Co-dominance and Incomplete Dominance | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis educational video script delves into the genetic concepts of dominance in traits, focusing on blood type as an example. It explains the terms homozygous and heterozygous, and clarifies the difference between dominant and recessive alleles, using 'A' being dominant over 'O'. The script then introduces three patterns of dominance: complete dominance, where one allele fully expresses the phenotype (e.g., blood type A from AO genotype); co-dominance, where both alleles influence the phenotype equally, as seen in a flower with both red and blue petals; and incomplete dominance, where a blend of alleles results in a new phenotype, such as a purple flower from red and blue petal alleles. The summary aims to clarify these genetic inheritance patterns for better understanding.
Takeaways
- 📚 Homozygous individuals have two identical alleles for a trait, while heterozygous individuals have two different alleles.
- 🔍 Dominant alleles mask the expression of recessive alleles in a heterozygous genotype.
- 🌟 The 'A' allele is an example of a dominant allele, overpowering the 'O' allele in determining blood type.
- 🌺 Complete dominance is when one allele completely masks the effect of the other allele in the phenotype.
- 🌷 Co-dominance occurs when both alleles in a heterozygous genotype are expressed in the phenotype simultaneously.
- 💐 Incomplete dominance results in a phenotype that is a blend of the two alleles' traits, rather than one being dominant.
- 🌹 The flower example illustrates three patterns of dominance: complete, co-, and incomplete dominance.
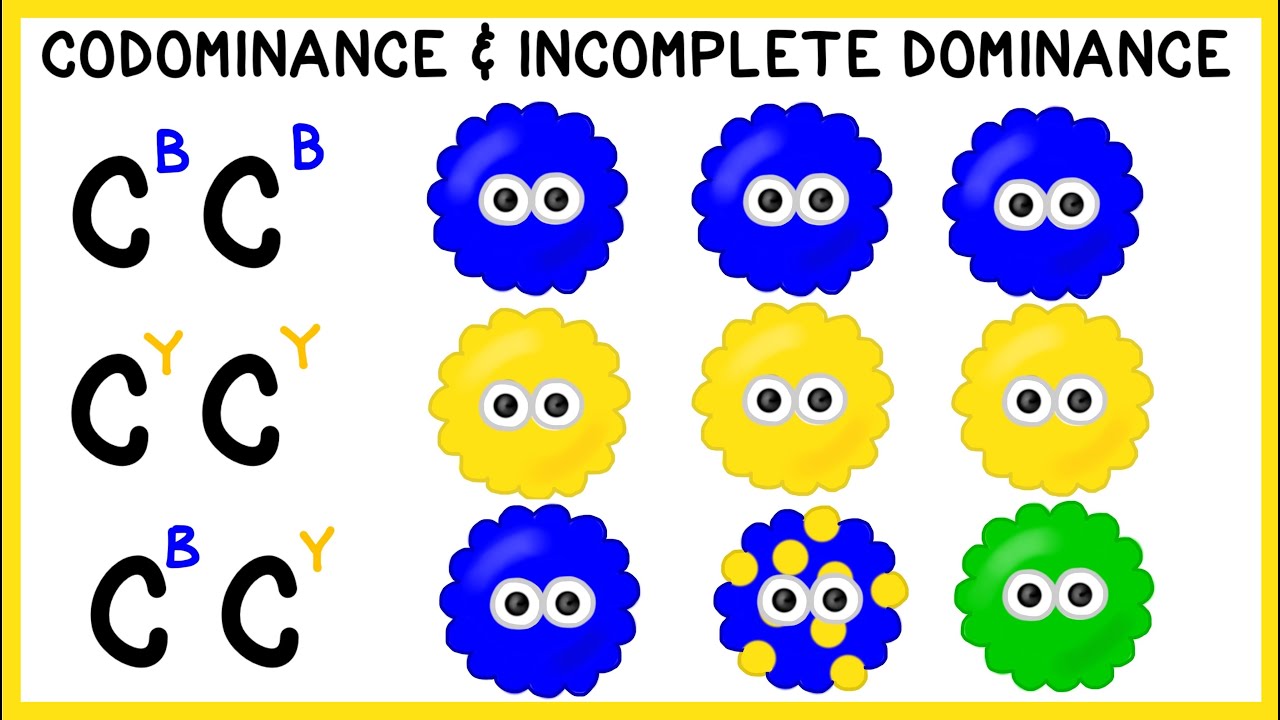
- 🔴 Under complete dominance, a heterozygous genotype (e.g., red R/blue R) would result in a red flower phenotype.
- 🌈 Co-dominance in the flower example would result in a flower with both red and blue petals.
- 🟪 In incomplete dominance, the flower's phenotype would be a mix, such as purple, from the combination of red and blue alleles.
- 🧬 Understanding these patterns of dominance is crucial for grasping how genetic traits are expressed in organisms.
Q & A
What is the definition of homozygous?
-Homozygous refers to having two identical alleles for a particular gene.
What is the definition of heterozygous?
-Heterozygous refers to having two different alleles for a particular gene.
What is an example of complete dominance mentioned in the script?
-An example of complete dominance is the blood type AO, where the A allele is completely dominant over the O allele, resulting in a blood type A phenotype.
How does co-dominance differ from complete dominance?
-In co-dominance, both alleles in the heterozygous genotype are fully expressed in the phenotype, whereas in complete dominance, only the dominant allele is expressed.
What example is used to explain incomplete dominance?
-The example of a flower with red and blue alleles resulting in a purple flower is used to explain incomplete dominance.
How is the heterozygous phenotype expressed in co-dominance?
-In co-dominance, the heterozygous phenotype shows a flower with some red petals and some blue petals.
What is the key characteristic of incomplete dominance?
-The key characteristic of incomplete dominance is that the heterozygous phenotype shows a mixture of the two alleles.
In the flower example, what phenotype is expected from a genotype with two red alleles?
-A genotype with two red alleles is expected to produce a flower with red petals in all dominance patterns.
What phenotype is expected from a genotype with two blue alleles in the flower example?
-A genotype with two blue alleles is expected to produce a flower with blue petals in all dominance patterns.
How does the phenotype change in the heterozygous example under different dominance patterns?
-In complete dominance, the heterozygous phenotype is a red flower. In co-dominance, the flower shows both red and blue petals. In incomplete dominance, the flower shows a mixture, resulting in a purple flower.
What do we learn from the examples of dominance patterns provided?
-We learn that the expression of the heterozygous genotype can vary significantly depending on the dominance pattern: complete dominance shows only the dominant allele, co-dominance shows traits of both alleles, and incomplete dominance shows a mixture of the two alleles.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Ethiopian Grade 11 Biology 4#8 Non Mendelian Inheritance
Codominance and Incomplete Dominance: Non-Mendelian Genetics

Non-Mendelian Inheritance I FULL VIDEO
Non-Mendelian Inheritance | Grade 9 Science Quarter 1 Week 4-5 | Maestrang Techy

Heredity: Crash Course Biology #9

Mendelian Inheritance & Punnett Square | Review | Science 8/9 - Quarter 1 (Review for MELC 3)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
