OSI Model: A Practical Perspective - Networking Fundamentals - Lesson 2a
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson delves into the OSI model, a foundational concept in networking. It illustrates how the seven layers of the OSI model facilitate data sharing between hosts, emphasizing the roles of the physical, data link, and network layers. The physical layer is responsible for transporting bits, while the data link layer ensures hop-to-hop delivery using MAC addresses. The network layer, utilizing IP addresses, achieves end-to-end delivery, with routers playing a key role. The lesson clarifies the necessity of both MAC and IP addresses in data transmission and hints at the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) for linking these addresses. The instructor invites viewers to engage with the content and contribute to the course's development.
Takeaways
- 📚 Start with lesson one for a complete understanding of the OSI model.
- 🌐 Networking allows hosts to share data automatically across wires, replacing manual data transfer.
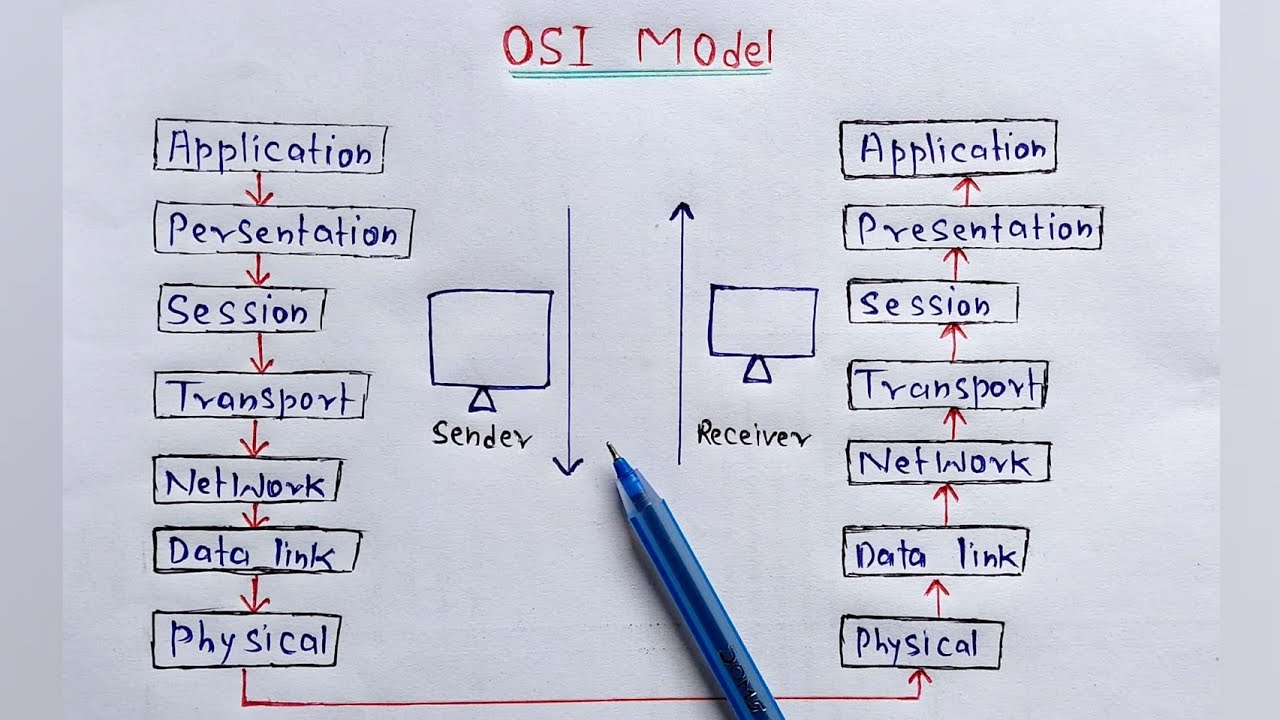
- 🖧 The OSI model divides networking rules into seven layers, each with a specific function.
- 🏗️ The physical layer (Layer 1) is responsible for transporting bits (ones and zeros) between hosts using cables or wireless technologies like Wi-Fi.
- 🔁 Devices like repeaters and hubs, which extend and amplify signals, are considered Layer 1 technologies.
- 🔌 Layer 2, the Data Link Layer, handles hop-to-hop delivery of data using network interface cards (NICs) and MAC addresses.
- 📟 Switches, which facilitate communication within a network, are Layer 2 devices.
- 📡 Layer 3, the Network Layer, is responsible for end-to-end delivery of data using IP addresses.
- 🖧 Routers are Layer 3 devices that help route data between networks.
- 🔗 The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) links IP addresses to MAC addresses, aiding in data flow through the network.
Q & A
What is the primary goal of networking as an industry?
-The primary goal of networking is to allow two hosts to share data with one another automatically across the wire, without the need for manual data transfer between hosts.
What is the OSI model and why is it important?
-The OSI model is a framework that divides the rules for networking into seven different layers. It is important because it standardizes the way data is transmitted between devices, similar to how language rules standardize communication between people.
What is the purpose of the Physical Layer (Layer 1) in the OSI model?
-The purpose of the Physical Layer is to transport bits (ones and zeros) from one computer to another. This includes various types of cables and wireless technologies like Wi-Fi, which are considered Layer 1 technologies.
What is a repeater and why is it considered a Layer 1 device?
-A repeater is a device that amplifies signals from one end to the other, effectively extending a wire. It is considered a Layer 1 device because its primary function is to contribute to the transportation of bits, which aligns with the goal of the Physical Layer.
What is the role of Layer 2 in the OSI model?
-Layer 2, also known as the Data Link Layer, is responsible for hop-to-hop delivery of data. It uses MAC addresses to facilitate the movement of data between network interface cards (NICs) or Wi-Fi access points.
What is a MAC address and why is it used in Layer 2?
-A MAC address is a 48-bit address that uniquely identifies a network interface card. It is used in Layer 2 to enable the hop-to-hop delivery of data by identifying the source and destination NICs for each data packet.
What is the difference between a switch and a hub, and why are they both considered Layer 2 devices?
-A switch is a more intelligent device that facilitates communication within a network and can connect many devices, while a hub is a simpler device that connects multiple devices without much intelligence. Both are considered Layer 2 devices because they aid in the delivery of data between NICs.
What is the purpose of Layer 3 in the OSI model?
-Layer 3, known as the Network Layer, is responsible for end-to-end delivery of data. It uses IP addresses to identify hosts and routers, ensuring that data reaches its intended destination across multiple hops.
Why are both MAC and IP addresses necessary in networking?
-Both MAC and IP addresses are necessary because they serve different purposes. MAC addresses are used for hop-to-hop delivery within a local network, while IP addresses are used for end-to-end delivery across multiple networks or hops.
What is the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) and its role in networking?
-The Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) is a protocol that links a Layer 3 address (IP address) to a Layer 2 address (MAC address). It is crucial for understanding how data flows through a network by facilitating the translation between these two types of addresses.
What will be the focus of the next part of the discussion on the OSI model?
-The next part of the discussion will focus on the Transport Layer, which is Layer 4 of the OSI model. This layer is responsible for end-to-end communication and ensures the reliable delivery of data.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)