What is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
Summary
TLDRThe script delves into the complexities of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR), highlighting the necessity for companies to adopt ethical practices beyond mere compliance and charity. It emphasizes the importance of integrating social and ecological values into core business operations, the role of individual and institutional ethics, and the challenges posed by globalization. The discourse also touches on the influence of 'soft laws' and the mixed reality of CSR implementation, urging a critical yet supportive approach to fostering a good and fair society through corporate actions.
Takeaways
- 📈 CSR stands for Corporate Social Responsibility, which is about companies' moral and ethical obligations beyond just making profits.
- 🤔 The script raises questions about justice for current and future generations in the context of business practices.
- 💼 The story of Angelo Ugolotti highlights the issue of corporate fraud, emphasizing the need for transparency and accountability in business.
- 🚫 CSR is not just about preventing bad practices like corruption and fraud; it's also about contributing positively to society through good business practices.
- 💰 The focus of CSR should be on how companies make profits, not merely on how they spend them, indicating a need for systemic change in business operations.
- 🛡 Compliance and risk management are important, but they are only part of the broader concept of CSR, which also includes ethical considerations and social impact.
- 🌐 CSR requires a new role for companies as both economic and moral actors, integrating social and ecological criteria into their core business.
- 👥 It's not enough to have virtuous managers; CSR requires employees of integrity at all levels and clear organizational structures to support ethical practices.
- 📚 The script suggests that CSR involves both individual ethics and institutional ethics, emphasizing the need for ethical reflection beyond just following rules.
- 🌳 The role of the state in promoting CSR is limited in a globalized world, where economic systems are highly internationalized and politics and law are more localized.
- 🔄 'Soft laws' like the UN Global Compact represent new governance mechanisms that rely on companies' self-commitment to social and ecological standards.
- 🛍️ The script ends by reminding us of consumer responsibility, suggesting that individuals also have a role to play in promoting CSR through their purchasing decisions.
Q & A
What is the primary focus of Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)?
-CSR focuses on how companies can contribute to a 'good society' through 'good business' practices, emphasizing moral practices in business that prevent reprehensible activities and promote justice for current and future generations.
Why did Angelo Ugolotti's story make headlines?
-Angelo Ugolotti made headlines because he was listed as the chairman of several companies set up by Parmalat, an Italian milk concern, without his knowledge. His actual role was managing the switchboard, highlighting a case of corporate fraud.
What are the limitations of viewing CSR solely through the lens of risk and compliance management?
-Risk and compliance management are limited in that they primarily aim to avoid financial risks and reputational damage, rather than addressing the broader ethical implications of a company's core business activities.
How does CSR differ from a company's philanthropic activities, such as creating a charity foundation or donating money?
-CSR is not just about philanthropy; it's about the ethical manner in which companies earn their profits, including how they treat employees, organize production, market products, and manage their supply chain.
What is meant by the term 'soft laws' in the context of CSR?
-'Soft laws' refer to collective individual commitments to adhere to certain social and ecological standards, such as industry agreements or the UN Global Compact, which are not legally binding but are meant to guide responsible corporate behavior.
Why is it important for CSR to be integrated into a company's core business rather than being an afterthought?
-Integrating CSR into a company's core business ensures that social and ecological criteria are considered in all aspects of operations, leading to systemic changes that contribute to a 'good society' beyond mere compliance or philanthropy.
What role do employees play in the realization of CSR within a company?
-Employees at all levels play a crucial role in realizing CSR by embodying integrity and ethical behavior, which, along with appropriate organizational structures and clear rules, helps to operationalize CSR within the company.
How does the concept of 'individual ethics' and 'institutional ethics' relate to CSR?
-CSR encompasses both individual ethics, which refers to the moral behavior of employees, and institutional ethics, which pertains to the ethical framework and practices embedded within the company's structure and policies.
In what ways can the state contribute to the implementation of corporate responsibility?
-The state, particularly through politics and law, can contribute by setting regulations and providing a framework that encourages responsible business practices, although its influence may be limited in a globalized economy.
What challenges do globalization and societal differentiation pose to the regulation of CSR?
-Globalization and societal differentiation make regulation difficult because while economic activities are highly internationalized, politics and law are often confined within national borders, leading to a complex landscape for effective CSR regulation.
How do NGOs and civil society influence CSR and corporate behavior?
-NGOs and civil society can influence CSR by acting as watchdogs to expose unethical practices and as partners to businesses, promoting responsible behavior and adherence to social and ecological standards.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Pengantar Bisnis Sesi 4 Etika Bisnis dan Konsep Tanggung Jawab Sosial
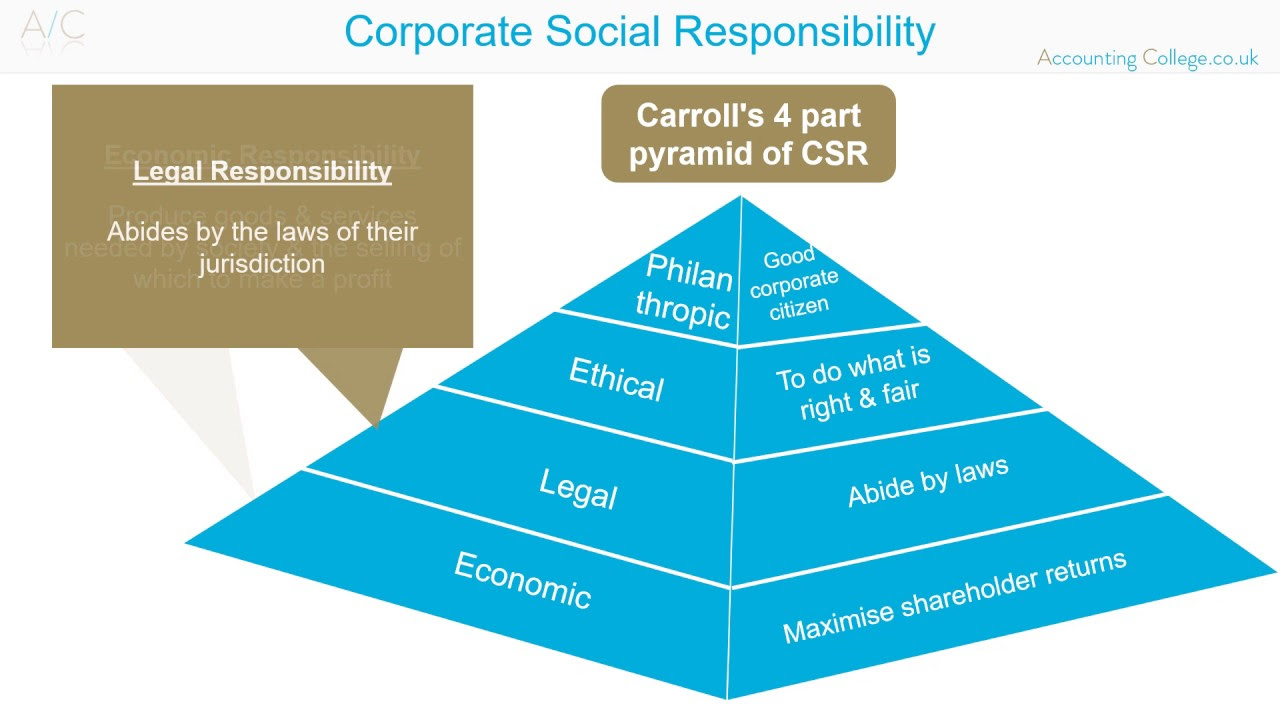
Corporate Social Responsibility - ACCA P1- Revision Theory

CSR: What is Corporate Social Responsibility? Definition Examples Benefits

ACCA F1 - 8 Ethics and corporate governance

Landasan Hukum CSR di Indonesia dan Dinamikanya

What Is Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR)? | Business: Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
