Redox Reactions Class 11 in 5 Minutes | Chemistry | Quick Revision | NEET, JEE & CBSE |
Summary
TLDRIn this video, the speaker introduces the concept of redox reactions, explaining the core principles of oxidation and reduction, along with key terminology such as oxidizing and reducing agents. The video dives into calculating oxidation numbers and provides examples of how to determine them in various compounds. It also covers different types of redox reactions, such as combination, decomposition, and displacement reactions. Furthermore, the speaker demonstrates how to balance redox reactions using the oxidation number method. The video also touches upon electrochemical cells, their reactions, and the importance of redox in electrochemistry, making it a comprehensive guide to understanding redox processes.
Takeaways
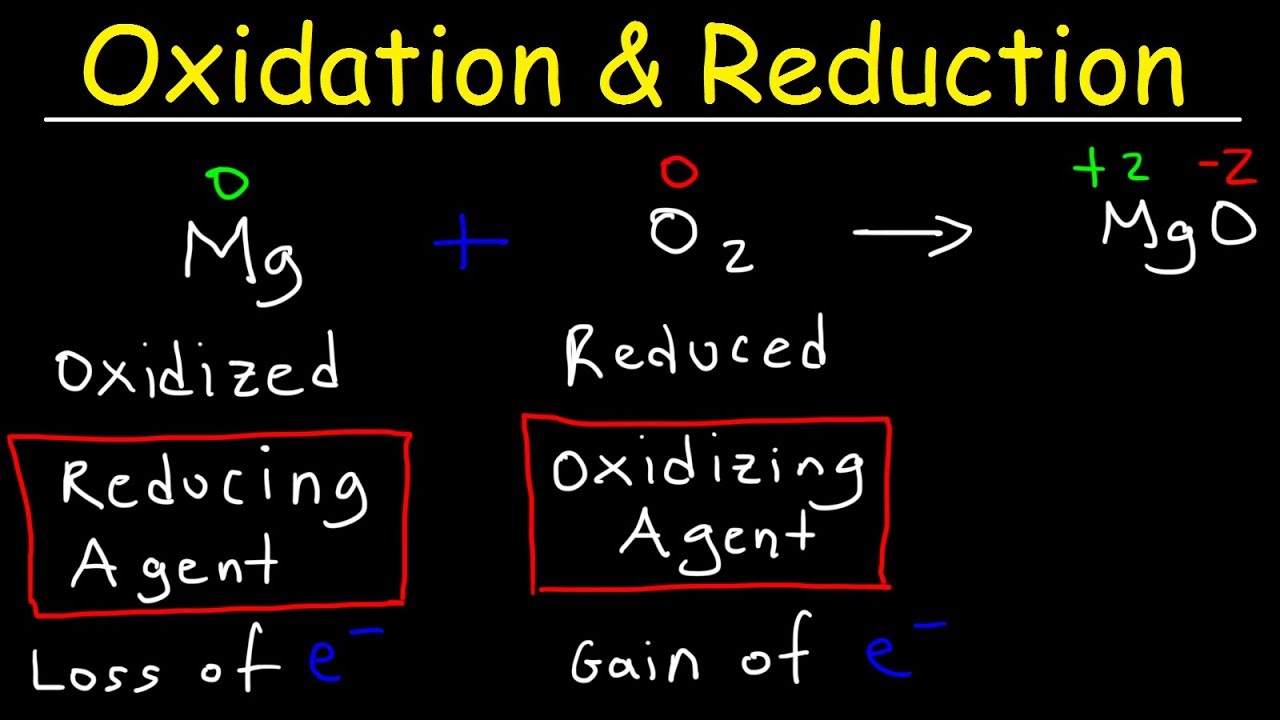
- 😀 Redox reactions involve both oxidation (loss of electrons) and reduction (gain of electrons) occurring simultaneously.
- 😀 Oxidizing agents gain electrons and get reduced, while reducing agents lose electrons and get oxidized.
- 😀 Oxidation numbers help determine the electron transfer in reactions, with common oxidation numbers assigned to elements like hydrogen, oxygen, and metals.
- 😀 In a neutral compound, the sum of oxidation numbers equals zero, while in a polyatomic ion, the sum equals the ion’s charge.
- 😀 Example of balancing redox reactions involves assigning oxidation numbers, equating electron loss and gain, and balancing atoms and charges.
- 😀 Types of redox reactions include combination (two or more substances combine), decomposition (one substance breaks down into multiple), and displacement (more reactive elements replace less reactive ones).
- 😀 Redox reactions can be balanced using the oxidation number method or the ion-electron (half-reaction) method.
- 😀 In electrochemistry, Galvanic cells generate electricity through spontaneous redox reactions, while electrolytic cells require external voltage to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
- 😀 In a Galvanic cell, oxidation occurs at the anode (negative electrode), and reduction occurs at the cathode (positive electrode).
- 😀 Important for redox reactions in electrochemistry: stronger oxidizing agents have a high reduction potential, meaning they easily gain electrons.
- 😀 A strong oxidant will have a high reduction potential because it readily gains electrons, making the overall reaction more favorable.
Q & A
What is oxidation and how can it be defined?
-Oxidation refers to the loss of electrons by an element or ion. It can also be defined as an increase in oxidation number of an element in a chemical reaction.
What happens during a reduction reaction?
-Reduction is the process where an element or ion gains electrons, or the oxidation number decreases during a chemical reaction.
What is a redox reaction?
-A redox reaction is a type of chemical reaction where both oxidation and reduction occur simultaneously.
What are oxidizing agents and reducing agents?
-Oxidizing agents are substances that gain electrons and get reduced. Reducing agents are substances that lose electrons and get oxidized.
How do you calculate the oxidation number of an element?
-The oxidation number of an element is calculated based on specific rules, such as the oxidation number of oxygen is generally -2, hydrogen is +1, and for neutral compounds, the sum of oxidation numbers is zero.
What is the oxidation number of sulfur in H2SO4?
-The oxidation number of sulfur in H2SO4 is +6.
What are the types of redox reactions discussed in the video?
-The video discusses combination reactions, decomposition reactions, and displacement reactions as types of redox reactions.
How is a redox reaction balanced using oxidation numbers?
-A redox reaction can be balanced by ensuring that the total loss of electrons in oxidation equals the total gain of electrons in reduction. This requires adjusting the coefficients of the reactants and products, and adding H+ ions or water molecules to balance hydrogen and oxygen atoms.
What is the difference between an electrolytic cell and a galvanic cell?
-A galvanic cell generates electricity through spontaneous redox reactions, whereas an electrolytic cell uses external voltage to drive non-spontaneous reactions.
Why do strong oxidizing agents have high reduction potential?
-Strong oxidizing agents have a high reduction potential because they readily gain electrons, making them effective at causing reductions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)