Gagal Berpisah Meiosis I Non Disjunction I BAB POLA HEREDITAS
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concept of nondisjunction, a genetic phenomenon where chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis. It leads to genetic disorders such as Super Female Syndrome, Turner Syndrome, Klinefelter Syndrome, and Down Syndrome. The video illustrates the process of chromosome separation and the resulting chromosomal abnormalities. Nondisjunction can cause cells to have extra or missing chromosomes, affecting both sex chromosomes and autosomes. Understanding this process is crucial for comprehending human heredity and genetic conditions.
Takeaways
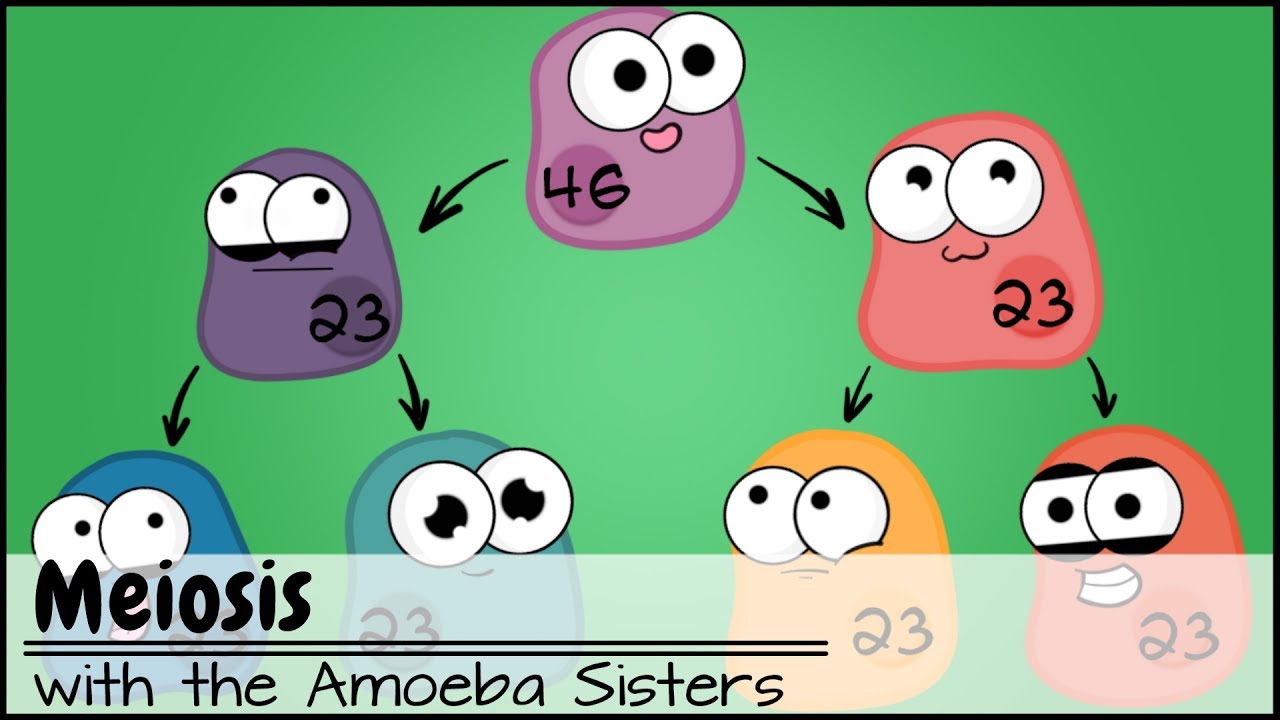
- 😀 Nondisjunction is a genetic phenomenon where chromosomes fail to separate properly during meiosis.
- 😀 This process can occur during either Meiosis I or Meiosis II, leading to unequal chromosome distribution.
- 😀 During the metaphase stage of meiosis, chromosomes align at the cell's equator before moving to opposite poles.
- 😀 Nondisjunction occurs when chromosomes do not separate evenly, resulting in one daughter cell with extra chromosomes and one with fewer.
- 😀 An example of nondisjunction involves two chromosomes moving together to one side of the cell, instead of each chromatid going to opposite poles.
- 😀 Nondisjunction can lead to several syndromes in humans due to abnormal chromosome numbers.
- 😀 One such condition is Turner Syndrome, where a female has only one X chromosome instead of two.
- 😀 Klinefelter Syndrome occurs when a male has an extra X chromosome (XXY instead of XY), leading to some female-like traits.
- 😀 Down Syndrome is caused by a nondisjunction event affecting an autosome, specifically chromosome 21, leading to an individual with three copies of chromosome 21.
- 😀 Superfemale Syndrome occurs when a female has three X chromosomes (XXX) instead of the typical two X chromosomes (XX).
- 😀 Nondisjunction leads to unequal chromosome numbers, causing some cells to have too many chromosomes while others have too few.
- 😀 Understanding the effects of nondisjunction is crucial for grasping genetic disorders and their impact on human health.
Q & A
What is nondisjunction?
-Nondisjunction is the failure of one or more chromosomes to separate properly during anaphase of meiosis 1 or meiosis 2. This results in an uneven distribution of chromosomes between the resulting cells.
At which stages of meiosis does nondisjunction occur?
-Nondisjunction can occur during anaphase of either meiosis 1 or meiosis 2, which are stages when chromosomes or chromatids should separate to opposite poles of the cell.
What happens to the chromosomes during nondisjunction?
-During nondisjunction, chromosomes do not separate evenly. Some chromosomes may move to one side of the cell, while others may fail to move, leading to an unequal distribution in the daughter cells.
What is the result of nondisjunction in the daughter cells?
-The result of nondisjunction is that one daughter cell will have an extra chromosome, while the other will lack one, leading to an imbalance in chromosome number.
How does nondisjunction affect human chromosomes?
-Nondisjunction can cause genetic disorders due to abnormal chromosome numbers. For example, it can lead to conditions like Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Triple X syndrome.
What is Triple X syndrome?
-Triple X syndrome occurs in females when they have an extra X chromosome. Instead of the typical karyotype of 44A+XX, individuals with Triple X syndrome have 44A+XXX.
What is Turner syndrome?
-Turner syndrome occurs when a female has a missing or incomplete X chromosome, resulting in a karyotype of 44A+X instead of 44A+XX.
What is Klinefelter syndrome?
-Klinefelter syndrome occurs in males who have an extra X chromosome, giving them a karyotype of 44A+XXY. These individuals may exhibit some feminine physical traits.
What is Down syndrome and how is it related to nondisjunction?
-Down syndrome is caused by the presence of an extra chromosome 21, resulting in a karyotype of 45A+XX or 45A+XY. It occurs due to nondisjunction during the formation of gametes.
How does nondisjunction lead to different genetic disorders?
-Nondisjunction leads to genetic disorders by causing an imbalance in chromosome number. Depending on which chromosome is affected, this can result in syndromes such as Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Klinefelter syndrome, and Triple X syndrome.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)