testt
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of mitosis, the type of cell division that creates two identical daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. The video covers key stages including interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, detailing the preparation and division processes. It also introduces cytokinesis, the division of the cytoplasm, which finalizes the creation of two daughter cells. The video offers an in-depth yet accessible explanation of each phase, enhancing viewers' understanding of cell division.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mitosis is a cell division process that results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell.
- 😀 Mitosis occurs in somatic cells, not in gametes (sex cells), and is responsible for growth, repair, and regeneration.
- 😀 There are four main phases of mitosis: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase, with an interphase (preparation phase) preceding them.
- 😀 In interphase, the cell prepares for division by replicating DNA and synthesizing proteins needed for the division process.
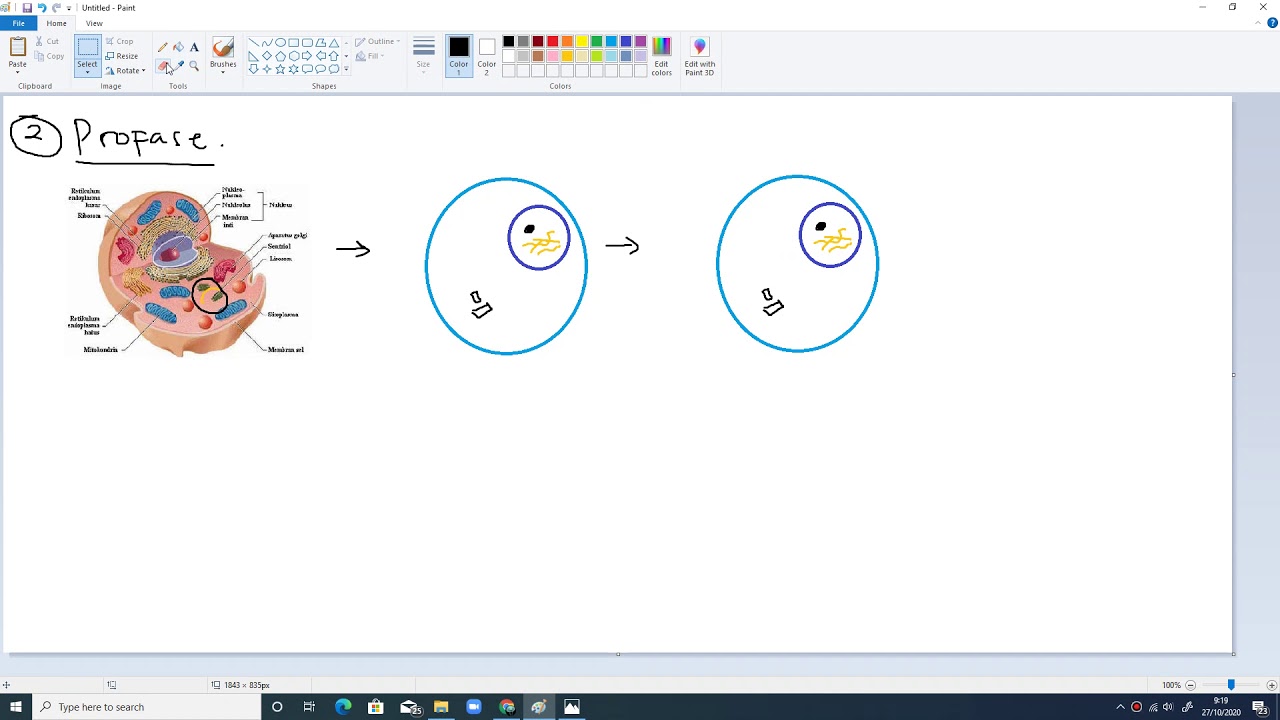
- 😀 Prophase marks the start of mitosis, where centrosomes replicate, microtubules form spindle threads, and chromosomes begin to condense.
- 😀 In metaphase, chromosomes align at the cell's equatorial plane, making them visible for counting and observation.
- 😀 Anaphase is characterized by the separation of chromatids at the centromere, forming new chromosomes that are pulled to opposite poles.
- 😀 Cytokinesis begins during anaphase and completes after telophase, resulting in the division of the cytoplasm and the formation of two daughter cells.
- 😀 Telophase is the final phase of mitosis, where chromosomes reach the poles, the spindle fibers disappear, and the nuclear membrane reforms.
- 😀 Cytokinesis, which overlaps with telophase, divides the cytoplasm and other cell contents, ensuring the creation of two separate daughter cells.
Q & A
What is mitosis, and what is its purpose?
-Mitosis is a process of cell division that results in two daughter cells with the same number of chromosomes as the parent cell. Its purposes include cell growth, replacing damaged body cells, regeneration, and maintaining the chromosome number in the body cells (somatic cells).
What are the four main stages of mitosis?
-The four main stages of mitosis are prophase, metaphase, anaphase, and telophase. These stages describe the process of chromosome alignment, separation, and cell division.
What is interphase, and why is it important?
-Interphase is the preliminary phase before mitosis begins. During this phase, the cell prepares for division by storing energy, replicating DNA, and synthesizing proteins necessary for cell division. It is crucial for ensuring that the cell is fully ready for the subsequent stages of mitosis.
What happens during the G1 phase of interphase?
-The G1 phase is the cell growth and development phase. During this phase, the cytoplasm develops, cell organelles form, and materials are synthesized to prepare for the next phase, which is the S phase.
What occurs during the S phase of interphase?
-During the S phase, DNA replication takes place, creating two identical copies of the genetic material that will be passed on to the daughter cells.
How does the G2 phase prepare the cell for mitosis?
-In the G2 phase, the cell undergoes further growth, synthesizing proteins and completing preparations for mitosis. This ensures that the cell is ready to divide efficiently.
What happens during prophase in mitosis?
-In prophase, the centrosome replicates and moves to opposite poles of the cell. Microtubules start to form, becoming spindle fibers. The chromatin condenses into visible chromosomes, each consisting of two chromatids connected at the centromere. The nucleolus and nuclear membrane begin to disappear.
What is the significance of the metaphase stage?
-In metaphase, the chromosomes align along the cell’s equatorial plane, known as the metaphase plate. This alignment makes it possible to precisely count the chromosomes and observe their shape, ensuring accurate chromosome distribution in the next phase.
What occurs during anaphase?
-In anaphase, the chromatids are separated from the centromere and pulled toward opposite poles of the cell by the spindle fibers. This results in the formation of new chromosomes, ensuring that each daughter cell will receive an identical set of chromosomes.
What is cytokinesis, and when does it occur in mitosis?
-Cytokinesis is the process in which the cytoplasm, organelles, and cell membrane divide to form two daughter cells. This process typically begins during anaphase and continues through telophase, completing after the nuclear division in mitosis.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)