CI/CD Pipeline Explained in 5 Minutes
Summary
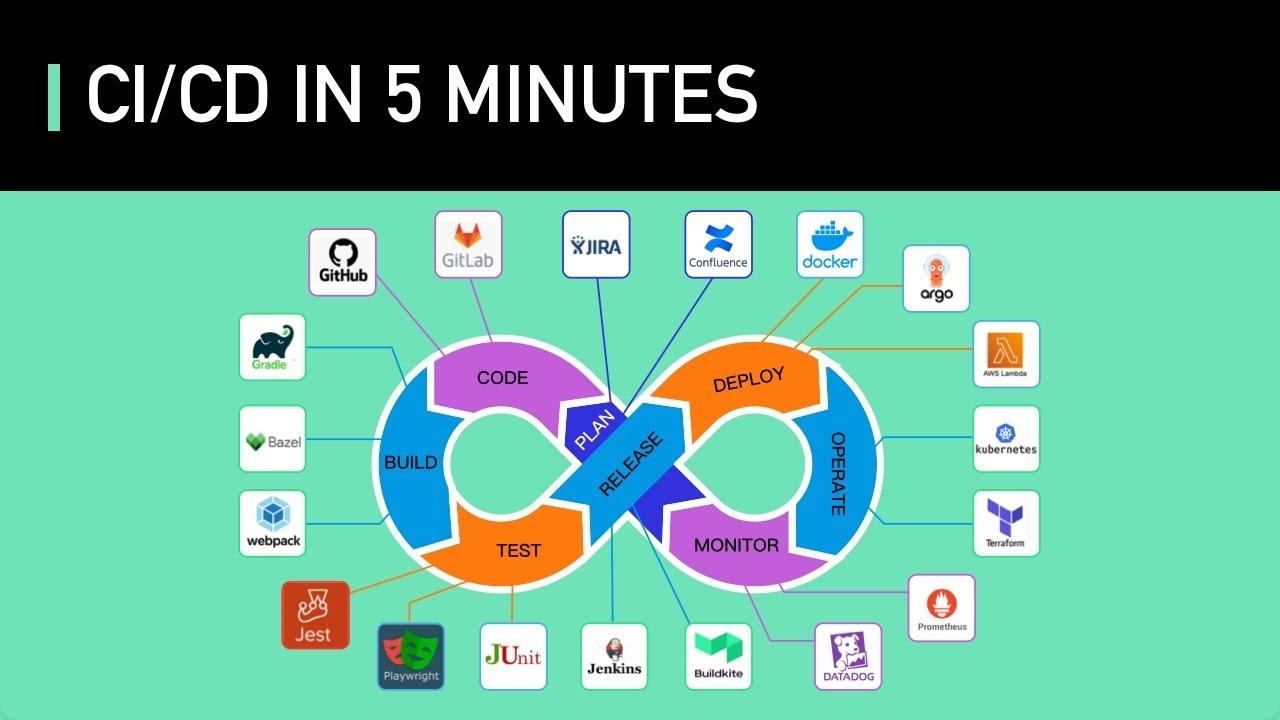
TLDRThis video provides a clear, step-by-step explanation of the CI/CD pipeline, a key practice in modern software development that automates code integration, testing, and deployment. Viewers will learn how code moves from version control to build, automated testing, security scans, artifact storage, staging deployment, and optionally to production deployment. The video also covers deployment strategies and monitoring tools, emphasizing how CI/CD ensures faster, safer, and more reliable software releases. By illustrating each stage, the video empowers development teams to confidently deliver high-quality code efficiently, minimizing errors and maximizing productivity.
Takeaways
- 🚀 CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery/Deployment, helping teams deliver code changes more frequently and reliably.
- 💻 Developers start the pipeline by writing code and pushing it to a version control system like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket.
- 🔔 Code commits automatically trigger the CI/CD pipeline, usually via webhooks, ensuring continuous integration.
- 🛠️ The build stage compiles the code, installs dependencies, and prepares the application for execution, stopping the pipeline if the build fails.
- ✅ Automated testing—including unit, integration, and UI tests—ensures that new code doesn’t break existing functionality.
- 🔍 Static code analysis and security scanning catch bugs, vulnerabilities, and bad coding practices early in the process.
- 📦 Successful builds are stored in artifact repositories like JFrog, Nexus, or AWS S3, making them reusable and version-controlled.
- 🏗️ Continuous Delivery deploys approved builds to staging environments for safe testing and possible manual approval before production.
- 🚢 Continuous Deployment automatically pushes successful staging builds to production using strategies like blue-green, canary, or rolling updates.
- 📊 Monitoring tools such as Prometheus, Grafana, Datadog, or New Relic track performance, uptime, and errors, closing the feedback loop after deployment.
- ⚡ CI/CD pipelines streamline the software delivery process, making releases faster, safer, and more consistent while maintaining high-quality code.
Q & A
What does CI/CD stand for in software development?
-CI/CD stands for Continuous Integration and Continuous Delivery or Continuous Deployment. It is a set of practices that automate the process of building, testing, and deploying code changes.
Why is CI/CD important for development teams?
-CI/CD is important because it automates the software delivery process, making releases faster, safer, and more consistent. It ensures that code changes are tested and deployed efficiently without manual intervention.
What triggers a CI/CD pipeline to start?
-A CI/CD pipeline is typically triggered automatically when a developer commits code to a version control system like GitHub, GitLab, or Bitbucket, often using webhooks that listen for changes in the repository.
What happens during the build stage of a CI/CD pipeline?
-During the build stage, the system compiles the code, installs dependencies, and prepares the application in an executable format. If the build fails, the pipeline stops and notifies the developers.
Why is automated testing critical in CI/CD?
-Automated testing ensures that new code changes do not break existing functionality. It runs unit, integration, and sometimes UI tests automatically, halting the pipeline if any test fails to maintain code quality.
What role do static code analysis and security scanning play in CI/CD?
-Static code analysis and security scanning tools, like SonarQube or Snyk, detect bugs, vulnerabilities, and code quality issues early in the pipeline. This helps teams avoid security breaches and maintain coding standards.
What is an artifact repository and why is it used?
-An artifact repository, such as JFrog, Artifactory, or AWS S3, stores versioned builds of the application. It allows teams to track which build was deployed to which environment and facilitates easy rollbacks if needed.
What is the difference between continuous delivery and continuous deployment?
-Continuous delivery automatically deploys approved builds to a staging environment where manual testing may occur. Continuous deployment goes a step further, automatically pushing builds to production if staging succeeds, without manual intervention.
What are some deployment strategies used in CI/CD?
-Common deployment strategies include Blue-Green Deployments, Canary Releases, and Rolling Updates. These approaches minimize downtime and reduce risk when deploying new changes to production.
How does monitoring fit into the CI/CD pipeline?
-Monitoring tracks performance, uptime, errors, and user behavior after deployment using tools like Prometheus, Grafana, or Datadog. Alerts notify the team of issues, ensuring a responsive and healthy system, closing the CI/CD feedback loop.
What is the overall benefit of implementing a CI/CD pipeline?
-The overall benefit of CI/CD is that it enables development teams to deliver high-quality code quickly and reliably, automating the path from code commit to production deployment while ensuring stability and security.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)