Features of the Ocean Basin
Summary
TLDRThis video provides a comprehensive review of key oceanic features, focusing on the continental margin and ocean basin. The instructor explains important structures like the continental shelf, slope, and rise, highlighting their transition from land to oceanic crust. Key terms such as abyssal plains, deep ocean trenches, and mid-oceanic ridges are explored, along with their formation and significance in plate tectonics. The video also covers seamounts, guyots, and islands, offering a clear breakdown of each feature and its role in the ocean environment, essential for upcoming tests.
Takeaways
- 😀 The **continental shelf** is the shallow extension of the continents under the ocean, primarily made of continental crust, marking the transition zone from land to ocean.
- 😀 The **continental slope** represents the major transition zone where the continental crust meets the oceanic crust, forming the boundary between land and ocean.
- 😀 The **continental rise** is where oceanic crust begins and sediment from the continental slope accumulates, marking the true start of the ocean environment.
- 😀 The **continental margin** consists of the continental shelf, slope, and rise, forming the zone of transition from land to deep ocean.
- 😀 **Abyssal plains** are the flattest parts of the ocean floor, located in deeper areas, and are characterized by a lack of significant features.
- 😀 **Ocean trenches** are the deepest parts of the ocean, formed by the subduction of one tectonic plate beneath another at convergent boundaries. These areas are associated with earthquakes and volcanic activity.
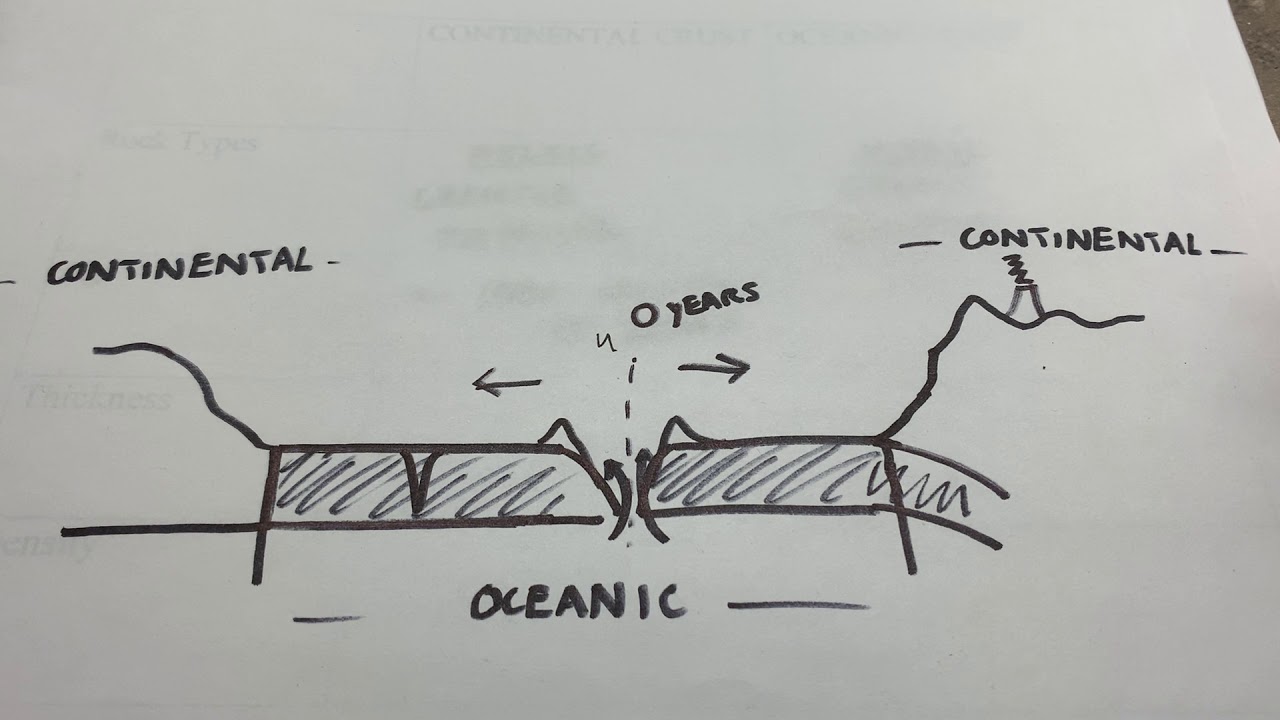
- 😀 **Mid-oceanic ridges** are formed at divergent boundaries, where oceanic crust spreads apart, contributing to the formation of new oceanic crust.
- 😀 **Seamounts**, **guyots**, and **atolls** are underwater mountains with varying shapes, with guyots having flat tops and atolls surrounded by coral.
- 😀 **Islands** are considered features of the ocean basin because they extend up from the ocean floor, not just floating land masses.
- 😀 The **ocean basin** refers to the entire area from one continental margin to the other, encompassing all features from abyssal plains to ocean ridges and trenches.
Q & A
What is the continental shelf, and why is it important?
-The continental shelf is the shallow, underwater extension of the continents. It is composed of continental crust and is considered a transition zone from land to ocean. It's important because it marks the area where ocean water begins, and it is typically rich in marine life and resources.
What is the continental slope and what does it signify?
-The continental slope is a steep drop-off area after the continental shelf, marking the transition from continental crust to oceanic crust. It is a key feature because it represents the boundary between the continental and oceanic crusts.
What is the role of the continental rise in the ocean basin?
-The continental rise is the area where oceanic crust begins. It collects sediment from the continental slope, forming a gradual incline before leading to the abyssal plains. This is where most oceanic rocks, like basalt, are found.
How are the abyssal plains different from other ocean features?
-Abyssal plains are the flattest and most featureless areas of the ocean floor. They are not the deepest parts of the ocean but are known for their lack of major topographic features. Life exists here, but it's sparse due to the lack of sunlight.
What causes oceanic trenches, and what is their significance?
-Oceanic trenches are formed by convergent boundaries, where one tectonic plate is subducted beneath another. These trenches represent the deepest parts of the ocean and are associated with intense geological activity like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
What is the difference between a seamount, guyot, and atoll?
-A seamount is a submerged, rounded or jagged mountain under the water, while a guyot is a flat-topped seamount. An atoll is a ring-shaped coral structure that forms around a submerged seamount or guyot, often creating a lagoon in the center.
Why are mid-oceanic ridges important in plate tectonics?
-Mid-oceanic ridges are divergent boundaries where oceanic plates move apart, allowing magma to rise and create new oceanic crust. These ridges provided key evidence for the theory of plate tectonics by showing how the ocean floor spreads.
What is the difference between convergent and divergent boundaries in relation to ocean features?
-Convergent boundaries, like those that form oceanic trenches, involve the collision and subduction of tectonic plates. Divergent boundaries, like those found at mid-oceanic ridges, involve the separation of plates and the formation of new crust from rising magma.
What geological features are associated with the transition from the continental crust to oceanic crust?
-The transition from continental crust to oceanic crust occurs at the continental slope, a major boundary zone. This zone marks the beginning of the oceanic crust, and it is followed by the continental rise, where sediment and oceanic rocks accumulate.
How do the ocean's features impact marine life?
-Different ocean features create unique environments for marine life. Shallow areas like the continental shelf support diverse ecosystems, while deeper areas like abyssal plains are more sparse. Trenches can harbor specialized life forms adapted to extreme pressure and darkness, while mid-ocean ridges support unique organisms due to geothermal energy.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)