Resumo - ORGANELAS CELULARES
Summary
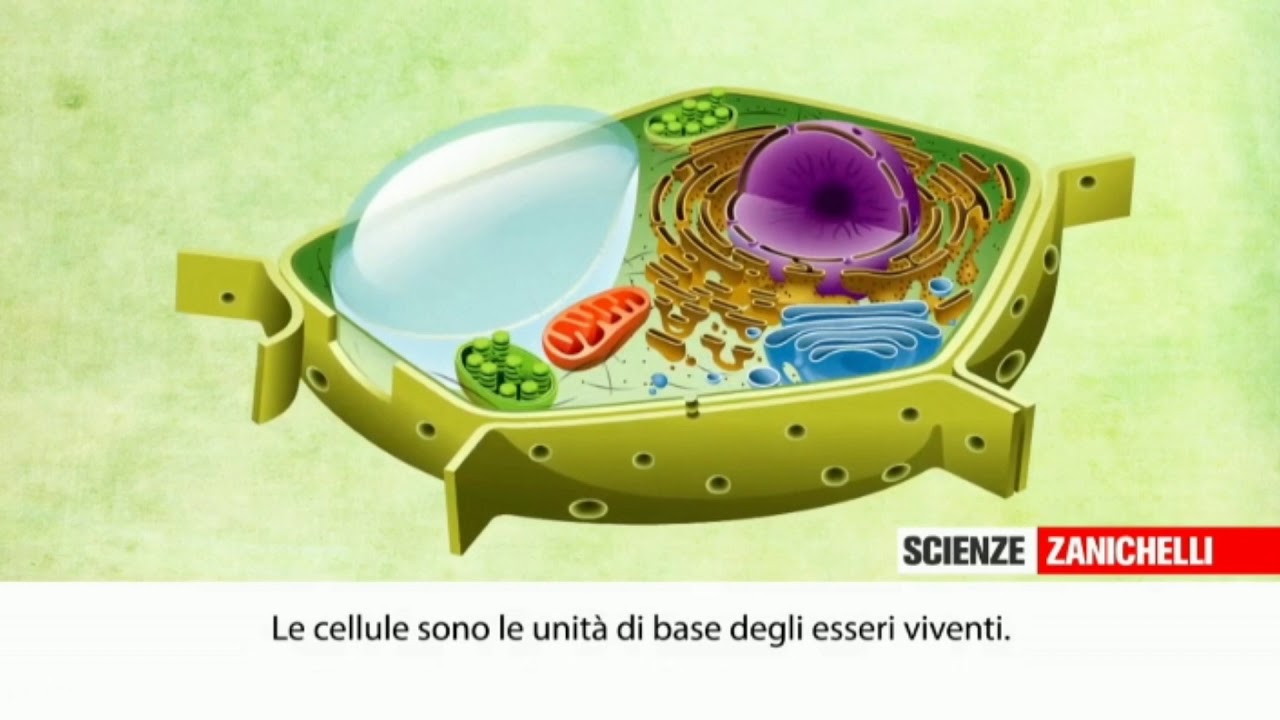
TLDRThis video provides an informative overview of cellular organelles, comparing them to small organs that perform essential cellular functions. It explains the roles and structures of key organelles such as the nucleus, mitochondria, lysosomes, and chloroplasts. The video also discusses the functions of the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, peroxisomes, and vacuoles. Key processes like energy production, protein synthesis, and cellular digestion are explored, along with the importance of DNA and ribosomes. Ideal for those looking to understand the cellular structures that keep life processes running smoothly.
Takeaways
- 😀 Organelles are small structures within cells that perform essential cellular functions.
- 😀 The nucleus is the most prominent organelle in eukaryotic cells and controls cell activities and stores genetic information.
- 😀 Mitochondria are double-membraned organelles responsible for energy production through cellular respiration.
- 😀 Lysosomes are irregular-shaped organelles that digest organic molecules such as proteins, lipids, carbohydrates, and nucleic acids.
- 😀 The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) consists of rough and smooth types; rough ER synthesizes proteins, while smooth ER is involved in lipid synthesis and detoxification.
- 😀 The Golgi apparatus modifies, stores, and exports proteins synthesized in the rough ER and produces primary lysosomes.
- 😀 Peroxisomes are spherical organelles involved in neutralizing toxic substances, like alcohol, and producing bile salts.
- 😀 Chloroplasts, found only in plant cells and algae, contain chlorophyll and are essential for photosynthesis.
- 😀 Vacuoles, which are membrane-bound structures, regulate water intake and excretion, control pH, and help with digestion in plant cells.
- 😀 Ribosomes are non-membranous organelles responsible for protein synthesis, found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells.
Q & A
What are cellular organelles and what is their function?
-Cellular organelles are like small organs within cells that perform essential cellular activities necessary for the cell's function. These structures are composed of internal membranes with different shapes and functions.
What is the role of the nucleus in eukaryotic cells?
-The nucleus controls the activities within the cell and stores genetic information. It is surrounded by a double membrane known as the nuclear envelope, which separates its contents from the cytoplasm. Inside the nucleus, there are chromosomes and the nucleolus, where ribosomal subunits are formed.
How do mitochondria contribute to the cell's energy production?
-Mitochondria are responsible for producing energy through cellular respiration. They have a double membrane structure, with the inner membrane having many folds called cristae. Mitochondria contain circular DNA, and the number of mitochondria in a cell correlates with its energy metabolism, being higher in energy-demanding cells like muscle cells.
What is the function of lysosomes?
-Lysosomes are irregularly shaped organelles that digest organic molecules such as lipids, carbohydrates, proteins, and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA). They use digestive enzymes to break down molecules into smaller components that the cell can use, typically after these molecules are engulfed in vesicles.
What are the differences between rough and smooth endoplasmic reticulum?
-The rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) has ribosomes attached to its membrane, which synthesizes proteins that are either used within the cell or integrated into its membrane. The smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) lacks ribosomes and is involved in lipid synthesis, carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification processes.
What does the Golgi apparatus do?
-The Golgi apparatus modifies, stores, and exports proteins synthesized in the rough endoplasmic reticulum. It also produces vesicles that detach and can form primary lysosomes, aiding in the secretion of substances from the cell.
What are peroxisomes and how do they function?
-Peroxisomes are spherical organelles responsible for breaking down organic substrates through reactions that produce hydrogen peroxide. They are most prominent in the liver and kidney cells, where they neutralize toxins such as alcohol and participate in the production of bile salts.
How do chloroplasts function in plant cells?
-Chloroplasts are present only in plant cells and algae and are rich in chlorophyll, the green pigment responsible for photosynthesis. Chloroplasts have a double membrane structure and contain thylakoids, which are flattened sacs that help in the photosynthesis process to produce energy for the plant.
What is the role of vacuoles in cells?
-Vacuoles are membrane-bound structures in plant cells, protozoa, and some animal cells. They have various functions such as regulating pH, controlling water entry and exit through osmoregulation, storing substances, and participating in digestion and waste excretion.
Are ribosomes considered organelles?
-Ribosomes are not considered membrane-bound organelles because they do not have membranes. However, they are still referred to as organelles in some contexts, as they play a vital role in synthesizing proteins. Ribosomes are present in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)