GENERAL BIOLOGY 1: Cell Types and Cell Modifications
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces Lesson 2 on cell types and modifications, focusing on classifying plant and animal tissues and their functions. It engages viewers with activities to identify biological organization and answer questions about tissue types. The lesson covers epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues, explaining their structures, functions, and adaptations for specialized roles in the body. It concludes with an assessment to reinforce learning, promising a follow-up on the cell cycle and mitosis.
Takeaways
- 📚 The lesson focuses on classifying different cell types and understanding cell modifications that lead to adaptations for specialized functions.
- 🔬 The biological organization hierarchy is cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the organism itself.
- 🌿 Living organisms can be either unicellular, consisting of one cell, or multicellular, consisting of many cells working together.
- 💪 Organs are essential for adaptation and survival, and they are made up of tissues that perform specific functions.
- 🧬 The human body is composed of four basic types of tissues: epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues.
- 🧱 Epithelial tissues are tightly packed cells that cover body surfaces and line internal organs, serving functions like protection and secretion.
- 🤝 Connective tissues join, support, protect, transport, and store nutrients and energy, and play a role in immunity.
- 🏋️ Muscular tissues are responsible for causing movement and are composed of cells with contractile proteins.
- 🧠 Nervous tissues sense stimuli and transmit nerve impulses, consisting of neurons with dendrites and axons.
- 🧬 The lesson included an activity to identify pictures based on the hierarchy of biological organization and another to answer questions about tissue types.
- 📝 The session concluded with an assessment matching tissues to organs and descriptions, reinforcing the lesson's concepts.
Q & A
What are the two main objectives of the lesson on cell types and cell modifications?
-The two main objectives are to classify different cell types found in plant and animal tissues and to specify the functions of each, and to describe some cell modifications that lead to adaptation for carrying out specialized functions.
What is the correct sequence of the biological organization hierarchy?
-The correct sequence is cells, tissues, organs, organ systems, and the organism.
What are the four basic types of tissues in the human body?
-The four basic types of tissues are epithelial, connective, muscular, and nervous tissues.
What are the main functions of epithelial tissues?
-Epithelial tissues mainly perform functions such as protection, secretion, absorption, excretion, filtration, diffusion, enzyme production, and sensory reception.
How are epithelial tissues named according to the number of cell layers they have?
-Epithelial tissues are named as simple if they have a single layer of cells, and stratified if they have multiple layers.
What is the difference between simple and stratified epithelial tissues?
-Simple epithelial tissues have a single layer of cells, while stratified epithelial tissues have multiple layers of cells.
What are the seven functions of connective tissues?
-The seven functions of connective tissues are joining other tissues, support, protection, transport of blood, nutritive functions, immune function, and storage and insulation.
What are the three major types of muscular tissues and their functions?
-The three major types of muscular tissues are cardiac muscle (found in the heart and responsible for involuntary movement), skeletal muscle (attached to bones and responsible for voluntary movement), and smooth muscle (found in the walls of organs and responsible for involuntary movement).
What is the function of nervous tissue and what makes up a typical nerve cell or neuron?
-Nervous tissue senses stimuli and transmits signals called nerve impulses from one part of the body to another. A typical nerve cell or neuron consists of a cell body containing the nucleus and several slender extensions, including dendrites that convey signals toward the neuron and an axon that transmits signals to another neuron or muscle cell.
What is the purpose of the second activity in the lesson?
-The purpose of the second activity is to answer five questions related to the types of tissues that make up specific parts of the body, such as the brain, epidermis, ligaments, heart, and blood vessels.
What is the significance of cell modifications in adaptation for specialized functions?
-Cell modifications are significant in adaptation as they allow cells to better perform their specialized functions within the body, such as microvilli in the simple columnar epithelial tissue that increase the surface area for absorption.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
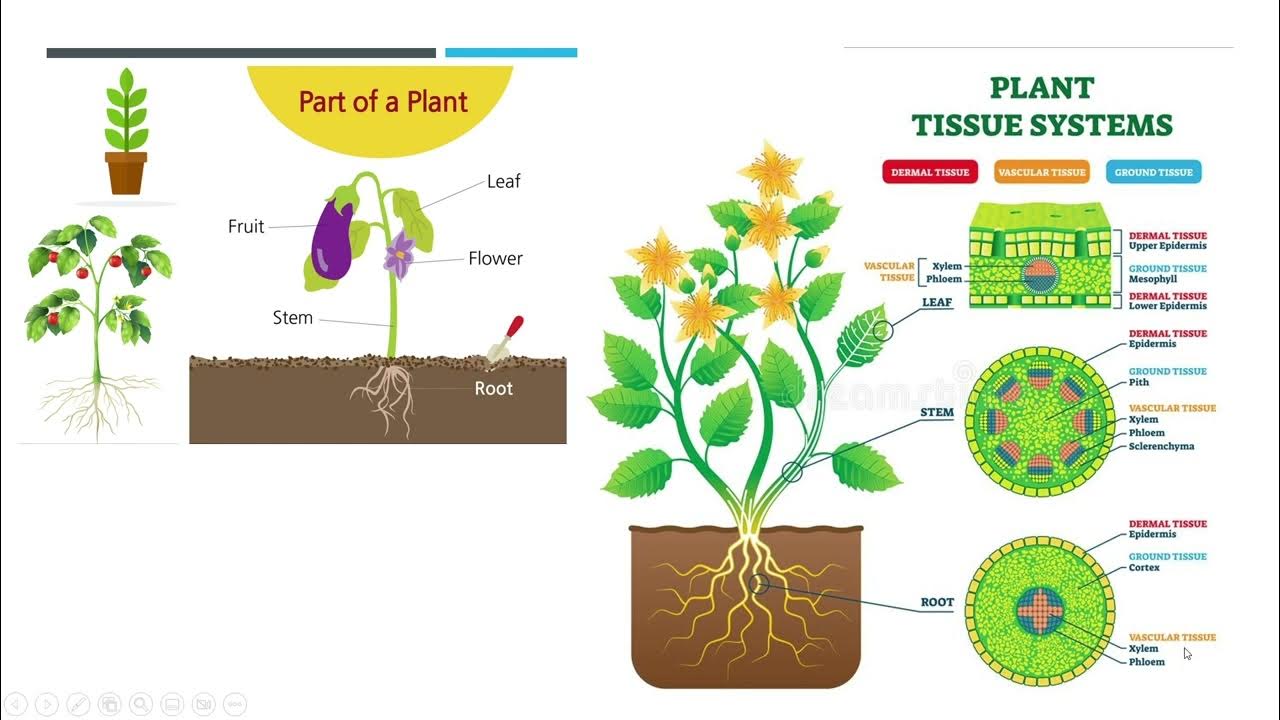
Module 6: Cell Modifications- General Biology I

General Biology 1. Cell Types of Plant and Animal Tissues

Science Form 1: 2.1: Cell - Structure, Function & Organisation (part 2)

Jaringan Penguat (Mekanik) || Jaringan Tumbuhan #Part_3
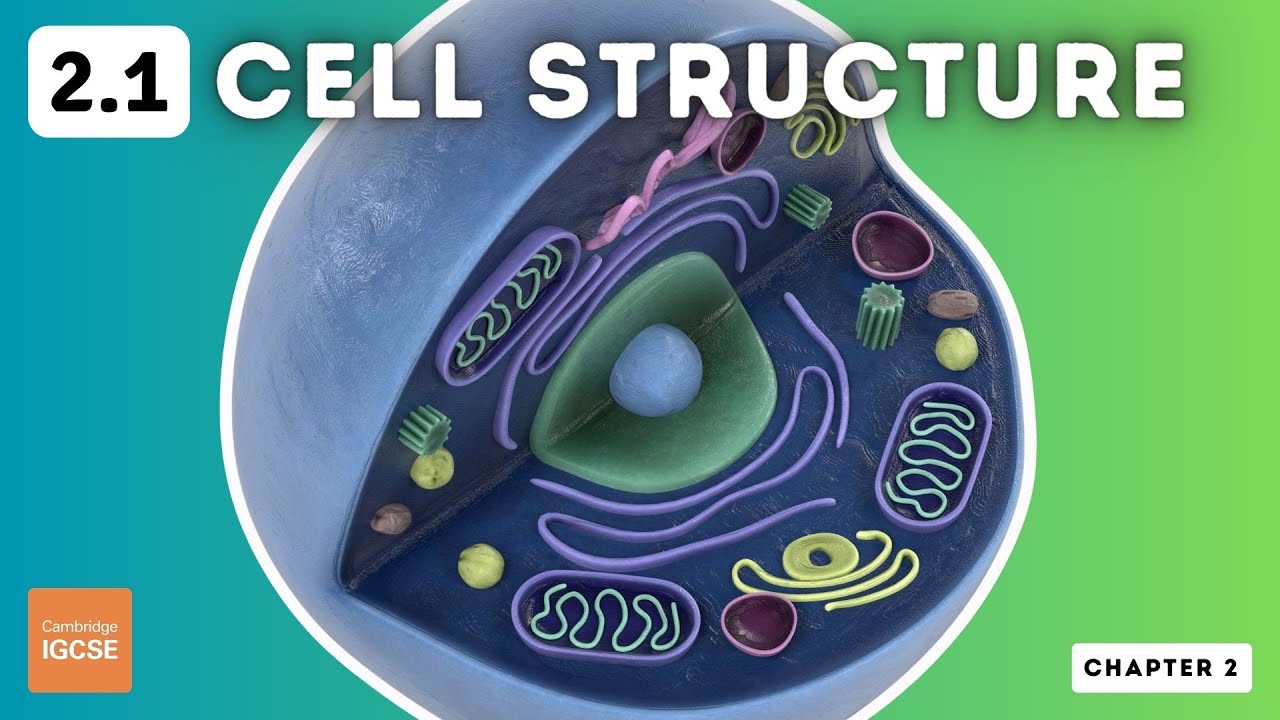
IGCSE Biology - Cell Structure and Organisation (2.1)

Állati és növényi szövetek
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
