Introduction to circuits and Ohm's law | Circuits | Physics | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script introduces the core concepts of electric circuits and Ohm's Law, using the water flow analogy to clarify voltage, current, and resistance. Voltage is likened to potential energy per unit charge, measured in volts, while current represents the flow of charge over time, expressed in amperes. Resistance is compared to a pipe's narrowing, impeding flow. Ohm's Law is presented as a simple formula: current equals voltage divided by resistance. The script also explains the historical convention of current direction, which is opposite to electron flow.
Takeaways
- 🌟 Ohm's law is the fundamental principle in understanding electric circuits, connecting voltage, current, and resistance.
- 🔋 Voltage is analogous to electric potential energy, measured in volts, and is the potential energy per unit charge.
- 💧 Current is represented by I and is the flow of electric charge, measured in amperes (A) or coulombs per second.
- 🛡 Resistance, denoted by R, is what impedes the flow of charge in a circuit and is measured in ohms.
- 🌊 The water flow metaphor helps to understand the relationship between voltage, current, and resistance in an electric circuit.
- 🔌 Ohm's law formula is V = I * R, where V is voltage, I is current, and R is resistance.
- ⚡ To find the current in a circuit, use the rearranged Ohm's law formula I = V / R.
- 🔄 When a circuit is open, no current flows, similar to a closed pipe preventing water flow.
- 🔄 Closing the circuit allows electrons to flow, analogous to opening a pipe and allowing water to flow.
- 🔄 The direction of conventional current is from the positive to the negative terminal, opposite to the actual flow of electrons.
- 🔍 Even in simple wires, there is some resistance, which is denoted by a jagged line in circuit diagrams.
Q & A
What is the fundamental law introduced in the video script related to electric circuits?
-The fundamental law introduced in the video script is Ohm's Law, which is the most basic law when dealing with electric circuits.
What does Ohm's Law connect in the context of circuits?
-Ohm's Law connects the concepts of voltage, current, and resistance, showing the relationship between these three electrical quantities.
What is the mathematical relationship given by Ohm's Law?
-The mathematical relationship given by Ohm's Law is that voltage (V) is equal to current (I) times resistance (R), or rearranged, current (I) is equal to voltage (V) divided by resistance (R).
What is the symbol used to denote current in the script?
-The symbol used to denote current in the script is the capital letter 'I'.
What is the intuitive explanation for voltage in the script?
-Voltage is intuitively explained as electric potential energy, specifically potential energy per unit charge, with the units being volts.
How is current analogous to the flow of water in the provided metaphor?
-In the water flow metaphor, current is analogous to the amount of water flowing through a pipe per unit of time, measured in coulombs per second.
What is the role of resistance in the context of the water flow metaphor?
-In the water flow metaphor, resistance is analogous to a narrowing of the pipe, which impedes the flow of water, similar to how resistance impedes the flow of electric charge in a circuit.
What is the unit of resistance and how is it denoted?
-The unit of resistance is the ohm, denoted with the Greek letter omega (Ω).
How is the direction of current flow determined in electric circuits, according to the script?
-The direction of current flow is determined by the convention set by Benjamin Franklin, which is from the positive to the negative terminal, despite this being opposite to the actual flow of electrons.
What is the relationship between the amount of water flowing through different parts of the pipe in the water flow metaphor?
-In the water flow metaphor, the amount of water flowing through different parts of the pipe in a second must be the same due to the continuity of flow, similar to the current being the same at different points in an electric circuit.
How is the current in the example circuit calculated using Ohm's Law?
-The current in the example circuit is calculated using Ohm's Law by dividing the voltage (16 volts) by the resistance (8 ohms), resulting in a current of 2 amperes.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Hukum Ohm Ilustrasi dan Contoh Praktis
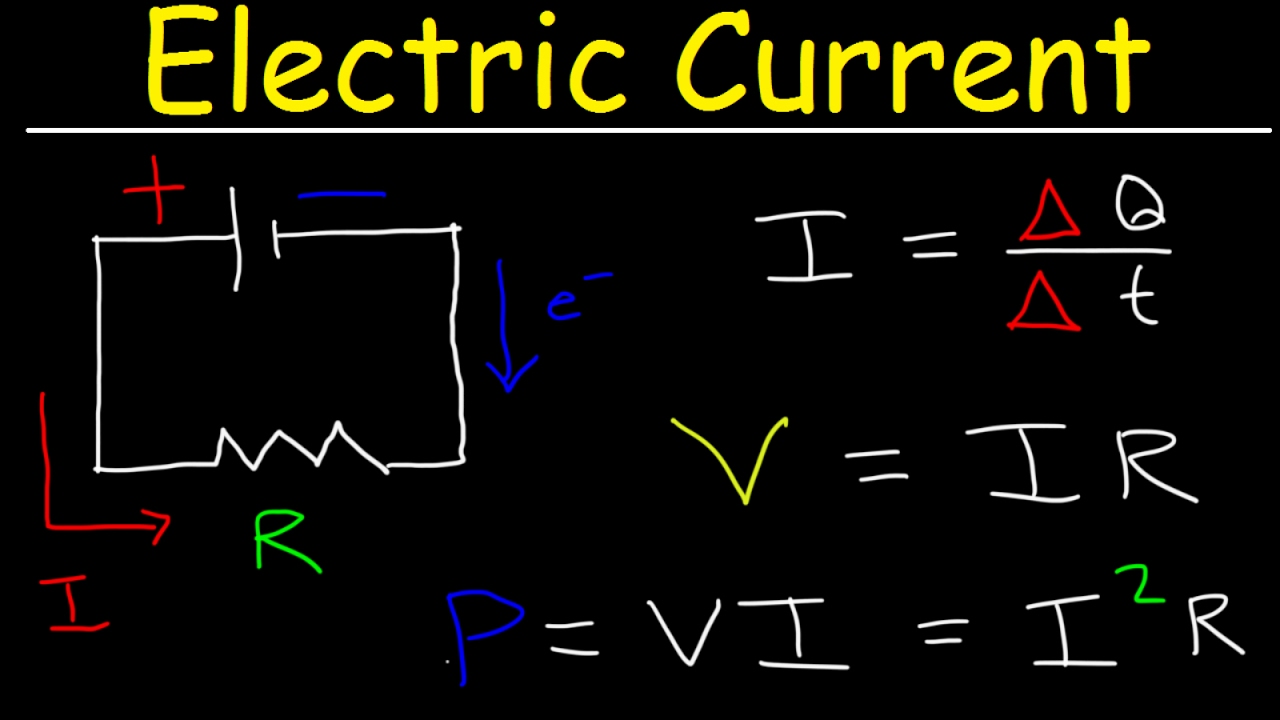
Electric Current & Circuits Explained, Ohm's Law, Charge, Power, Physics Problems, Basic Electricity
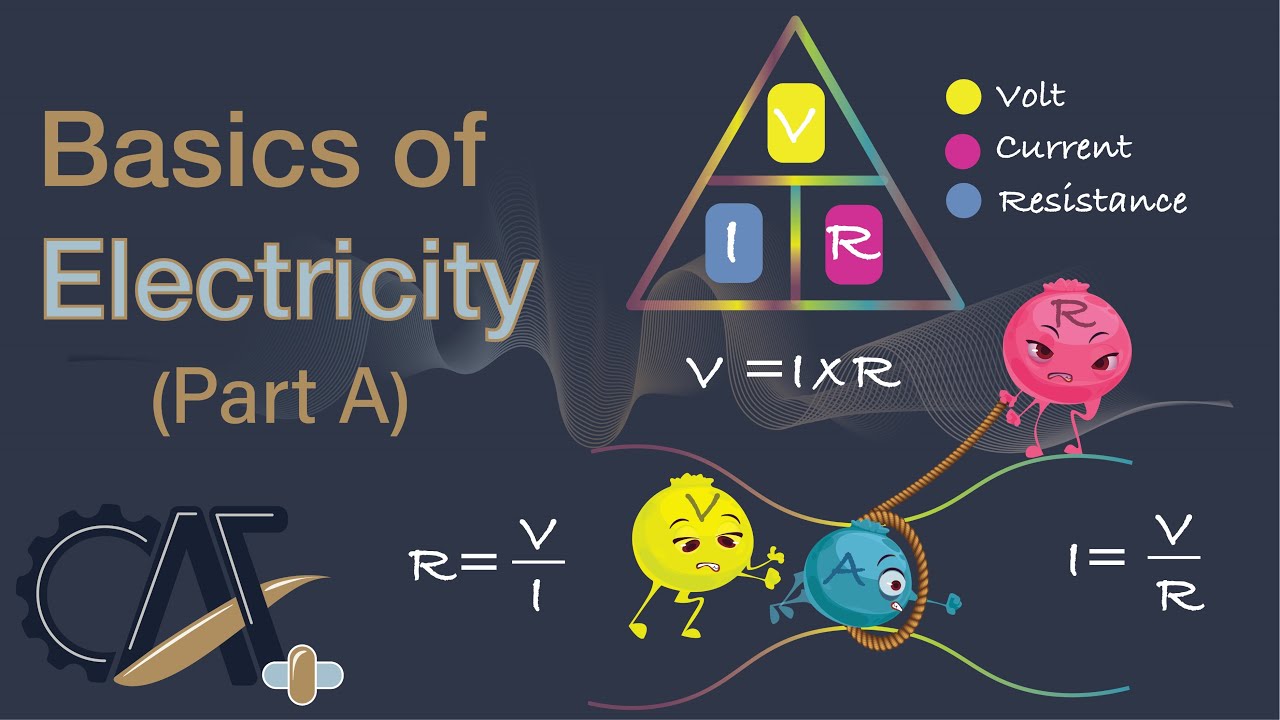
Basics of Electricity-Part A [Voltage, Current, Resistance, and Ohm's Law]

Elektronika Dasar 001 Resistor 01 Universitas Jember

Arus, Tegangan, dan Hambatan | Rangkaian DC | Part 1 | Fisika Dasar
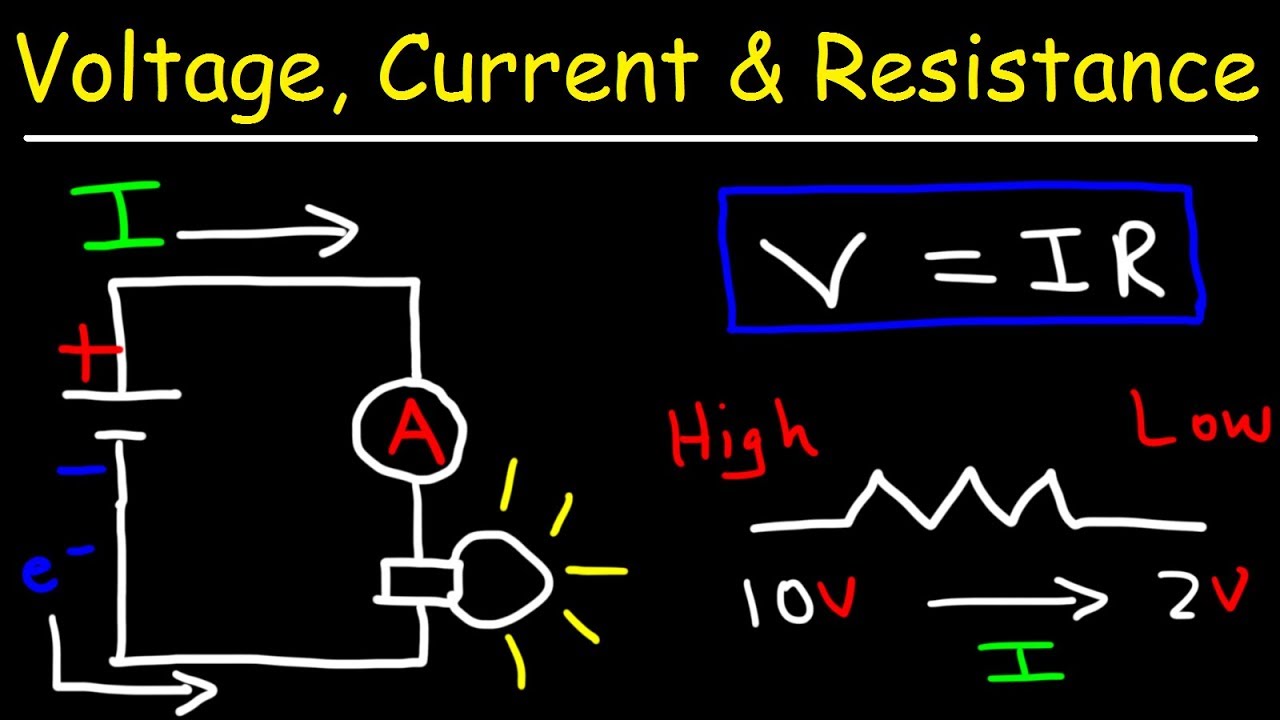
Voltage Current and Resistance
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
