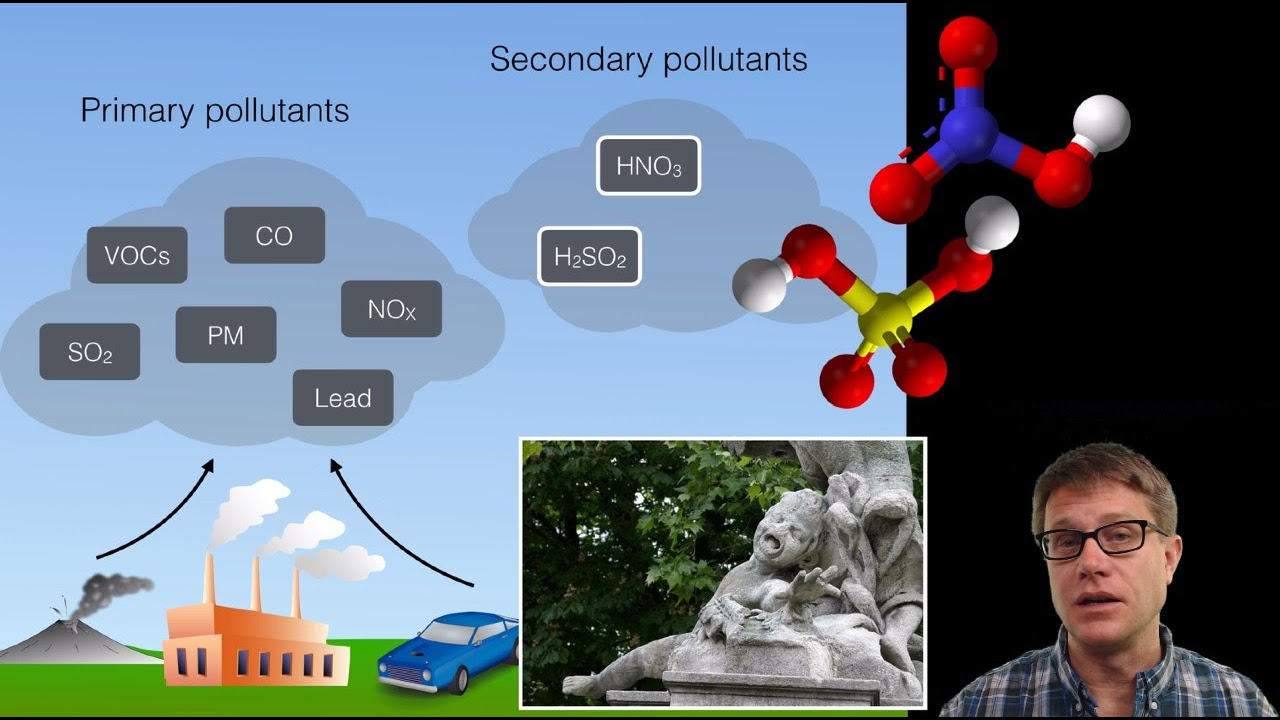
TLDRVog, or volcanic smog, is an often-overlooked form of air pollution consisting of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and sulfur dioxide. Sulfur dioxide reacts with the atmosphere, forming fine particles that scatter sunlight and create a visible haze. Vog poses health risks, including lung damage and respiratory difficulties, even for those without pre-existing conditions. To mitigate exposure, limit outdoor time, especially during rain or fog, as these conditions can lead to acid rain. Long-term effects of vog may include prolonged presence in populated areas, potentially spreading hundreds of miles away from the volcanic source.
Takeaways
- 🌋 Volcanoes are not just about lava and fire; they also produce a significant environmental impact known as vog.
- 🌫️ Vog stands for volcanic smog, a form of air pollution that can have lasting effects on the environment.
- 💨 Vog is composed of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and sulfur dioxide, with sulfur dioxide being the most critical component.
- ⚗️ Sulfur dioxide from volcanic eruptions reacts with the atmosphere, forming fine particles that scatter sunlight and create a visible haze.
- ⚠️ Vog can be dangerous, posing risks to both the environment and living beings, including humans and animals.
- 👤 Exposure to vog can cause respiratory issues, headaches, watery eyes, sore throats, and even breathing difficulties in some individuals.
- 🏠 To mitigate the effects of vog, it is advised to limit outdoor activities and stay indoors when vog is present.
- 🌧️ Rain and fog can combine to form acid rain, which is another harmful consequence of vog, and should be avoided.
- 🛁 If acid rain occurs, it is important to wash off any contact as soon as possible to minimize its effects.
- 📅 The duration of vog can vary, potentially lasting for several weeks and spreading to more populated areas far from the volcano.
- 🌆 The long-term presence of vog can affect more populated cities, even those located hundreds of miles away from the volcanic source.
Q & A
What is the term 'vog' referring to in the context of volcanoes?
-Vog stands for volcanic smog, which is a form of air pollution consisting of carbon dioxide, water vapor, and sulfur dioxide that is released from volcanic activities.
How does sulfur dioxide contribute to the formation of vog?
-Sulfur dioxide is released from the volcano and reacts with the atmosphere, converting to very fine particles within hours to days, which scatter sunlight and create a visible haze.
Is vog considered a danger to the environment and living beings?
-Yes, vog can be dangerous as it can damage the environment, humans, and animals by causing respiratory issues, headaches, watery eyes, sore throats, and breathing difficulties.
What are the potential health effects of vog on humans?
-Vog can damage the lungs, trigger headaches, watery eyes, sore throats, and even breathing difficulties, affecting even those with no history of respiratory problems.
What precautions should be taken when encountering vog?
-It is advised to limit time outdoors and be cautious during rain and fog, as fog can cause acid rain. If acid rain occurs, stay indoors and wash off any contact as soon as possible.
What is acid rain, and why should it be avoided?
-Acid rain is caused by the presence of fog and rain in the atmosphere, which can lead to harmful chemical reactions. It should be avoided to prevent exposure to potentially harmful substances.
How long can vog persist in the environment?
-Vog can be present for several weeks, depending on the volcano and the location of the volcanic smog, and it can spread to more populated areas even hundreds of miles away.
Can vog affect areas that are far from the volcano?
-Yes, vog can spread to more populated cities even hundreds of miles away from the volcano, depending on weather conditions and the intensity of the volcanic activity.
What can be inferred about the visibility of the area during vog events?
-During vog events, visibility can be significantly reduced due to the scattering of sunlight by the fine particles in the air, creating a visible haze.
Is there any specific advice for individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions during vog events?
-While the script does not specify advice for individuals with pre-existing conditions, it is generally recommended that all individuals, especially those with respiratory issues, limit outdoor exposure during vog events.
What measures can be taken to mitigate the effects of vog on a community level?
-Communities can monitor air quality, issue warnings, and advise residents to stay indoors during high vog levels. They can also educate the public about the dangers of vog and how to protect themselves.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)