Project Based Learning: Why, How, and Examples
Summary
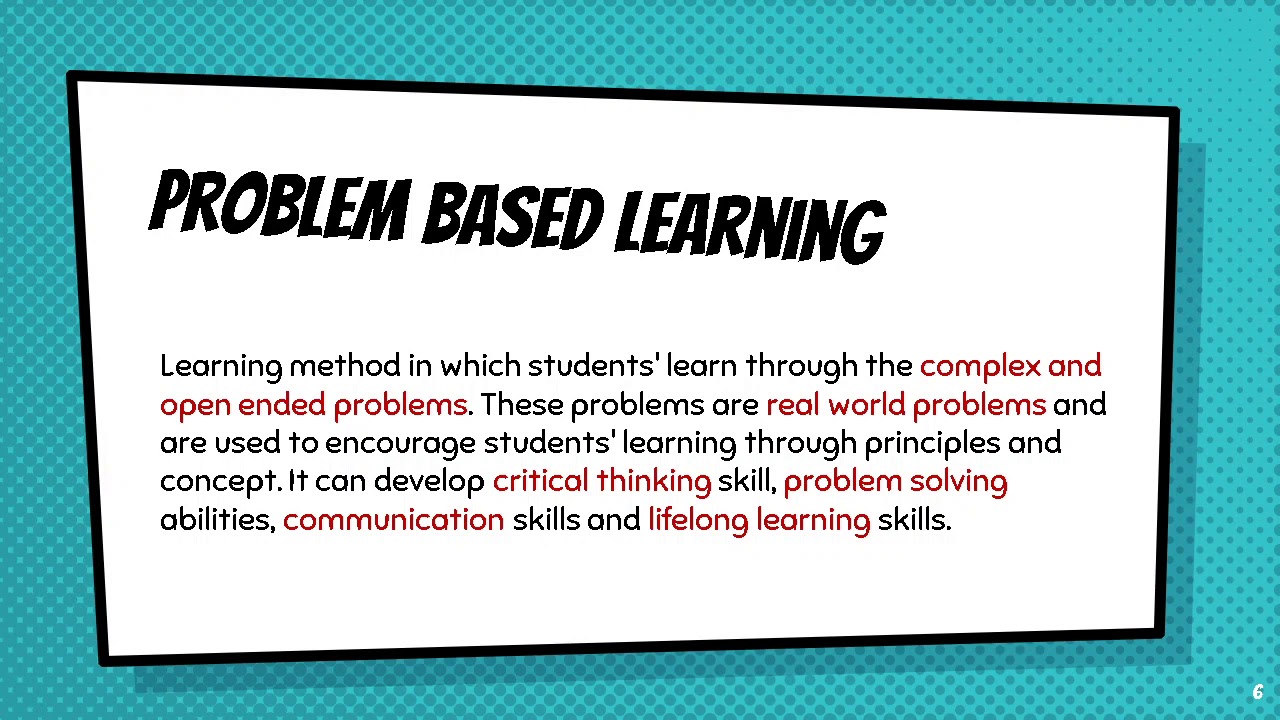
TLDRThis video introduces Project-Based Learning (PBL), a dynamic approach to engaging students by incorporating real-world problems into classroom projects. PBL encourages skills like communication, collaboration, and critical thinking. It is especially beneficial for at-risk students, but can be implemented across all grade levels and subjects. The process begins with a driving question aligned to learning goals, followed by inquiry, problem-solving, and the creation of tangible solutions. Examples include building a model of the Titanic, designing a house scale frame, and creating a miniature basketball court. PBL boosts student engagement and gives students a voice in their learning.
Takeaways
- 😀 Project-based learning (PBL) enhances student engagement by allowing them to work on real-world problems.
- 😀 PBL improves communication skills through presentations and group activities.
- 😀 Hands-on projects develop essential 21st-century life skills.
- 😀 PBL fosters collaboration by encouraging students to work together, a key skill for many professions.
- 😀 PBL is particularly effective for students who are disengaged by traditional lecture-based learning.
- 😀 At-risk students benefit significantly from PBL due to its hands-on and engaging nature.
- 😀 PBL can be applied to various subjects, especially social studies, science, and art classes.
- 😀 PBL can be used from kindergarten to 12th grade, dispelling the misconception that it’s only for older students.
- 😀 Successful PBL starts with a driving question aligned to a learning goal, which guides the project.
- 😀 The inquiry process encourages students to ask critical questions, apply knowledge, and find solutions.
- 😀 The final step of PBL allows students to present their projects to the public, giving them a voice and sense of ownership.
Q & A
What is project-based learning (PBL)?
-Project-based learning (PBL) is an educational approach where students engage in projects to learn by doing, often involving real-world problems and tasks. This method emphasizes collaboration, critical thinking, and hands-on learning.
Why should educators use PBL in their classrooms?
-Educators should use PBL because it boosts student engagement, helps develop important 21st-century skills like communication and teamwork, and allows students to apply knowledge in practical ways.
How does PBL help students develop communication skills?
-PBL often includes presentations as part of the project, giving students regular opportunities to practice speaking in front of others, enhancing their communication abilities.
What types of skills are developed through project-based learning?
-PBL helps students develop essential 21st-century skills, including problem-solving, collaboration, critical thinking, and creativity, alongside specific academic skills.
How does PBL support group work and collaboration?
-PBL typically involves group projects, which require students to collaborate, share responsibilities, and solve problems together—skills that are valuable in most professional environments.
Who benefits the most from PBL?
-At-risk students, who might struggle with traditional classroom learning, tend to benefit the most from PBL as it provides more engaging, hands-on experiences.
Is PBL only for higher-grade students?
-No, PBL can be used with students from kindergarten through 12th grade. While it's common in higher-grade classes, it can be adapted for younger students as well.
What is the first step in implementing PBL in the classroom?
-The first step is to design a driving question for the project, ensuring it is aligned with the learning goals of the class. The complexity of this question should match the level of the students.
What role does the inquiry process play in PBL?
-The inquiry process allows students to apply their knowledge, ask critical thinking questions, and locate resources to explore solutions to the driving question of the project.
Can you give an example of a PBL project for 6th grade?
-One example is a social studies project where students build a model of the Titanic and analyze how the ship could have been constructed more effectively. This involves reasoning, research, and writing.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)