Phases of meiosis I | Cells | MCAT | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the intricacies of meiosis I, highlighting the unique chromosomal crossover during prophase I, the alignment of chromosomes in metaphase I, and the separation of homologous pairs in anaphase I. It also touches on the formation of haploid cells in telophase I, setting the stage for meiosis II.
Takeaways
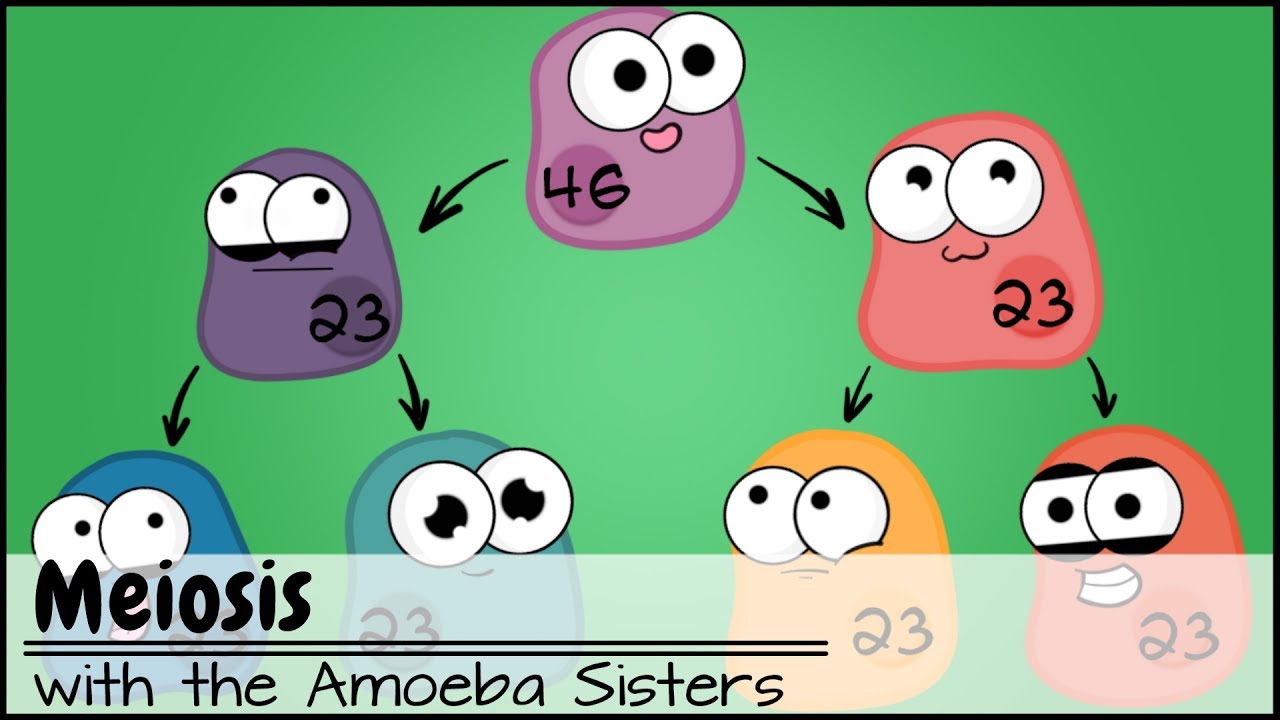
- 🌟 Meiosis I is a specialized type of cell division that occurs in reproductive cells, leading to the production of gametes with half the number of chromosomes.
- 🔬 During prophase I of meiosis, the nuclear envelope breaks down, chromosomes condense, and homologous chromosomes undergo crossover, increasing genetic variation.
- 🧬 Chromosomal crossover involves the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, which can result in different combinations of alleles.
- 📏 Metaphase I is characterized by the alignment of homologous pairs of chromosomes along the cell's equatorial plane, similar to metaphase in mitosis.
- 🔄 Centrosomes play a significant role in metaphase I, organizing microtubules that attach to the kinetochores of chromosomes and facilitate their movement.
- 🤔 The complexity of meiosis, including the movement of chromosomes by microtubules and motor proteins, is a result of billions of years of evolution and is not fully understood.
- 🔄 Anaphase I is distinct from anaphase in mitosis because it is the homologous pairs of chromosomes, not the sister chromatids, that are separated and pulled to opposite poles of the cell.
- 🎯 The separation of homologous pairs in anaphase I is random, contributing to the genetic diversity of the resulting gametes.
- 🧬 Telophase I involves the unraveling of chromosomes back into a chromatin state, the reformation of the nuclear membrane, and the dissolution of microtubules.
- 🌱 Cytokinesis in meiosis I results in two haploid cells, each with a unique combination of genetic material due to the previous stages of meiosis.
- 🚀 The process of meiosis I is a critical step towards the formation of gametes, setting the stage for meiosis II, which will further reduce the chromosome number by separating sister chromatids.
Q & A
What is the main event that occurs during prophase I of meiosis?
-During prophase I of meiosis, the main event is the chromosomal crossover where homologous sections of chromosomes exchange genetic material, adding genetic variation.
What is the role of the nuclear envelope during prophase I in meiosis?
-The nuclear envelope starts to disappear during prophase I, allowing the chromosomes to condense and prepare for the crossover event.
How does metaphase I in meiosis differ from metaphase in mitosis?
-Metaphase I in meiosis involves the alignment of homologous pairs of chromosomes along the cell's central axis, whereas in mitosis, sister chromatids align instead.
What are the functions of the centrosomes during metaphase I of meiosis?
-The centrosomes play a significant role in metaphase I by organizing the microtubules that attach to the kinetochores of the chromosomes, facilitating their movement to the cell's equator.
What is the key difference between anaphase I of meiosis and anaphase in mitosis?
-In anaphase I of meiosis, it is the homologous pairs of chromosomes that are pulled apart, not the sister chromatids as in mitosis.
Why is the separation of homologous pairs during anaphase I significant for genetic variation?
-The random separation of homologous pairs during anaphase I contributes to genetic variation by ensuring that each resulting gamete has a unique combination of maternal and paternal genetic material.
What process occurs during telophase I of meiosis that is similar to mitosis?
-During telophase I of meiosis, the nuclear membrane begins to reform around the separated chromosomes, similar to the process in mitosis, and cytokinesis starts to separate the cells.
How does the process of meiosis I result in cells with a haploid number of chromosomes?
-After meiosis I, the cell divides into two daughter cells, each with a haploid number of chromosomes, which is half the original diploid number, due to the separation of homologous pairs.
What will occur in meiosis II that is similar to mitosis?
-In meiosis II, the sister chromatids of each chromosome will be separated, similar to what happens in mitosis, resulting in four haploid gametes from the original germ cell.
What is the role of microtubules in the process of meiosis I?
-Microtubules play a crucial role in meiosis I by connecting to the kinetochores of chromosomes and facilitating their movement to opposite ends of the cell during anaphase I.
How does the chromosomal crossover during prophase I contribute to genetic diversity in sexual reproduction?
-The chromosomal crossover during prophase I allows for the exchange of genetic material between homologous chromosomes, creating new combinations of genes in the offspring, thus increasing genetic diversity.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)