slide 18
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Brainy Pandas introduces the concept of primary active transport, explaining how it differs from passive transport. The focus is on the sodium-potassium pump, which uses ATP to move sodium and potassium ions against their concentration gradients. The process involves binding and releasing ions through a carrier protein, maintaining proper ion balance inside and outside the cell. This is a crucial mechanism for cellular function. The video concludes by inviting viewers to ask questions in the comments and encouraging them to like and subscribe for more educational content on topics like resting membrane potential.
Takeaways
- 😀 Active transport is the movement of substances from a low concentration to a high concentration, opposite to passive transport.
- 😀 Primary active transport requires energy, specifically from ATP, to move substances against their concentration gradient.
- 😀 Primary active transport is different from passive transport, which does not use ATP and moves substances from high to low concentration via diffusion.
- 😀 The sodium-potassium pump is a key example of primary active transport, moving sodium and potassium ions across cell membranes.
- 😀 Sodium concentration is low inside cells (intracellular) and high outside (extracellular), while potassium concentration is the opposite.
- 😀 The sodium-potassium pump transports three sodium ions out of the cell and two potassium ions into the cell, against their concentration gradients.
- 😀 ATP is essential for the sodium-potassium pump to function; it releases a phosphate to provide the energy needed for the pump to change shape and transport ions.
- 😀 The sodium-potassium pump operates through a cyclical process where it binds sodium, hydrolyzes ATP, releases sodium, then binds potassium and returns to its initial shape.
- 😀 The cycle of the sodium-potassium pump continues to maintain proper ion gradients across the cell membrane.
- 😀 Understanding primary active transport, like the sodium-potassium pump, is important for comprehending how cells maintain homeostasis and perform various cellular functions.
Q & A
What is active transport and how does it differ from passive transport?
-Active transport is the movement of substances across a membrane from a region of lower concentration to a region of higher concentration, which requires energy. This is the opposite of passive transport, which moves substances from high to low concentration without the use of energy.
What is the main source of energy used in primary active transport?
-The main source of energy in primary active transport is ATP (adenosine triphosphate).
What are the two types of active transport mentioned in the script?
-The two types of active transport mentioned are primary active transport and secondary active transport.
What is the sodium-potassium pump, and why is it important?
-The sodium-potassium pump is a carrier protein that transports sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell, both against their concentration gradients. It is crucial for maintaining proper ion balance in the cell, which is necessary for many cellular functions, including nerve transmission and muscle contraction.
How does the sodium-potassium pump work step by step?
-The sodium-potassium pump works in the following steps: 1) It binds three sodium ions from inside the cell. 2) It uses energy from ATP, which donates a phosphate group, to change shape. 3) It releases the sodium ions outside the cell. 4) It binds two potassium ions from outside the cell. 5) It releases the phosphate group, which returns the pump to its original shape and releases the potassium ions inside the cell.
What is the role of ATP in the sodium-potassium pump mechanism?
-ATP provides the energy required for the sodium-potassium pump to change shape and transport ions against their concentration gradients. This energy comes from the phosphate group that is transferred from ATP to the pump.
What happens to ATP when it is used by the sodium-potassium pump?
-When ATP is used by the sodium-potassium pump, it is converted into ADP (adenosine diphosphate) after losing a phosphate group, which provides the necessary energy for the pump to function.
Why does the sodium-potassium pump transport sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell?
-The sodium-potassium pump transports sodium ions out of the cell and potassium ions into the cell to maintain the proper concentration of these ions inside and outside the cell. Sodium has a high concentration outside the cell and a low concentration inside, while potassium has a low concentration outside the cell and a high concentration inside.
What is the importance of maintaining the concentration gradients of sodium and potassium in cells?
-Maintaining the concentration gradients of sodium and potassium is essential for the function of many cellular processes, such as nerve impulse transmission, muscle contraction, and maintaining the cell's overall stability and function.
What happens if the sodium-potassium pump is not functioning properly?
-If the sodium-potassium pump is not working properly, the cell's ion balance will be disrupted. This can lead to problems like impaired nerve function, muscle weakness, or cell death due to an inability to maintain the proper concentrations of sodium and potassium inside and outside the cell.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Active Transport

Cell Membrane Transport - Transport Across A Membrane - How Do Things Move Across A Cell Membrane

3. Movement into and out of cells (Cambridge IGCSE Biology 0610 for exams in 2023,2024 and 2025)

Transpor membran: Bagaimana molekul bergerak menembus membran plasma?

Cellular Transport Project
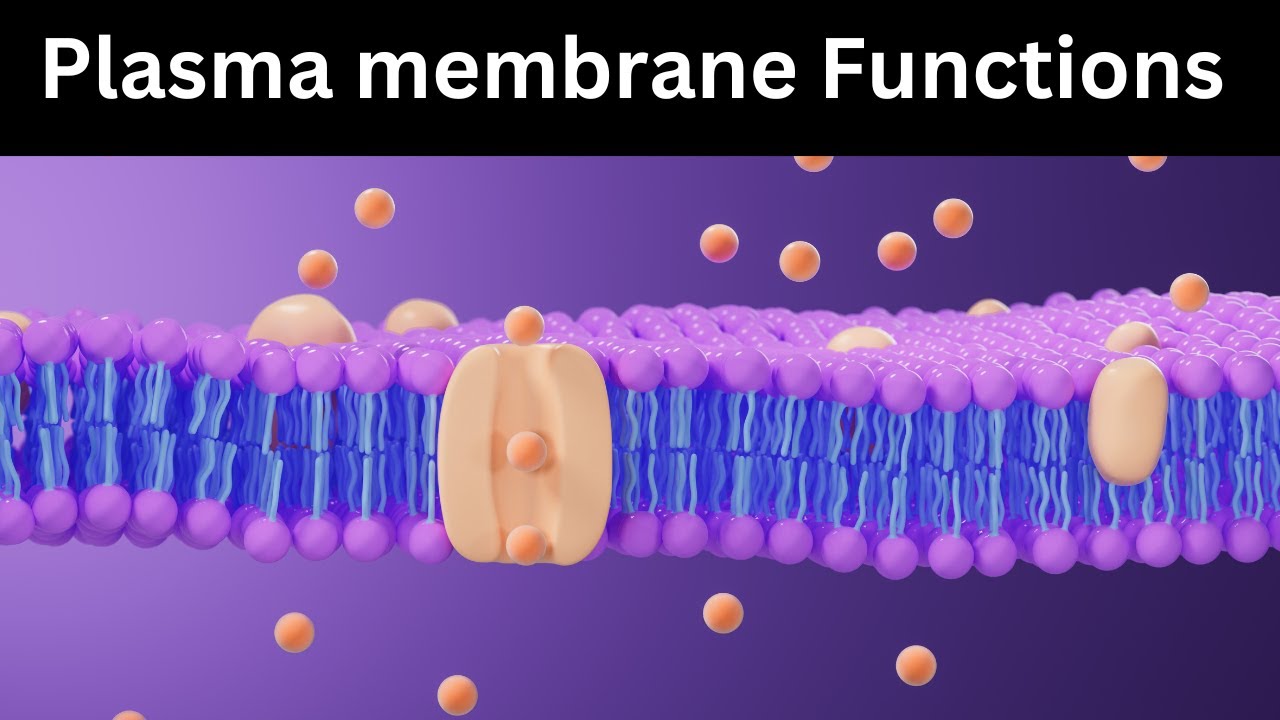
Cell Membrane Functions Explained | Transport Mechanisms & Structure | Biology Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
