Biokimia: Sistem Biologi (Struktur dan Fungsi Sel)
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the biological systems of life, focusing on the structure and function of cells. It explains the biological hierarchy, from biosphere to individual cells, and delves into the differences between prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. The video highlights key organelles, such as the nucleus, ribosomes, mitochondria, chloroplasts, and more, emphasizing their functions in cellular processes. The lecturer provides a thorough explanation of how cells are organized, how they contribute to the larger biological systems, and how the different components work together to sustain life. This knowledge forms the foundation for understanding biochemistry and metabolism.
Takeaways
- 😀 The study of biology involves understanding the structure and functions of cells and their organelles.
- 😀 The biological hierarchy starts from the biosphere and scales down to the atom level, with ecosystems, populations, and organisms at intermediate levels.
- 😀 A cell is the smallest unit of life, and its study forms the basis for biochemistry and metabolism.
- 😀 There are two major types of cells: prokaryotic and eukaryotic, with key structural differences including the presence or absence of a membrane-bound nucleus.
- 😀 Prokaryotic cells, like bacteria, have a simpler structure and lack a membrane-bound nucleus, containing only a nucleoid.
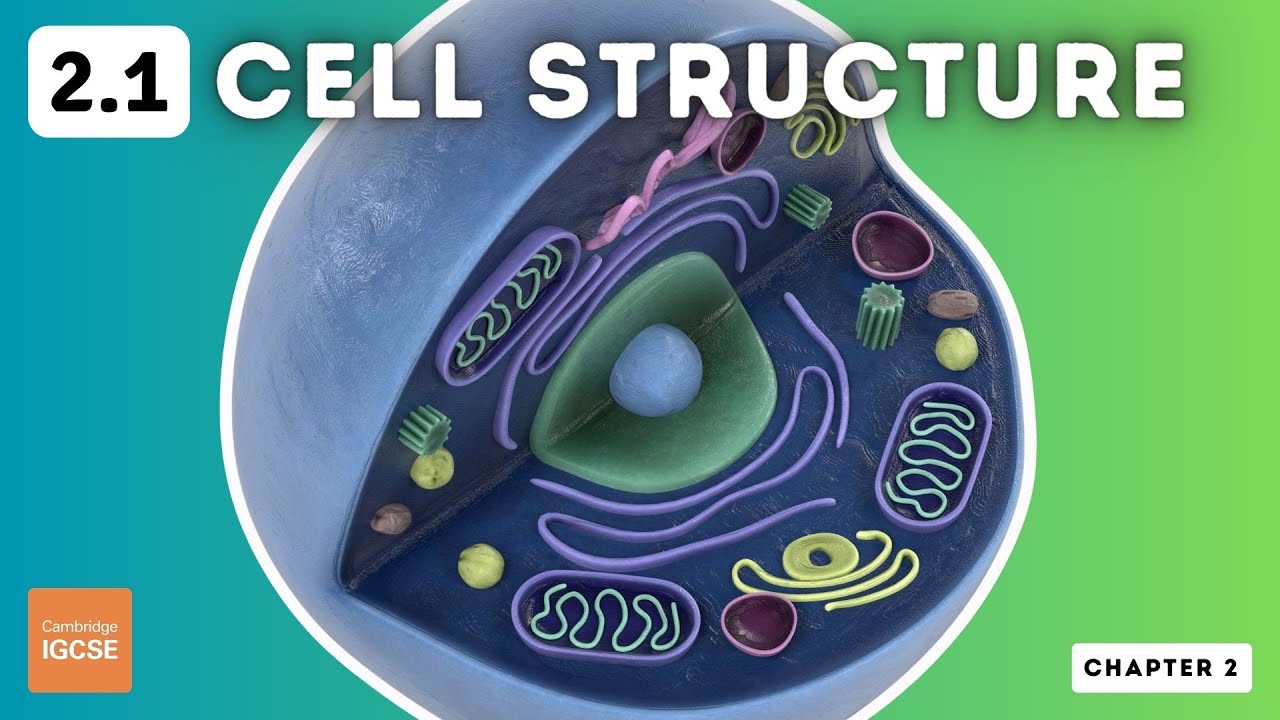
- 😀 Eukaryotic cells, found in multicellular organisms, have a membrane-bound nucleus and a variety of specialized organelles.
- 😀 The cell membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer and functions in protection, substance transfer, and cell communication.
- 😀 The plant cell wall is made of cellulose and provides structural rigidity and protection, while bacterial cell walls are made of peptidoglycan.
- 😀 Key organelles include the nucleus (which houses genetic material), ribosomes (protein synthesis), and mitochondria (energy production via ATP).
- 😀 Chloroplasts are found in plant cells and are responsible for photosynthesis, while vacuoles serve as storage spaces in both plant and animal cells.
- 😀 Other organelles like lysosomes, peroxisomes, and Golgi bodies play roles in digestion, detoxification, and processing proteins respectively.
Q & A
What is the hierarchy of biological systems as described in the transcript?
-The hierarchy of biological systems, as explained in the transcript, starts with the biosphere (the largest scale), followed by ecosystems, populations, organisms, organ systems, organs, tissues, cells, molecules, and atoms. Each level represents a more specific organization of life, from the whole planet down to the atomic level.
What distinguishes prokaryotic cells from eukaryotic cells?
-Prokaryotic cells, like those of bacteria, do not have a membrane-bound nucleus and their genetic material is found in a region called the nucleoid. In contrast, eukaryotic cells, which are found in plants and animals, have a defined nucleus enclosed by a membrane. Additionally, prokaryotic cells are generally smaller and simpler in structure than eukaryotic cells.
What are organelles, and what role do they play in a cell?
-Organelles are specialized structures within a cell that perform distinct functions essential for the cell's survival. Examples include the nucleus, mitochondria, ribosomes, and chloroplasts. Each organelle carries out specific tasks like energy production, protein synthesis, or photosynthesis.
What is the role of the cell membrane, and what is its structure?
-The cell membrane acts as a protective barrier, controlling the movement of substances in and out of the cell. It is composed of a phospholipid bilayer with embedded proteins. These proteins function in cell signaling, transport, and structural support. The membrane also contains glycoproteins that help in cell recognition and communication.
How do prokaryotic cells manage their genetic material without a nucleus?
-In prokaryotic cells, genetic material is not enclosed in a nucleus but is instead found in a region called the nucleoid. This region is not separated by a membrane, so the genetic material is in direct contact with the cytoplasm.
What is the function of the mitochondria in eukaryotic cells?
-The mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell, responsible for producing energy in the form of ATP through cellular respiration. They also play a role in various metabolic processes, including oxidative phosphorylation and the electron transport chain.
What are ribosomes, and where are they located in the cell?
-Ribosomes are small molecular machines composed of RNA and protein that are responsible for synthesizing proteins in the process of translation. They can be found either freely floating in the cytoplasm or attached to the rough endoplasmic reticulum.
What is the difference between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
-The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) is studded with ribosomes on its surface, making it the site of protein synthesis and folding. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis, detoxification of toxins, and calcium ion storage.
What is the purpose of chloroplasts in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are the organelles responsible for photosynthesis in plant cells. They contain chlorophyll, a green pigment that captures light energy, which is then used to convert carbon dioxide and water into glucose, the cell's energy source.
What is the function of the Golgi apparatus in a cell?
-The Golgi apparatus is involved in processing and modifying proteins that have been synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It also plays a role in packaging proteins and lipids into vesicles for transport within or outside the cell. It is essential for post-translational modifications such as glycosylation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)