Ultrafiltration in the Kidney | Excretion
Summary
TLDRThis educational video delves into the process of ultrafiltration in the kidneys, a vital function for waste removal and regulation of useful substances. It explains how the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule work together in the nephron to filter blood, creating a filtrate that contains waste products and useful substances like glucose and amino acids. The video also highlights the importance of the afferent and efferent arterioles in maintaining blood pressure for effective filtration, and introduces the concept of podocytes that contribute to the selective filtration process.
Takeaways
- 🧐 Ultrafiltration is the body's process of removing both useful and waste products from the blood.
- 📍 Ultrafiltration occurs in the glomerulus, part of the nephron, which is made up of a capillary network and the Bowman's capsule.
- 🌟 The glomerulus is supplied by the afferent arteriole and drained by the efferent arteriole, with the afferent being wider to maintain blood pressure for filtration.
- 🔍 The filtration process involves two layers: the endothelium of the glomerulus and the podocyte slits of the Bowman's capsule.
- 🕊️ Useful substances such as glucose, amino acids, and waste products like urea and salts can pass through the filtration layers into the filtrate.
- 🚫 Larger substances like red blood cells, platelets, and large plasma proteins are too big to pass through and remain in the blood.
- 💧 Filtrate is the liquid produced after ultrafiltration, which is not yet urine but will become so after further processing in the nephron.
- 🔄 The filtration process is continuous and helps regulate the levels of useful substances and waste in the body.
- 🔬 Understanding the structure and function of the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule is crucial for grasping the concept of ultrafiltration.
- 📝 The script emphasizes the importance of terminology in understanding and explaining the ultrafiltration process for exam preparation.
Q & A
What is ultrafiltration in the context of the kidney?
-Ultrafiltration is the process by which the body removes both useful and waste products from the blood, occurring specifically in the glomerulus of the nephron.
Where does ultrafiltration take place in the nephron?
-Ultrafiltration occurs at the beginning of the nephron in the Malpighian body, which is composed of the glomerulus and Bowman's capsule.
What are the two main components of the Malpighian body?
-The two main components of the Malpighian body are the glomerulus, a network of capillaries, and Bowman's capsule, which surrounds the glomerulus.
Why is the afferent arteriole wider than the efferent arteriole?
-The afferent arteriole is wider than the efferent arteriole to maintain high blood pressure and hydrostatic pressure within the glomerulus, facilitating the filtration process.
What is the role of the glomerulus in ultrafiltration?
-The glomerulus, with its network of capillaries, increases the surface area for blood filtration, allowing a large amount of blood to pass through and be filtered.
What is the function of the endothelium in the glomerulus?
-The endothelium is the thin lining of the glomerulus capillaries and is the first filtration layer, allowing certain substances to pass through its pores.
What are podocytes and how do they assist in ultrafiltration?
-Podocytes are specialized cells in Bowman's capsule that have slit-like openings, which serve as the second filtration layer, allowing only certain substances to pass through.
What substances can pass through the ultrafiltration process to become part of the filtrate?
-Substances such as urea, salts, glucose, and amino acids can pass through the ultrafiltration process due to their small size, becoming part of the filtrate.
What substances remain in the blood after ultrafiltration?
-Larger substances like red blood cells, platelets, and large blood plasma proteins remain in the blood as they cannot pass through the filtration layers.
What is the difference between filtrate and urine?
-Filtrate is the liquid produced after ultrafiltration and contains useful substances and wastes. It becomes urine only at the end of the nephron's process in the distal convoluted tubule.
Why is the maintenance of blood pressure important in the ultrafiltration process?
-Maintaining blood pressure is crucial for the ultrafiltration process as it ensures that the hydrostatic pressure is sufficient to force particles through the filtration layers and into the filtrate.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
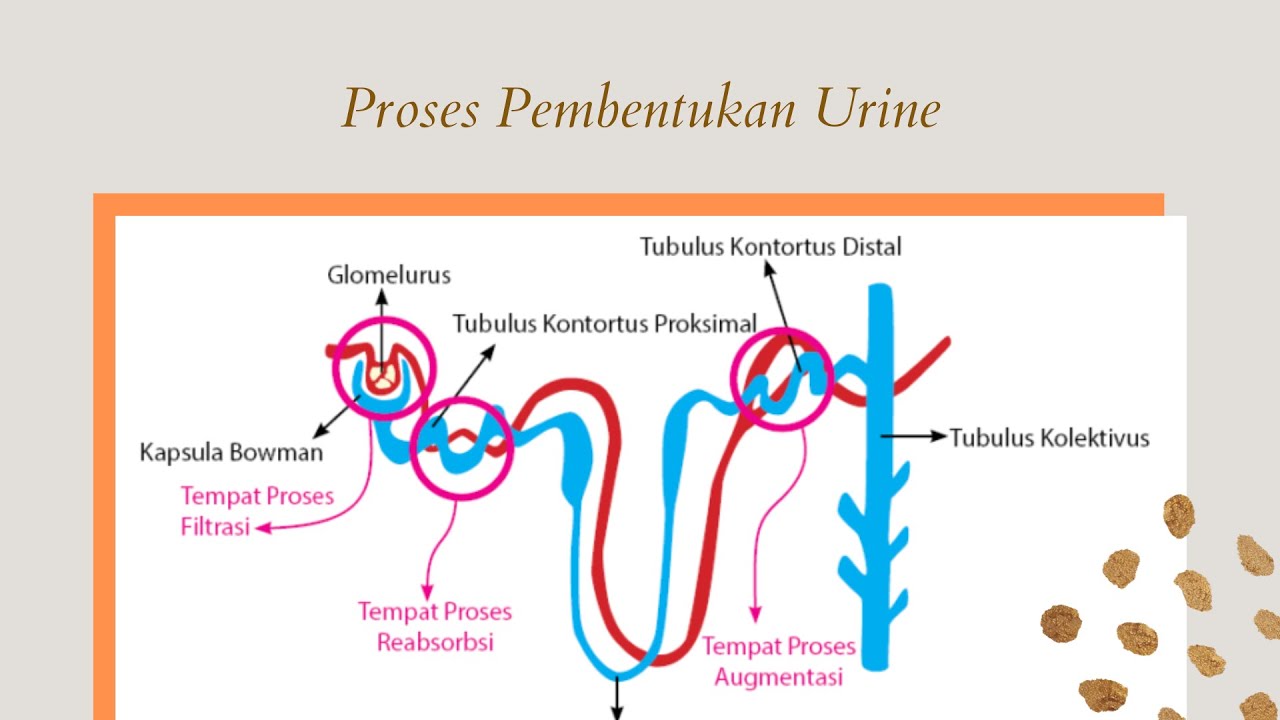
Proses Pembentukan Urine (Filtrasi, dan Reabsorpsi, dan Augmentasi)

Structure and Working Of Kidney | Life Process | Biology class 10 | Prashant Kirad
Bagaimana cara kerja ginjal dalam menyaring darah???
How do your kidneys work? - Emma Bryce
Sistem Ekskresi Manusia Kelas 8 SMP

Sistem Ekskresi Manusia (Bagaimana Proses Cuci Darah?)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
