Physics: Waves in General (MinutePhysics)
Summary
TLDRWaves are vibrations that transfer energy without transferring matter. They can either require a medium (like sound waves) or travel through a vacuum (like light waves). Waves are categorized into transverse and longitudinal types, based on how the vibrations move in relation to the wave's direction. Key characteristics of waves include amplitude, wavelength, and frequency, which influence properties like loudness and pitch. The speed of a wave can be calculated using its frequency and wavelength. Understanding wave basics is essential for exploring various wave phenomena, from sound and light to radio waves.
Takeaways
- 😀 Waves are vibrations that transfer energy without transferring matter, like a Mexican wave at a football match.
- 😀 Waves need a medium (solid, liquid, or gas) to travel, except for electromagnetic waves like light, which don't require a medium.
- 😀 Sound waves require a medium (like air) to travel but cannot travel through a vacuum.
- 😀 Electromagnetic waves, such as infrared rays, X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves, can pass through a medium but don't need one to travel.
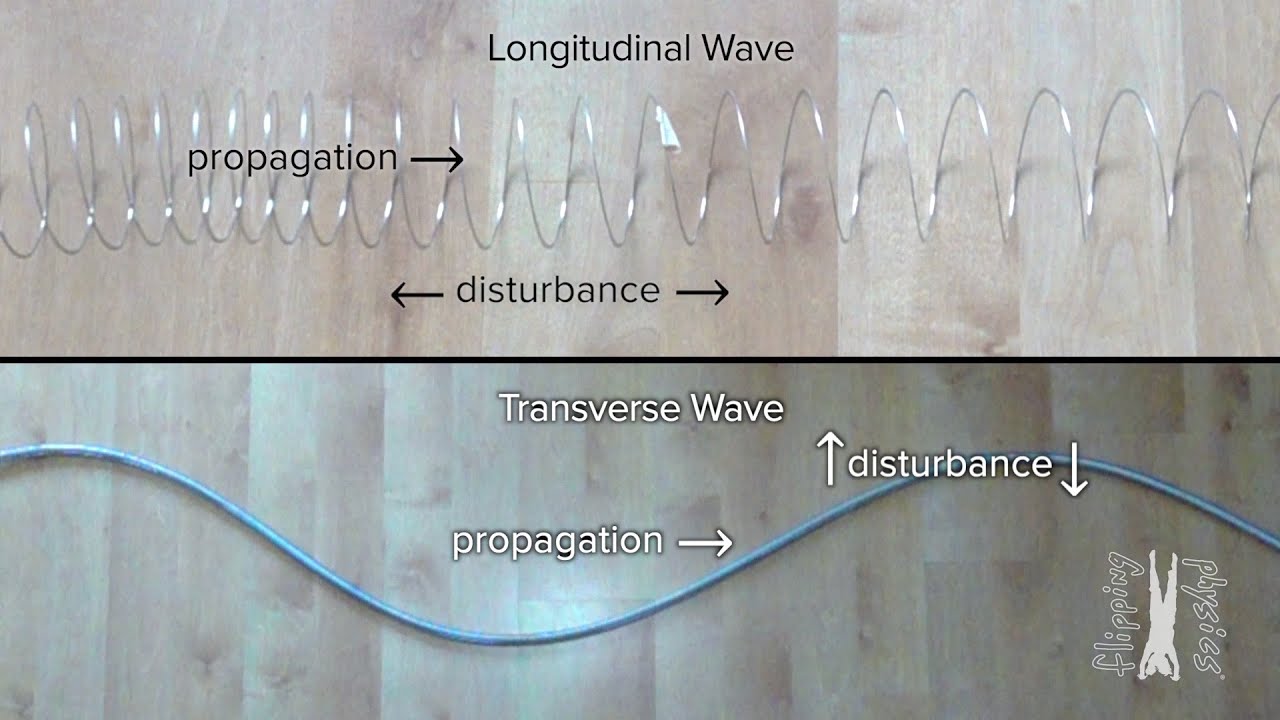
- 😀 There are two main types of waves: transverse waves (where vibrations are at right angles to wave travel) and longitudinal waves (where vibrations are in the same direction as wave travel).
- 😀 Examples of transverse waves include water waves, S-waves (seismic), and all electromagnetic waves.
- 😀 Longitudinal waves include sound waves, where the vibrations move parallel to the wave's direction.
- 😀 A wave's amplitude refers to how much the medium vibrates, determining the wave's strength or loudness.
- 😀 Wavelength is the distance between two corresponding points on consecutive waves, and frequency refers to the number of waves produced per second (measured in Hertz).
- 😀 The speed of a wave is calculated by multiplying its frequency by its wavelength (speed = frequency × wavelength).
Q & A
What is a wave?
-A wave is a vibration that transfers energy from one place to another without transferring matter. It can be observed in many everyday situations like sound or light.
What is the medium in a wave?
-The medium is the substance through which a wave travels. It can be a solid, liquid, or gas, and is essential for certain types of waves, like sound waves.
Can sound waves travel in a vacuum?
-No, sound waves cannot travel through a vacuum because they require a medium (like air) to transfer the energy.
What are electromagnetic waves?
-Electromagnetic waves, such as infrared rays, X-rays, microwaves, and radio waves, do not require a medium to travel through and can propagate through a vacuum.
What are the two main types of waves?
-The two main types of waves are transverse waves and longitudinal waves. In transverse waves, vibrations occur at right angles to the direction of travel, while in longitudinal waves, the vibrations are along the same direction as the wave's travel.
Can you give examples of transverse waves?
-Yes, electromagnetic waves, water waves, and S-waves (a type of seismic wave) are all examples of transverse waves.
What are longitudinal waves, and can you give an example?
-Longitudinal waves are waves where the vibrations move in the same direction as the wave's travel. An example of a longitudinal wave is a sound wave.
What does amplitude mean in relation to waves?
-Amplitude refers to how much the medium is being vibrated or the strength of the wave. In sound waves, amplitude affects the loudness.
What is the significance of wavelength and frequency in a wave?
-Wavelength is the distance between points on consecutive waves, and frequency is the number of waves produced by the source per second. Together, they help determine the wave's properties.
How is wave speed calculated?
-Wave speed is calculated using the formula: speed = frequency × wavelength, where speed is in meters per second, frequency is in Hertz, and wavelength is in meters.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)