SOLUÇÃO TAMPÃO | EQUILÍBRIO QUÍMICO | Aula 26
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the concept of buffer solutions and their crucial role in maintaining pH stability in biological and chemical systems. It highlights the interaction between weak acids and their conjugate bases, which resist drastic pH changes when acids or bases are added. The script covers the Bronsted-Lowry theory of acids and bases, provides examples like acetic acid and its conjugate base, sodium acetate, and discusses the physiological buffering systems in the human body. The script concludes with the importance of buffer solutions and how the pH of buffer systems can be calculated using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation.
Takeaways
- 😀 pH fluctuations can lead to dangerous conditions like alkalosis and acidosis, which can be life-threatening.
- 😀 The body has a highly efficient system for regulating pH, known as the buffer solution.
- 😀 Buffer solutions are aqueous systems that resist drastic pH changes when small amounts of acids or bases are added.
- 😀 A buffer is created by mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base, or a weak base with its conjugate acid.
- 😀 The Bronsted-Lowry theory explains acids as proton donors and bases as proton acceptors.
- 😀 Acetic acid and acetate salts form a classic buffer solution, helping maintain pH stability.
- 😀 Buffer solutions are able to neutralize added acids by the base conjugate, or neutralize added bases by the acid in the buffer.
- 😀 In buffer solutions, the weak acid and its conjugate base exist in a delicate equilibrium, crucial for pH regulation.
- 😀 In the human body, the blood's pH is maintained by buffer systems like bicarbonate and phosphate, ensuring it stays around 7.4.
- 😀 The body’s buffering systems can handle changes in pH from activities like eating or exercise, but extreme changes (e.g., from acidosis or diabetes) can be harmful.
Q & A
What is pH and why is it important for human health?
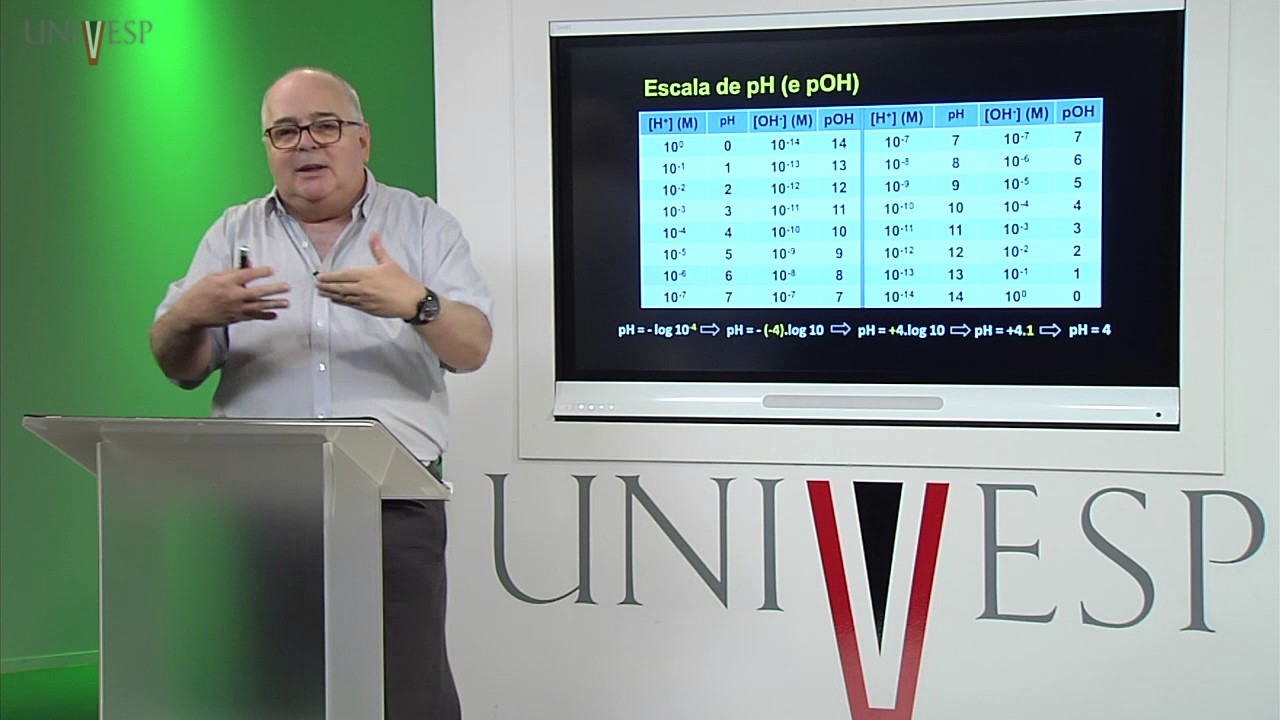
-pH is a measure of how acidic or basic a solution is, with a scale ranging from 0 to 14. Maintaining a stable pH in the body is critical because significant fluctuations can lead to metabolic issues like acidosis or alkalosis, which can be harmful and even fatal.
What is a buffer solution and how does it work?
-A buffer solution is an aqueous system that resists changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or base are added. It works by neutralizing excess hydrogen ions (H+) or hydroxide ions (OH-), maintaining a stable pH.
What are the components of a buffer solution?
-A buffer solution typically consists of a weak acid and its conjugate base, or a weak base and its conjugate acid. These components work together to stabilize the pH by neutralizing added acids or bases.
How is a buffer solution formed?
-A buffer solution is formed by mixing a weak acid with its conjugate base or a weak base with its conjugate acid. This combination allows the solution to resist changes in pH when small amounts of an acid or base are introduced.
Can you give an example of a commonly used buffer solution?
-A classic example of a buffer solution is a mixture of acetic acid (a weak acid) and sodium acetate (its conjugate base). This is commonly used in laboratory and biological applications.
Why is it necessary to mix both an acid and its conjugate base to form a buffer?
-It is necessary to mix both components because a weak acid alone would not provide enough of its conjugate base to neutralize added bases efficiently. Similarly, a conjugate base alone would not neutralize added acids effectively. Together, they maintain a stable pH.
How does the presence of acetic acid and acetate buffer against pH changes when a base is added?
-When a base like sodium hydroxide is added, the acetic acid in the buffer neutralizes the hydroxide ions (OH-) by forming water and acetate ions. This prevents a significant increase in pH.
How does the buffer solution react when an acid is added?
-When an acid, such as hydrochloric acid, is added to a buffer solution, the conjugate base of the acid (like acetate) neutralizes the added hydrogen ions (H+), preventing a drastic decrease in pH.
What happens when a buffer system in the body is overwhelmed?
-If the buffer system is overwhelmed by excessive amounts of acid or base, the pH of the body can change drastically, leading to conditions like acidosis or alkalosis, which can be dangerous and affect bodily functions.
How does the body maintain a stable pH, particularly in the blood?
-The body maintains a stable blood pH (around 7.4) through buffer systems like the bicarbonate buffer system, which uses carbonic acid and bicarbonate ions to regulate pH. Other buffers, such as phosphate and proteins, also play critical roles in stabilizing pH.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Bioquímica - Aula 03 - Alguns conceitos químicos importantes - 2

Larutan Penyangga • Part 1: Sifat, Komponen & Peran Larutan Buffer / Penyangga

ATAR QCE Chemistry Unit 3 Topic 1: Buffers

Sistemas amortiguadores

Stimulus Pertemuan 1 (Larutan Penyangga)

Larutan Penyangga | Jenis dan Prinsip Kerja Larutan Penyangga - Bagian 1
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
