The Philosophy Of Democritus And The Atomists
Summary
TLDRThe video explores the life and philosophy of Democritus, the 'laughing philosopher,' known for his atomic theory of matter. Born in Thrace around 460 B.C.E., Democritus believed the universe was composed of atoms and void, with atoms being eternal and in constant motion. He rejected the notion of chance and purpose in the universe, advocating a life of moderate pleasure and cheerfulness, free from fear and superstition. His ideas influenced later philosophers and laid the groundwork for mechanistic explanations of the world.
Takeaways
- 🔍 Democritus, known as the 'laughing philosopher,' was praised for his wealth of knowledge and logical thinking.
- 📚 Democritus is mostly known through the writings of others, especially Aristotle, as his original works did not survive.
- 👥 Democritus and his teacher Leucippus are often mentioned together, with some even questioning Leucippus's existence.
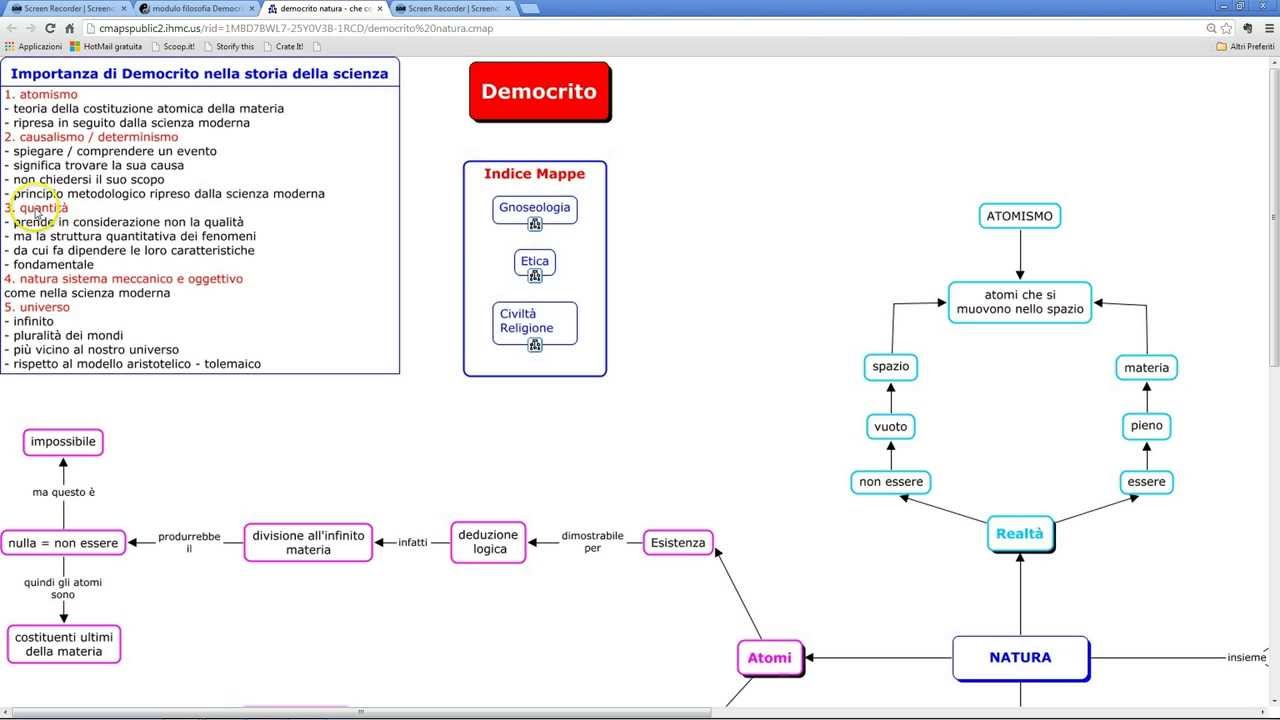
- 🌍 Democritus developed the atomic theory of matter, proposing that everything is composed of atoms and the void.
- 🔬 Atoms were described as eternal, impenetrable, and in constant motion, forming the basis of all phenomena.
- 🌌 The void, according to Democritus, is infinite space where atoms move without any specific direction or purpose.
- 🎨 All sensations, such as taste and color, are the result of interactions between atoms in the external world and within our sensory organs.
- ❓ Aristotle questioned how the initial motion of atoms began, but Democritus rejected the need for a purpose or final cause.
- 💭 Democritus believed in pursuing pleasure and cheerfulness in life, advocating for moderation and rejecting violence and superstition.
- 🔥 The influence of the Atomists extended to later philosophers like Epicurus, Montaigne, and Spinoza, despite their theories lacking empirical evidence.
Q & A
Who is Democritus known as among the Pre-Socratic philosophers?
-Democritus is known as the 'laughing philosopher' among the Pre-Socratic philosophers.
What is the main challenge in studying Democritus' philosophy?
-The main challenge in studying Democritus' philosophy is that we only know him through the writings of others, most notably Aristotle, and it is difficult to separate his ideas from those of his teacher Leucippus.
When and where was Democritus born?
-Democritus was born around 460 B.C.E. in the northern Greek territory of Thrace.
How did the scholars of Athens initially respond to Democritus' philosophy?
-Initially, the enlightened scholars of Athens ignored Democritus' philosophy, but around 420 B.C.E., his philosophic prestige reached its maturity and he became well-known throughout the ancient world.
What is the atomic theory of matter attributed to Democritus and Leucippus?
-The atomic theory of matter posits that the universe is composed of two things: atoms and the void. Atoms are eternal, impenetrable, and incompressible, and they move in continuous motion, forming various phenomena in the universe.
What is the role of the void in Democritus' atomic theory?
-In Democritus' atomic theory, the void is the infinite space through which atoms move perpetually. It is considered real and necessary for the existence and movement of atoms.
How did Democritus view the concept of sensation?
-Democritus viewed sensation as the interaction of external atoms with the atoms present within our sensory organs, and he famously stated that 'By convention sweet, by convention bitter; by convention hot, by convention cold; by convention color; but in reality: atoms and the void.'
What was Aristotle's issue with the atomic theory?
-Aristotle's issue with the atomic theory was the question of how to account for the initial motions of the atoms, as all phenomena in the theory occur as a direct result of their antecedents.
What was Democritus' view on the existence of gods?
-Democritus rejected the popular religion and thought that gods were a way for the masses to explain and find comfort in the inexplicable, rather than actual entities.
What was the aim of life according to Democritus?
-According to Democritus, the aim of life should be to pursue pleasure and cheerfulness with moderation, seeking freedom from fear and superstition to achieve tranquility.
How did Democritus' philosophy influence later thinkers?
-Democritus' philosophy had a profound influence on later thinkers, including Aristotle, Epicurus, Montaigne, and Spinoza, who all drew inspiration from his mechanistic questions and answers.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Democritus. The great Greek philosopher

SCIENCE 8: Q2_WREK 1- DAY 1: GREEK PHILOSOPHERS AND THE ATOMOS ||MATATAG CURRICULUM

Seri Kimia Dasar - Atom, kok bisa ditemukan? (teori atom Democritus, Dalton, Thomson)
video lezione filosofia Democrito, 2^ parte: filosofia della natura

Teori dan Model Atom Dalton | Video Belajar Kelas 10 IPA - Kimia

Democritus | Ancient Philosophy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
