Statistics Grade 10: Box and whisker
Summary
TLDRIn this lesson, the teacher explains the five-number summary and how to create a box-and-whisker plot. The five-number summary includes the minimum value, lower quartile (Q1), median (Q2), upper quartile (Q3), and maximum value. Using a sequence of numbers, the teacher demonstrates calculating each component and plotting them on a box-and-whisker diagram. The lesson emphasizes the importance of using a ruler for accuracy and briefly discusses data skewness based on the whisker lengths. This provides a clear and concise understanding of these fundamental statistical concepts.
Takeaways
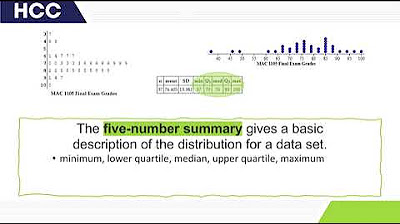
- 📚 The five number summary includes the minimum value, lower quartile (Q1), median (Q2), upper quartile (Q3), and the maximum value.
- 📏 To find the lower quartile (Q1), use the formula \( \frac{(n + 1)}{4} \) and interpolate between the values at the calculated position.
- 🔢 The median is found by using the formula \( \frac{(n + 1)}{2} \) and selecting the value at the resulting position in the data set.
- 📈 The upper quartile (Q3) is calculated similarly to Q1, but using \( \frac{3 \times (n + 1)}{4} \) to find the position.
- 🏁 The maximum and minimum values are the highest and lowest numbers in the data set, respectively.
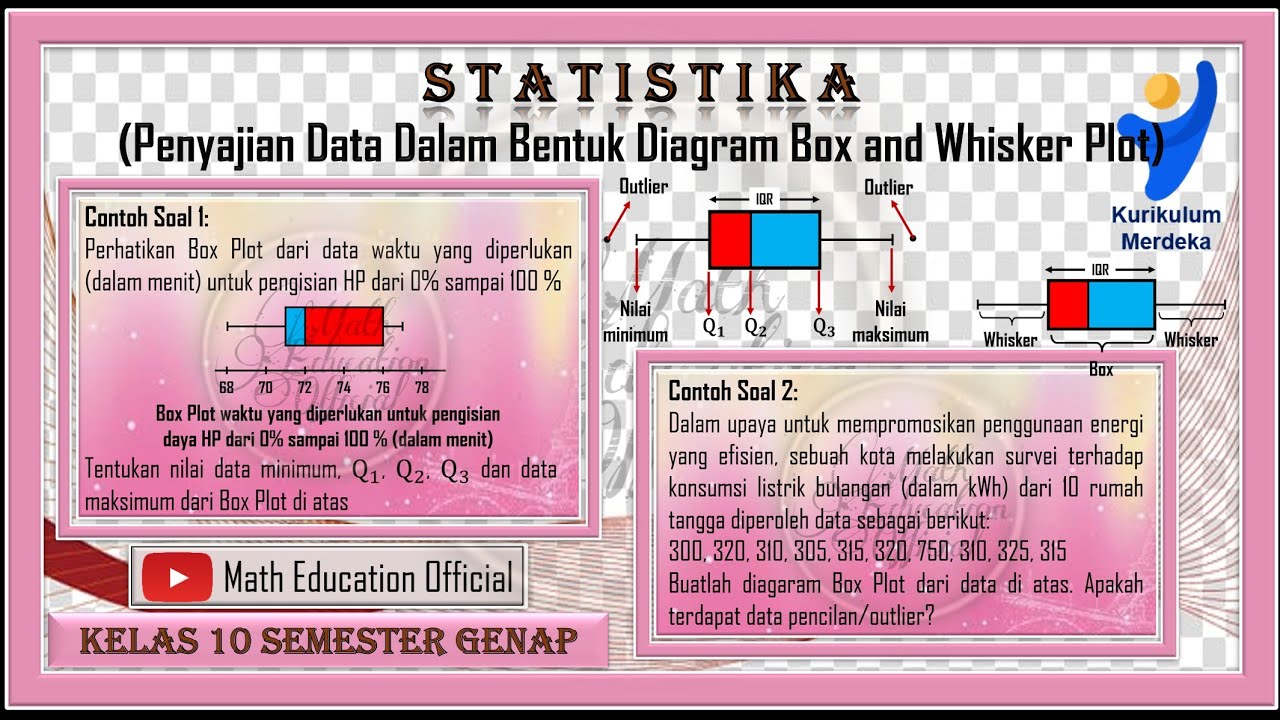
- 📊 A box and whisker diagram visually represents the five number summary, with a box for the interquartile range (IQR) and whiskers for the minimum and maximum values.
- 📐 It's important to use a ruler when drawing a box and whisker diagram to ensure accuracy in the representation.
- 📉 The length of the whiskers can indicate the skewness of the data; a longer whisker on one side suggests the data is skewed in that direction.
- 📝 The script provides a step-by-step guide on how to calculate each part of the five number summary using a specific data set.
- 🎓 Teachers may refer to the median as Q2, emphasizing its position as the halfway point in the data set.
- 🤔 Understanding the concept of skewness is simplified to recognizing which side the longer whisker is on, indicating the direction of skew.
Q & A
What is the five number summary in statistics?
-The five number summary includes the minimum value, the lower quartile (Q1), the median (Q2), the upper quartile (Q3), and the maximum value of a data set.
How is the lower quartile (Q1) calculated?
-Q1 is calculated by taking the position at (n + 1) / 4, where n is the number of values in the data set, and then finding the value at that position or the average of the values at that position.
What is the median and how is it found?
-The median is the middle value of a data set when it is ordered from least to greatest. It is found by taking the position at (n + 1) / 2 and locating the value at that position.
How do you calculate the upper quartile (Q3)?
-Q3 is calculated by taking the position at 3 * (n + 1) / 4, finding the value at that position, and then averaging it with the next value if necessary.
What is the maximum value in the five number summary?
-The maximum value is the highest number in the data set.
What is a box and whisker diagram and how is it related to the five number summary?
-A box and whisker diagram is a graphical representation of the five number summary, showing the minimum, Q1, median, Q3, and maximum values, with a box for the interquartile range and whiskers extending to the minimum and maximum values.
Why is it recommended to use a ruler when drawing a box and whisker diagram?
-Using a ruler helps to ensure that the diagram is accurately scaled and that the relative lengths of the box and whiskers correctly represent the data distribution.
What does the length of the whiskers in a box and whisker diagram represent?
-The length of the whiskers represents the spread of the data outside the interquartile range, indicating the variability of the data.
How can you determine if a box and whisker diagram is skewed to the right or left?
-A box and whisker diagram is considered skewed to the right if the right whisker is longer, indicating that the data tail extends more to the right. It is skewed to the left if the left whisker is longer.
What is the significance of the interquartile range (IQR) in a box and whisker diagram?
-The interquartile range (IQR), which is the distance between Q1 and Q3, represents the middle 50% of the data set and provides insight into the data's central tendency and dispersion.
Can you provide an example of how to calculate Q1, median, and Q3 from the given data sequence?
-For the given data sequence, the minimum is 8, Q1 is 12.5, the median (Q2) is 19, Q3 is 27, and the maximum is 40.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)