Biomolecules (Older Video 2016)
Summary
TLDRThis video script introduces the four major biomolecules that constitute all life: carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids. It explains their functions, monomers, and the importance of their structure in determining their properties. The script uses the mnemonic 'CHO, CHO, CHON, CHONP' to help remember the elements that make up these biomolecules, emphasizing the significance of carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, nitrogen, and phosphorus in their composition.
Takeaways
- 🍕 Food preferences vary widely among individuals, but all foods provide essential biomolecules necessary for life.
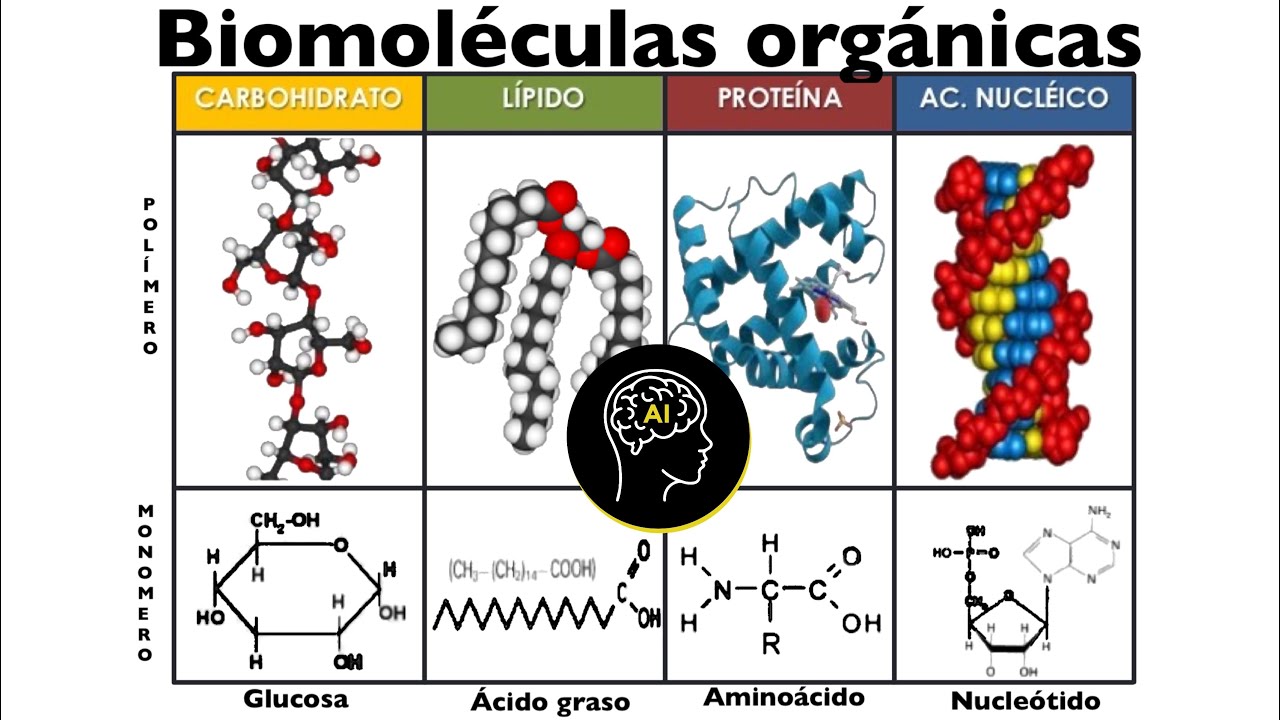
- 🧬 There are four major biomolecules that constitute all forms of life, which are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- 🏗️ Monomer is a term for the building blocks of substances, and understanding them is crucial for understanding biomolecules.
- 🍚 Carbohydrates are a primary source of quick energy, such as in the practice of 'pasta loading' by marathon runners.
- 🍬 The monomer of carbohydrates is called a monosaccharide, which forms the basis of these energy-providing molecules.
- 🧈 Lipids, also known as fats, have two types of building blocks: fatty acids and glycerol, and serve multiple functions including insulation and long-term energy storage.
- 🐠 Lipids are essential for the structure of cell membranes and are vital for life, but should be consumed in moderation for health.
- 💪 Proteins are fundamental for muscle building and are also involved in immune function and enzyme activity, with amino acids as their monomers.
- 🧬 Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are responsible for genetic information and are composed of nucleotides as their monomers.
- 🍓 Consuming foods from once-living organisms, such as strawberries, means you are also consuming their DNA, which is present in every cell.
- 🔬 The structure of biomolecules is vital to understand as it influences their properties and functions, and can be remembered with the mnemonic CHO, CHO, CHON, CHONP for carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids respectively.
- 🔍 The arrangement of elements within biomolecules, such as in ring or chain forms, significantly impacts their function and is worth further exploration through illustrations.
Q & A
What are the four major biomolecules that make up all of life?
-The four major biomolecules are carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids.
What is the primary function of carbohydrates in our body?
-Carbohydrates serve as a fast source of energy for the body, especially useful for activities like marathon running.
What is a monomer and why is it important to understand biomolecules?
-A monomer is a building block of larger substances. Understanding monomers is crucial because biomolecules are composed of these monomers, which determine their structure and function.
What is the monomer for carbohydrates known as?
-The monomer for carbohydrates is called a monosaccharide.
What are the two types of building blocks for lipids?
-The two types of building blocks for lipids are fatty acids and glycerol.
Why are lipids important for insulation and long-term energy storage?
-Lipids are important for insulation because they help retain body heat, as seen in animals like harp seals. They also serve as a long-term energy source, providing energy over extended periods for activities like swimming long distances.
What are the monomers of proteins called?
-The monomers of proteins are called amino acids.
How are proteins involved in the immune system and as enzymes?
-Proteins play a role in the immune system by acting as antibodies and other immune factors. They also function as enzymes, which catalyze biochemical reactions in the body.
What is the monomer of nucleic acids, and what do they do?
-The monomer of nucleic acids is called a nucleotide. Nucleic acids, including DNA and RNA, are involved in storing and transmitting genetic information.
What is the significance of the elements carbon (C), hydrogen (H), oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), and phosphorus (P) in biomolecules?
-These elements form the backbone of biomolecules. Carbohydrates and lipids are composed of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen (CHO), while proteins and nucleic acids contain these elements plus nitrogen (CHON), with nucleic acids also containing phosphorus (P).
What is the mnemonic device provided to remember the elements in the four biomolecules?
-The mnemonic device is 'CHO, CHO, CHON, CHONP', which represents the elements in carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids, respectively.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Biomoléculas presentes en células (orgánicas): carbohidratos, lípidos, proteínas y ácidos nucleicos

Biomoléculas (atualizado em 2023)

Beginners Guide to MACROMOLECULES

La Química de los Alimentos: Cómo los Compuestos Influyen en tu Nutrición y Salud
Macromolecules | Classes and Functions

Biological Molecules
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
