Keseimbangan Pasar (Market Equilibrium) - Materi Kelas 10 Ekonomi SMA Bab 4.3
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an insightful explanation of market equilibrium, focusing on the balance between supply and demand. It explores key concepts such as the equilibrium price, the factors that influence it, and the roles demand and supply play in determining market outcomes. The video also covers the functions of equilibrium in the economy, including how it helps producers, consumers, and businesses. Additionally, the presenter explains the mathematical approach to equilibrium and demonstrates it with an example, showing how the price and quantity are determined. The video emphasizes the importance of understanding market dynamics for economic decision-making.
Takeaways
- 😀 Market equilibrium refers to the price at which the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, resulting from the interaction of demand and supply.
- 😀 The equilibrium price is also known as the market price and is determined through the laws of demand and supply.
- 😀 Factors that affect market equilibrium include changes in demand, supply, production costs, and consumer preferences.
- 😀 The balance between demand for goods/services and limited supply is a key driver of equilibrium formation.
- 😀 The equilibrium price plays several roles, including reflecting societal needs, stimulating business innovation, and helping producers determine which goods to produce.
- 😀 Equilibrium price also helps sellers set appropriate prices and assists producers in selecting the most efficient production technology.
- 😀 The market equilibrium formula can be expressed mathematically, involving demand and supply functions.
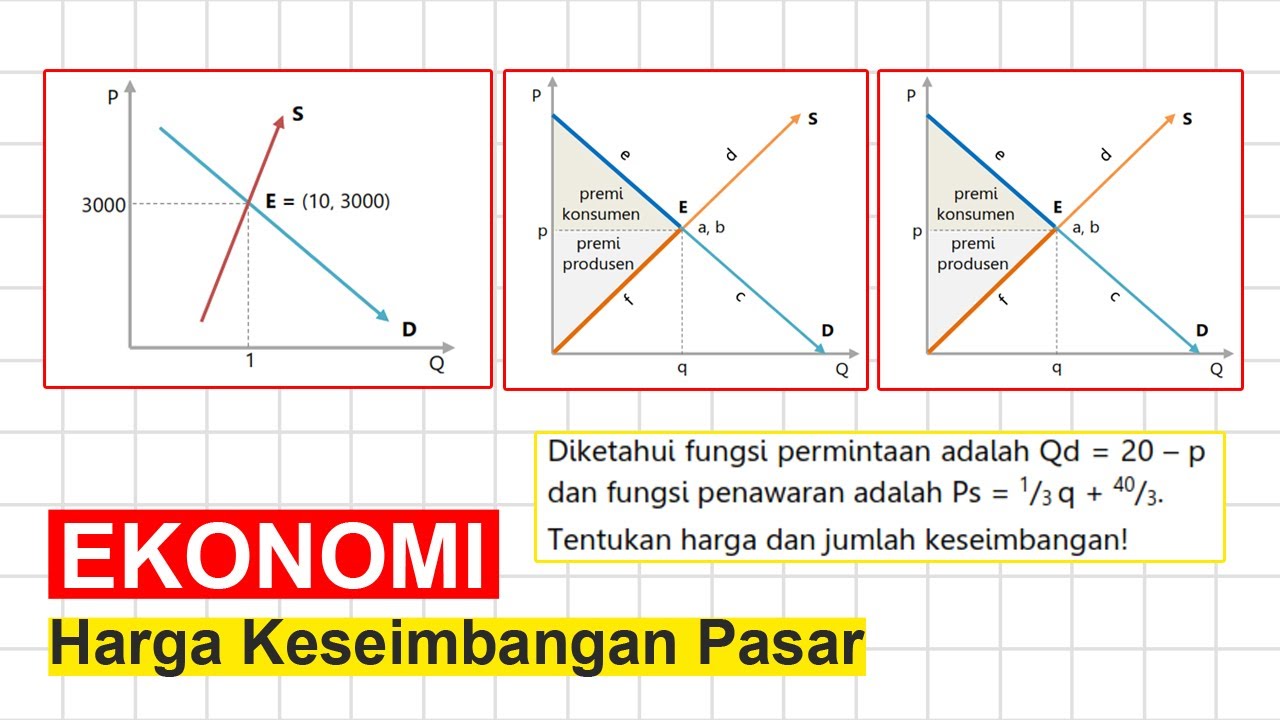
- 😀 The intersection of demand and supply curves determines the equilibrium point, where the price and quantity meet.
- 😀 A rightward shift of the demand curve indicates increased demand, while a leftward shift indicates decreased demand.
- 😀 Similarly, a rightward shift of the supply curve suggests increased supply, while a leftward shift indicates decreased supply.
- 😀 Through a practical example, the equilibrium price and quantity can be found by solving the demand and supply equations, resulting in the market equilibrium point.
Q & A
What is market equilibrium?
-Market equilibrium is the price at which the quantity of goods demanded by consumers equals the quantity supplied by producers. It is the point of balance where there is no excess demand or supply in the market.
What factors influence market equilibrium?
-Factors that influence market equilibrium include changes in demand, production costs, future outlooks by producers and consumers, consumer preferences, and shifts in purchasing power.
What is the role of equilibrium price in the market?
-The equilibrium price indicates the balance between supply and demand in the market. It helps producers and consumers make informed decisions about production, pricing, and purchasing.
How does the law of demand and law of supply affect market equilibrium?
-The law of demand states that as prices decrease, the quantity demanded increases. The law of supply suggests that as prices increase, producers are willing to supply more. These two laws interact to determine the equilibrium price.
What is the mathematical approach to determining market equilibrium?
-The mathematical approach involves using demand and supply functions. Market equilibrium occurs when the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied, and solving for the price and quantity gives the equilibrium point.
What happens when the demand curve shifts to the right?
-When the demand curve shifts to the right, it indicates an increase in demand. As a result, the equilibrium price and quantity may increase.
What does it mean when the supply curve shifts to the left?
-When the supply curve shifts to the left, it indicates a decrease in supply. This typically leads to higher equilibrium prices and lower equilibrium quantities.
How do producers and consumers use market equilibrium information?
-Producers use market equilibrium information to decide on the quantity of goods to produce, while consumers use it to determine whether to purchase a product at the given price.
What is the significance of price in determining market equilibrium?
-Price plays a crucial role in market equilibrium as it adjusts based on shifts in supply and demand, ensuring that the quantity demanded equals the quantity supplied at a given price.
Can you provide an example of calculating market equilibrium?
-For example, if the demand function is Q_d = 50 - 2P and the supply function is Q_s = -20 + 5P, solving these equations results in an equilibrium price of 10 and an equilibrium quantity of 30.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)