GENERAL EMBRYOLOGY -THE FIRST WEEK OF HUMAN DEVELOPMENT - DR ROSE JOSE MD DNB MNAMS
Summary
TLDRThis video script delves into the fascinating world of human embryology, detailing the formation of oocyte and sperm through oogesis and spermatogenesis. It explains the journey of the fertilized ovum from the ampulla to the uterus, where it undergoes cleavage division, compaction, and forms a blastocyst. The script also covers the critical process of implantation in the uterine cavity and the potential complications of ectopic pregnancy, providing a comprehensive overview of early human development.
Takeaways
- 😀 Human pregnancy lasts for approximately 40 weeks or 280 days, divided into the embryonic and fetal periods.
- 🔬 The embryonic period is from fertilization up to 8 weeks, while the fetal period extends from the 3rd month until birth.
- 🌱 The embryonic period itself is further divided into the germinal period and the embryonic period proper, with the germinal period being crucial for the formation of the three germ layers.
- 💡 The germinal period includes the time from fertilization to 3 weeks of development, resulting in the formation of the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
- 🚀 The embryonic period proper spans from the 4th to the 8th week of development, following the establishment of the germ layers.
- 🌟 The first week of development involves cleavage division, the formation of a morula, the development of a blastocyst, and implantation into the uterine wall.
- 🌀 Cleavage division is the process of repeated mitotic division that reduces the size of the zygote to a normal cell size.
- 🌐 The morula is a 16-cell stage where cells adhere to each other, forming a sphere covered by the zona pellucida.
- 🌌 The blastocyst is formed when the morula enters the uterine cavity, and the cells are pushed to one side, forming a large cavity known as the blastocoel.
- 🏥 Implantation is the process where the blastocyst attaches to the uterine endometrium, beginning with the disappearance of the zona pellucida and invasion of the endometrial layers.
- ⚠️ Ectopic pregnancies occur when the blastocyst implants outside the upper segment of the uterus, which can be intrauterine or extrauterine, with placenta previa being a specific type of intrauterine ectopic pregnancy.
Q & A
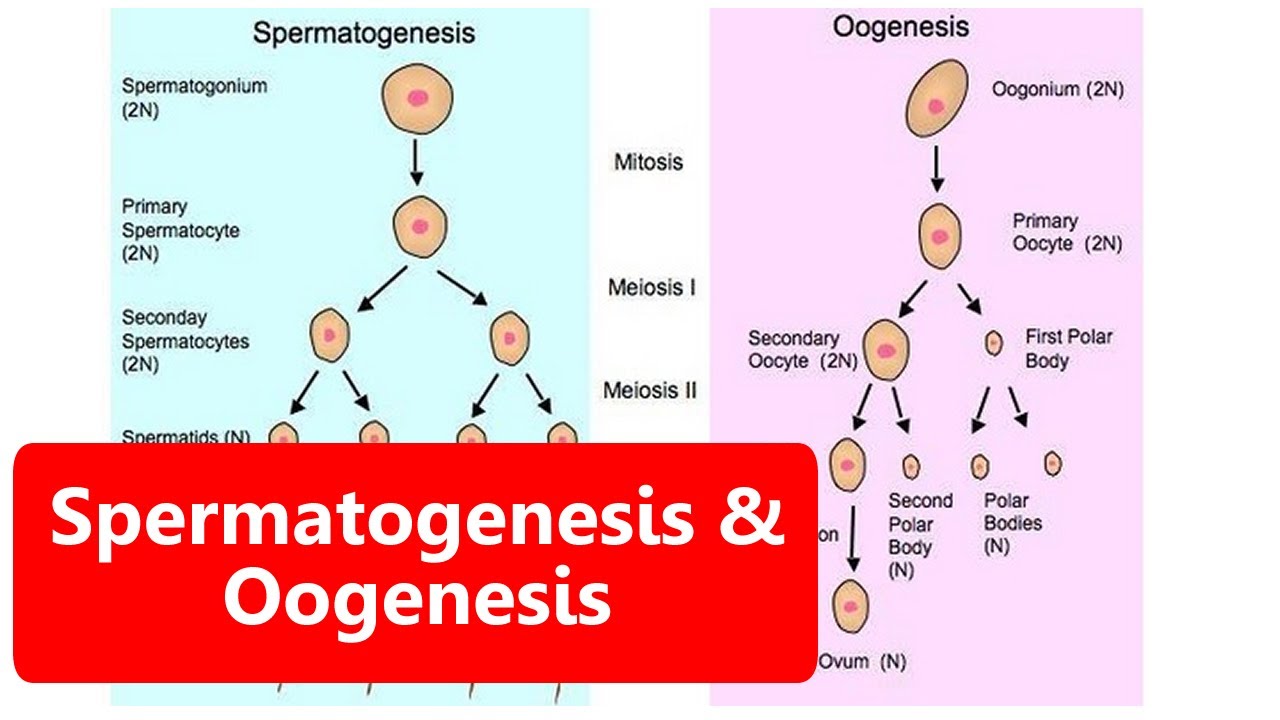
What are the two processes involved in the formation of oocyte and sperm?
-The two processes involved in the formation of oocyte and sperm are oogenesis and spermatogenesis, respectively.
What are the four parts of the uterine tube mentioned in the script?
-The four parts of the uterine tube are the intrapelvic part, the isthmus, the ampulla, and the infundibulum.
Where does fertilization typically occur in the female reproductive system?
-Fertilization typically occurs in the ampulla part of the uterine tube.
What is the duration of a full human pregnancy in terms of weeks and days?
-A full human pregnancy lasts for 40 weeks or 280 days.
How is the duration of pregnancy classified into two main periods?
-The duration of pregnancy is classified into the embryonic period and the fetal period.
What happens during the embryonic period of pregnancy?
-The embryonic period occurs from the point of fertilization up to 8 weeks of development, including the germinal period and the embryonic period proper.
What are the three germ layers formed during the germinal period?
-The three germ layers formed during the germinal period are the ectoderm, mesoderm, and endoderm.
What are the major events of the first week of development mentioned in the script?
-The major events of the first week of development are cleavage division, formation of the morula, formation of the blastocyst, and implantation.
What is the significance of the zona pellucida in the early development of the embryo?
-The zona pellucida is an outer covering that prevents the zygote from implanting prematurely during its travel from the ampulla to the uterine cavity.
What is the blastocyst and how is it formed?
-The blastocyst is a stage in embryonic development characterized by a cavity known as the blastocoel, formed by the compaction of cells into an outer cell mass (trophoblast) and an inner cell mass (embryoblast).
What are the different types of ectopic pregnancies mentioned in the script?
-The different types of ectopic pregnancies mentioned are intrauterine ectopic pregnancy (placenta previa) and extrauterine ectopic pregnancy, which can occur in the fallopian tube, ovary, or abdominal cavity.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

BIOLOGI Kelas 11 - Sistem Reproduksi (PART 1) | GIA Academy

Rangkuman Materi IPA Kelas 9 Bab 1 | Sistem Reproduksi Manusia

Reproductive System | Fertilization

GAMETOGENESIS #videopembelajaranipa @nova_scienceart9251
SPERMATOGENESIS DAN OOGENESIS - Sistem Reproduksi Pada Manusia | Belajar IPA Kelas 9 SMP/ MTS

PENCIPTAAN MANUSIA DALAM PERSPEKTIF AL-QUR'AN & SAINS /PROCESS OF HUMAN CREATION IN QUR’AN & SCIENCE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
