CN 5: Trigeminal Nerve (Scheme, Divisions, Pathway) | Neuroanatomy
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of the trigeminal nerve, its major branches (ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular), and their respective functions, including motor and sensory innervation to various facial muscles and regions. The video also highlights the role of the trigeminal nerve in conditions like HSV-1, where the virus can establish a latent infection in the trigeminal ganglion. The host walks viewers through complex anatomical structures in an accessible way, emphasizing how the trigeminal nerve impacts facial sensation and motor control, offering clear explanations and engaging visuals.
Takeaways
- 😀 The trigeminal nerve (Cranial Nerve V) has three main branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary, and mandibular nerves.
- 😀 The ophthalmic nerve supplies sensation to the scalp, forehead, and eyes, including the cornea and conjunctiva.
- 😀 The maxillary nerve provides sensation to the cheeks, upper teeth, palate, and nasal cavity.
- 😀 The mandibular nerve is responsible for sensation in the lower jaw, teeth, and part of the ear, and it also has motor functions.
- 😀 The mandibular nerve innervates muscles such as the masseter, temporalis, and pterygoid muscles for chewing.
- 😀 The deep temporal nerves (anterior and posterior) specifically innervate the temporalis muscle.
- 😀 The medial pterygoid nerve innervates the medial pterygoid muscle and also reaches the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini muscles.
- 😀 The nerve to the lateral pterygoid muscle controls the lateral pterygoid muscle, important for jaw movement.
- 😀 The masseteric nerve innervates both the masseter muscle and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ).
- 😀 Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1) can infect the trigeminal nerve, residing latently in the trigeminal ganglion and potentially reactivating in times of immune suppression.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the trigeminal nerve?
-The trigeminal nerve (cranial nerve V) is responsible for sensory innervation to the face and motor innervation to the muscles of mastication.
What are the three branches of the trigeminal nerve?
-The three branches of the trigeminal nerve are the ophthalmic branch (V1), the maxillary branch (V2), and the mandibular branch (V3).
What does the ophthalmic branch (V1) of the trigeminal nerve innervate?
-The ophthalmic branch (V1) provides sensory innervation to the forehead, scalp, eyes, and nose.
What structures does the maxillary branch (V2) of the trigeminal nerve innervate?
-The maxillary branch (V2) innervates the skin of the upper face, maxilla, upper teeth, gums, and mucosa of the nose, sinuses, and palate.
What muscles does the mandibular branch (V3) innervate?
-The mandibular branch (V3) innervates the muscles of mastication, including the masseter, temporalis, medial pterygoid, and lateral pterygoid muscles.
What is the role of the deep temporal nerves?
-The deep temporal nerves, which have anterior and posterior branches, innervate the temporalis muscle, aiding in the movement of the jaw.
What is the function of the medial pterygoid nerve?
-The medial pterygoid nerve innervates the medial pterygoid muscle and also supplies the tensor tympani and tensor veli palatini muscles.
What does the masseteric nerve innervate?
-The masseteric nerve innervates the masseter muscle and the temporomandibular joint (TMJ), both involved in jaw movement.
How does the herpes simplex virus (HSV-1) relate to the trigeminal nerve?
-HSV-1 is a neurotropic virus that infects the trigeminal ganglia, where it establishes a latent infection. It can reactivate when the immune system is weakened, leading to recurrent infections.
What does the term 'retrograde spread' mean in relation to HSV-1 infection?
-Retrograde spread refers to the movement of the HSV-1 virus from the epithelial cells to the nerve cells, where it travels along the axons toward the trigeminal ganglion, where it can remain dormant.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
2-Minute Neuroscience: Trigeminal Nerve (Cranial Nerve V)

Trigeminal Nerve Anatomy - Cranial Nerve 5 Course and Distribution
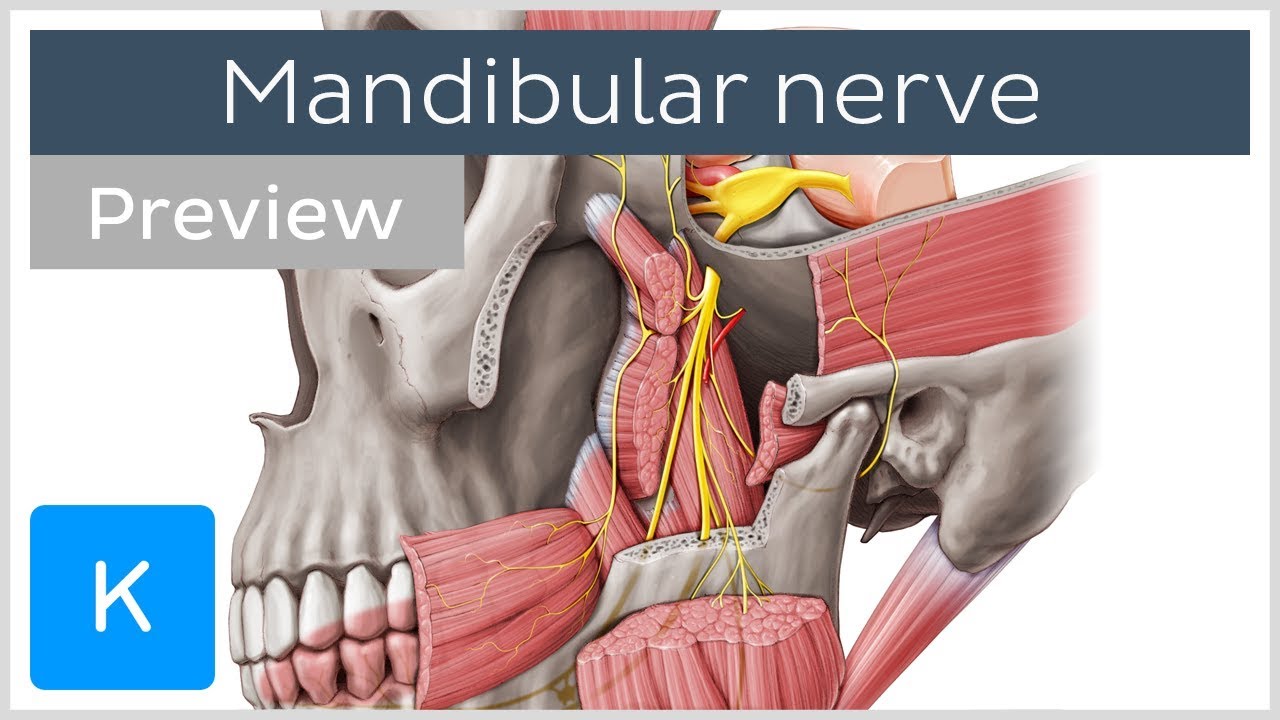
What is the Mandibular Nerve? (preview) - Human Anatomy | Kenhub
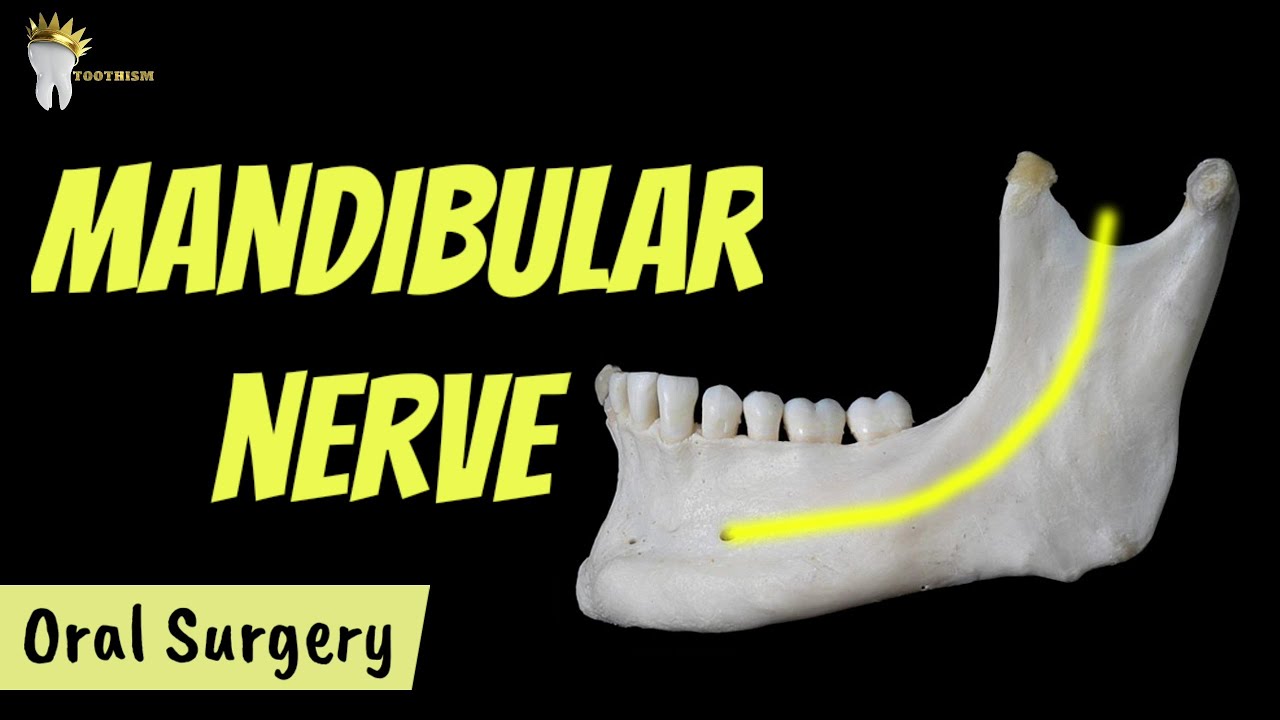
MANDIBULAR NERVE AND ITS BRANCHES

The Mandible: Anatomy and Muscles (3D Animation)
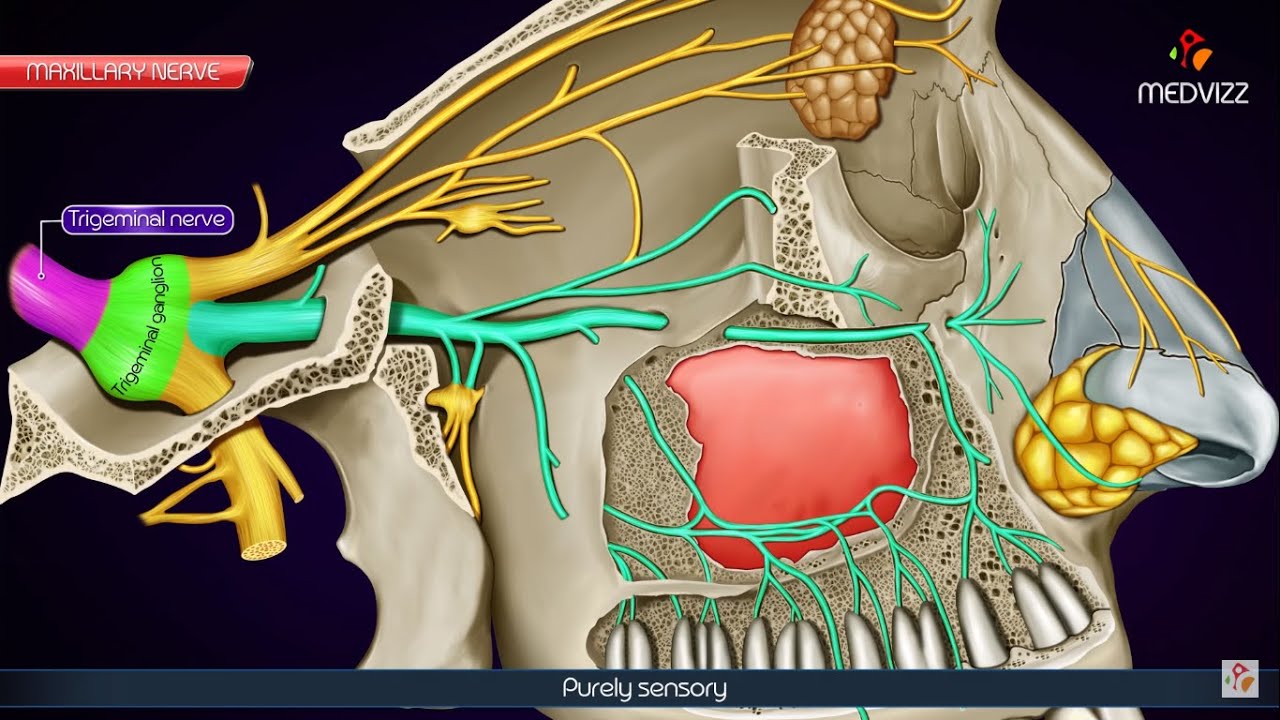
Maxillary division of Trigeminal nerve (V2 or Vb) / Maxillary nerve - Anatomy Animation
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
