5 - Zero Trust - Security+ SY0-701 - عربي
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains traditional network security methods and introduces the concept of Zero Trust security. It discusses how traditional models like castles and tunnels are used to protect networks, highlighting their limitations. The Zero Trust approach assumes that both external and internal threats exist, requiring segmentation of networks into security zones for better control. The process involves using control planes, data planes, and policy enforcement points to manage access and protect sensitive resources. The script also details the role of policy-driven access control and how to handle user authentication and authorization in a Zero Trust environment.
Takeaways
- 😀 Traditional network protection methods, such as the castle and moat concept, focus on perimeter defense, but fail to account for insider threats.
- 😀 The Zero Trust model assumes there may be a breach inside or outside the network and enforces strict verification of users and devices.
- 😀 Network segmentation plays a vital role in Zero Trust by dividing the network into smaller, more secure sections (trusted vs. untrusted zones).
- 😀 The Control Plane is responsible for managing access decisions, while the Data Plane executes the decisions, such as routing packets.
- 😀 Zero Trust security requires gathering more data from users (device type, location, role) beyond just usernames and passwords to validate access.
- 😀 Reducing entry points (e.g., VPN access) in a network lowers potential attack vectors, contributing to a more secure environment.
- 😀 Policy Enforcement Points (PEP) are responsible for receiving access requests and forwarding them to Policy Decision Points (PDP).
- 😀 Policy Decision Points (PDP) analyze access requests and determine whether they should be granted based on predefined security rules.
- 😀 Zero Trust involves restricting internal network access, assuming potential threats exist within the network, and enforcing least-privilege access policies.
- 😀 The division of the network into security zones helps improve network security by controlling access to sensitive areas, making it harder for unauthorized users to move laterally.
- 😀 The Zero Trust architecture ensures that security decisions are dynamic and based on real-time data, allowing for better response to emerging threats.
Q & A
What is the traditional method used for protecting networks, as mentioned in the script?
-The traditional method is the castle model, which uses the concepts of a castle, tunnel, and VPN to protect the network.
What issue does the traditional castle model face in network security?
-The problem with the castle model is that once an intruder gains access to the castle (network), they can move freely within it.
What is the core idea behind Zero Trust security?
-Zero Trust assumes that there is always a potential attacker both inside and outside the network, and continuous verification of users and devices is required to ensure security.
How is Zero Trust implemented in terms of network segmentation?
-Zero Trust is implemented by dividing the network into smaller parts called functional planes, generally into control planes and data planes.
What is the role of the control plane in Zero Trust security?
-The control plane is responsible for managing access requests, enforcing policies, and making decisions about who can enter the network.
What is the function of the data plane in network security?
-The data plane is responsible for routing traffic and implementing the decisions made by the control plane without making its own decisions.
What additional information is gathered in a Zero Trust network to authenticate users?
-In addition to a username and password, Zero Trust gathers information such as the type of device, location of the device, and the user’s relationship to the organization.
What is the purpose of reducing points of entry in a network as part of Zero Trust?
-Reducing points of entry ensures that only specific, trusted methods (like VPNs) are used to access the internal network, minimizing potential vulnerabilities.
How are security zones used in a Zero Trust network, according to the script?
-Security zones are used to control access between different areas of the network, ensuring that only authorized users can access trusted zones.
What is the role of the Policy Enforcement Point (PEP) in Zero Trust?
-The PEP executes access decisions, directing traffic to either trusted or untrusted zones based on the policies enforced by the Policy Decision Point (PDP).
What are the two main components inside the Policy Decision Point (PDP)?
-The two main components inside the PDP are the Policy Engine, which makes decisions, and the Administrator, which interacts with the Policy Enforcement Point to implement those decisions.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Zero Trust Explained | Real World Example

Zero Trust - CompTIA Security+ SY0-701 - 1.2

Network Segmentation - SY0-601 CompTIA Security+ : 3.3

Understanding and Getting Started with ZERO TRUST

What is Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) ?
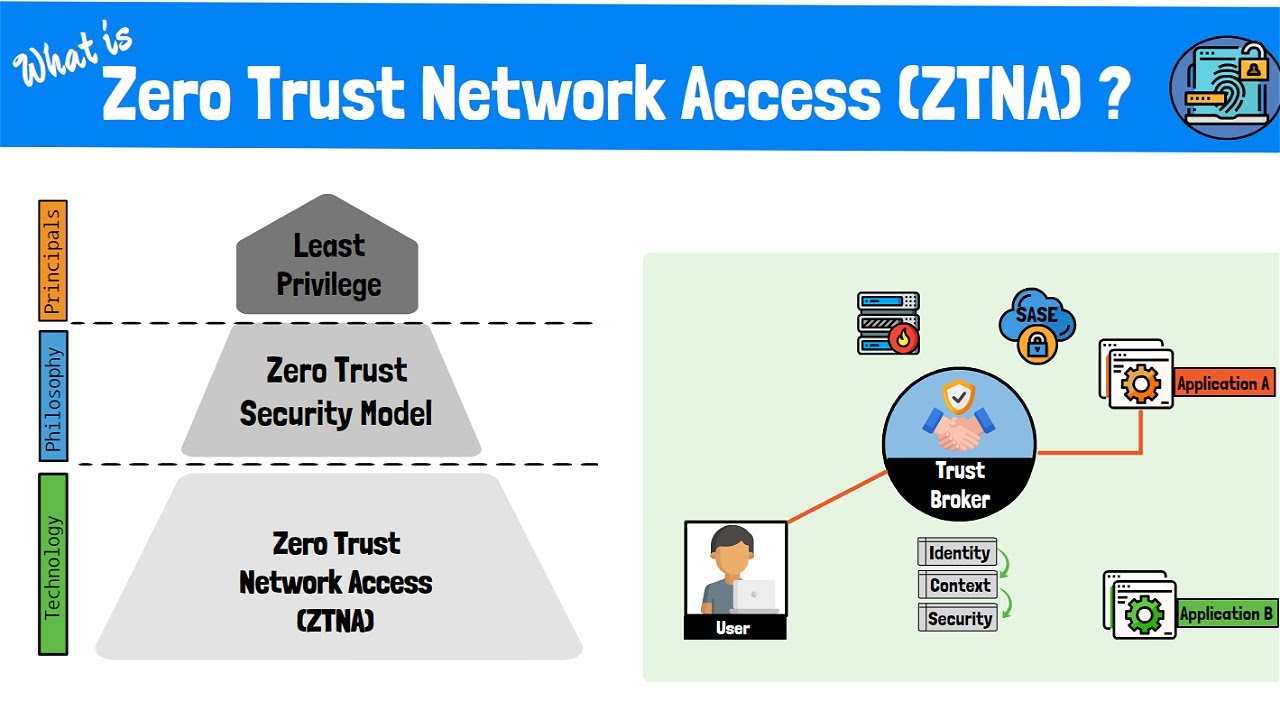
What is Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA)? The Zero Trust Model, Framework and Technologies Explained
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
