Parkinson's Disease Symptoms, Treatment, Nursing Care, Pathophysiology NCLEX Review
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive overview of Parkinson's disease, a movement disorder affecting dopaminergic neurons. It discusses the disease's impact on movement, the role of dopamine, and the imbalance with acetylcholine. The video also covers symptoms, treatments including medications like carbidopa-levodopa, and nursing interventions focusing on safety, psychosocial support, and nutrition.
Takeaways
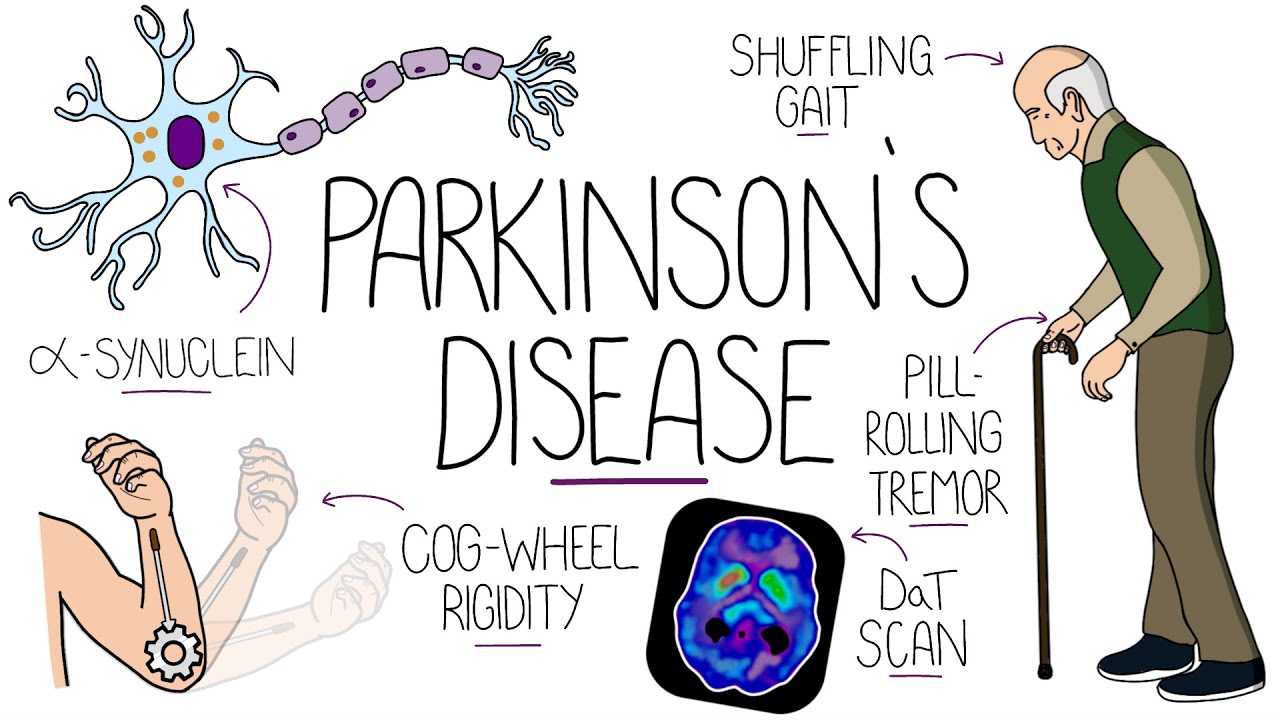
- 🧠 Parkinson's disease is a neurological condition that primarily affects movement, characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra.
- 💉 The reduction in dopamine, a neurotransmitter crucial for movement accuracy, leads to the characteristic symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
- 🔄 There is an imbalance in the nervous system between acetylcholine, an excitatory neurotransmitter, and dopamine, an inhibitory neurotransmitter, in Parkinson's disease.
- 💊 Medications for Parkinson's disease aim to restore the balance between acetylcholine and dopamine, with anticholinergic medications being a common treatment for younger patients experiencing tremors.
- 👴 Parkinson's disease typically affects older adults, but it can also occur in younger individuals, such as actor Michael J. Fox, who was diagnosed at age 29.
- 🚶♂️ Early signs of Parkinson's disease include subtle tremors, stiffness of extremities, and changes in gait, which can progress to affect the entire body over time.
- 🏠 Nursing interventions for Parkinson's disease focus on safety, psychosocial support, digestion and nutrition, and education about medication side effects and management.
- 🛠️ Assistive devices like canes, walkers, and handrails, as well as modifications to the home environment, can help improve safety and mobility for patients with Parkinson's disease.
- 🍽️ Dietary considerations for Parkinson's patients include a soft diet, high-fiber intake, and careful management of protein intake to optimize medication effectiveness.
- 💪 Encouraging physical activity and providing support for autonomy in daily living tasks can help maintain quality of life for individuals with Parkinson's disease.
Q & A
What is Parkinson's disease?
-Parkinson's disease is a neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement. It is characterized by the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, leading to a decrease in the neurotransmitter dopamine, which is crucial for movement accuracy.
Why are movements affected in Parkinson's disease?
-Movements are affected because the dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra start to die, resulting in less dopamine being produced. Since dopamine is essential for the accuracy of movements, its deficiency leads to various movement-related issues.
What is the role of the substantia nigra in Parkinson's disease?
-The substantia nigra is a part of the basal ganglia in the midbrain that controls movement. In Parkinson's disease, the dopaminergic neurons in this area degenerate, leading to a reduction in dopamine and affecting movement control.
How does the balance between acetylcholine and dopamine relate to Parkinson's disease?
-In Parkinson's disease, the reduction of dopamine leads to an imbalance with acetylcholine, an excitatory neurotransmitter. With less inhibitory dopamine, acetylcholine over-stimulates neurons, causing symptoms like tremors and rigidity.
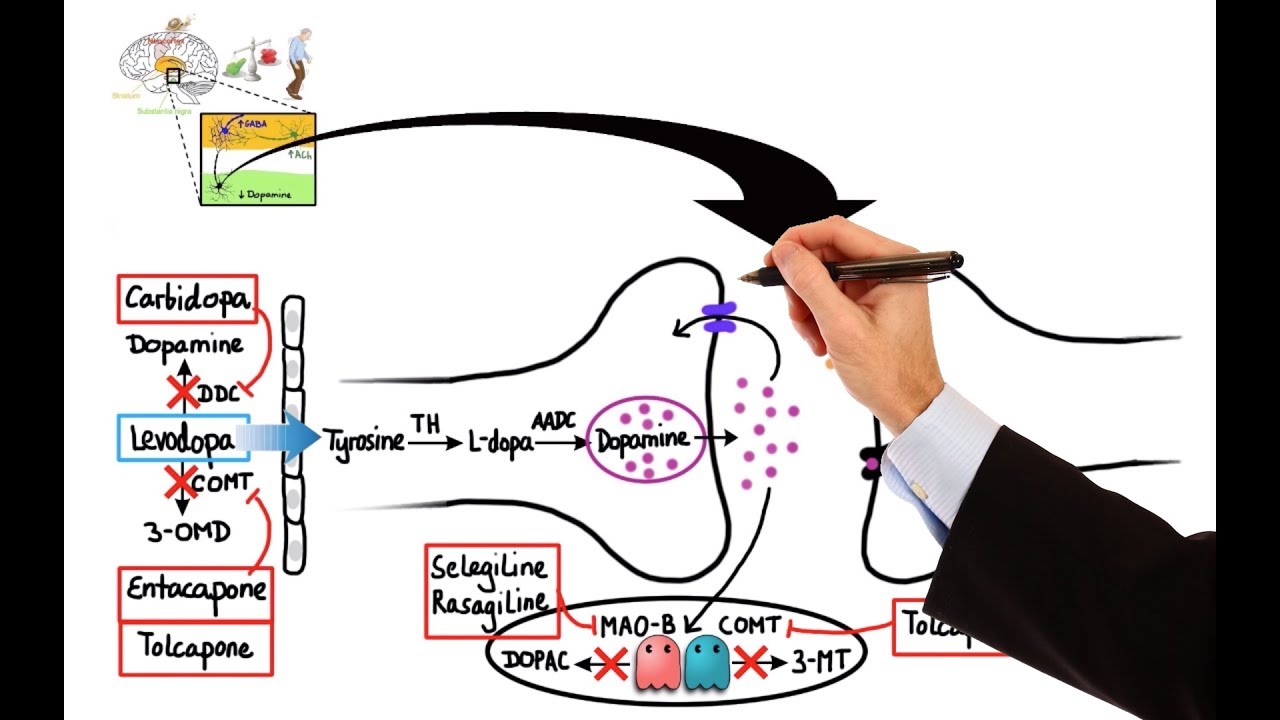
What is the significance of dopamine agonists in treating Parkinson's disease?
-Dopamine agonists, such as ropinirole, stimulate dopamine receptors and help improve the signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease by mimicking the effects of dopamine.
Why are anticholinergic medications used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease?
-Anticholinergic medications, like benztropine, are used to decrease the excessive cholinergic activity caused by the dopamine deficiency. They help reduce symptoms like tremors and rigidity but are typically prescribed to younger patients due to potential side effects.
Which group of patients is more likely to experience extreme tremors in Parkinson's disease?
-Younger patients with Parkinson's disease are more likely to experience extreme tremors and may be prescribed anticholinergic medications to help manage these symptoms.
What are some common early signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease?
-Early signs and symptoms of Parkinson's disease can be subtle and may include tremors at rest, stiffness of extremities, and changes in walking posture. These symptoms often start in one extremity or side of the body and can progress to affect the entire body over time.
How can patients with Parkinson's disease manage 'freeze ups' during walking?
-Patients can manage 'freeze ups' by changing the direction of movement, using a cane or walker with a laser pointer to guide their steps, or consciously making an effort to raise their legs high as if marching or stepping over an object.
What are some nursing interventions for patients with Parkinson's disease?
-Nursing interventions include ensuring safety through the use of assistive devices and education on preventing falls, addressing psychosocial needs to reduce isolation and depression, and managing digestion and nutrition issues such as constipation and difficulties with swallowing.
Why is it important for patients with Parkinson's disease to be cautious with their diet, especially protein intake?
-It is important because protein can compete with Parkinson's medications, such as carbidopa-levodopa, in the small intestine, potentially reducing the absorption of the medication and affecting its effectiveness.
What are some side effects of carbidopa-levodopa, and how can they be managed?
-Side effects of carbidopa-levodopa include nausea and involuntary movements. To manage these, patients may be prescribed COMT inhibitors, such as entacapone, to extend the effect of levodopa and reduce the 'wearing off' phenomenon.
How do monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors help in the treatment of Parkinson's disease?
-Monoamine oxidase type B inhibitors, such as selegiline, increase dopamine levels by inhibiting the enzyme that breaks down dopamine, leading to an improvement in motor symptoms.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Parkinson's Disease | Causes & Pathophysiology | Part 2
Understanding Parkinson's Disease (Including Direct and Indirect Pathways)
Pharmacology - DRUGS FOR PARKINSON'S DISEASE (MADE EASY)

Parkinson's disease - an Osmosis Preview

Sensorimotor Part 7

Putting it all together - Pathophysiology of Parkinson's disease | NCLEX-RN | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
