Genética Mendeliana
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the groundbreaking genetic discoveries of Gregor Mendel, an Austrian monk and biologist, who laid the foundation for modern genetics through his work with pea plants. By crossbreeding plants with dominant yellow seeds and recessive green seeds, Mendel revealed the principles of inheritance, such as dominant and recessive traits. His experiments introduced key concepts like homozygous and heterozygous genotypes, as well as phenotypes. Mendel's use of Punnett squares demonstrated how traits are passed from generation to generation, and while our understanding of genetics has advanced since his time, his work remains a cornerstone of genetic science.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mendel, an Austrian monk and biologist, discovered the principles of inheritance in the 19th century.
- 😀 Through experiments with pea plants, Mendel observed how traits like seed color are passed down through generations.
- 😀 He introduced the concept of dominant and recessive traits, with dominant traits always appearing in offspring.
- 😀 Mendel's pea plant experiment with yellow and green seeds led to the identification of these dominant and recessive traits.
- 😀 He concluded that each trait is determined by a pair of factors (alleles), one from each parent.
- 😀 Alleles can be identical (homozygous) or different (heterozygous), forming the organism's genotype.
- 😀 The physical expression of a genotype (such as yellow or green seeds) is called the phenotype.
- 😀 Mendel used Punnett squares to predict allele combinations and the resulting phenotypes in offspring.
- 😀 In the second generation, heterozygous offspring can produce three possible genotypes, with a 3:1 phenotypic ratio.
- 😀 Modern genetics has expanded on Mendel's work, revealing more complex inheritance patterns beyond simple dominance and recessiveness.
Q & A
What is Mendelian inheritance?
-Mendelian inheritance refers to the principles of heredity discovered by Gregor Mendel in the 19th century, which explain how traits are passed from parents to offspring. It involves the inheritance of dominant and recessive traits, with each trait being governed by a pair of alleles.
Who was Gregor Mendel and what was his contribution to genetics?
-Gregor Mendel was an Austrian monk and biologist who is considered the father of genetics. He conducted experiments with pea plants and discovered the basic principles of heredity, including the concepts of dominant and recessive traits.
What is the difference between dominant and recessive traits?
-A dominant trait is one that is expressed in the offspring even if only one parent passes down the dominant allele. A recessive trait only appears when both parents contribute a recessive allele.
How did Mendel perform his experiments with pea plants?
-Mendel crossed pea plants with pure yellow seeds and pure green seeds. The first generation showed only yellow seeds, which he identified as the dominant trait. In the second generation, he observed both yellow and green seeds, which indicated that the green trait was recessive and hidden in the first generation.
What are alleles and how do they relate to Mendel's findings?
-Alleles are different versions of a gene. Mendel found that each trait is determined by a pair of alleles, one inherited from each parent. The combination of these alleles determines the genotype and phenotype of the offspring.
What is the difference between homozygous and heterozygous genotypes?
-A homozygous genotype has two identical alleles for a trait (either both dominant or both recessive), while a heterozygous genotype has two different alleles (one dominant and one recessive).
How can we predict the inheritance of traits using a Punnett square?
-A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the possible genetic outcomes in offspring. By placing the alleles of the parents on the axes of the square and combining them, we can determine the likelihood of different genotypes and phenotypes in the offspring.
What was the result of Mendel's second generation of pea plants?
-In the second generation, Mendel's hybrid yellow seed plants produced offspring with both yellow and green seeds. This demonstrated that the green seed trait, though hidden in the first generation, was still present and could be passed down.
What other traits, apart from seed color, did Mendel observe in his pea plants?
-Mendel also observed traits like seed shape, where peas could be round or wrinkled. He combined different traits to study the inheritance patterns of more complex genetic combinations.
Why is Mendel's work considered foundational in modern genetics?
-Mendel's work laid the foundation for modern genetics because it introduced the concepts of inheritance patterns, dominant and recessive alleles, and the use of Punnett squares to predict genetic outcomes. His discoveries helped explain how traits are passed from generation to generation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

How Mendel's pea plants helped us understand genetics - Hortensia Jiménez Díaz

História de GREGOR MENDEL - GENÉTICA

O Monge e a Ervilha - A vida de Gregor Mendel

028 Gregor Mendel & die klassische Genetik Meilensteine der Naturwissenschaft & Technik
Genetics - Lost and Found: Crash Course History of Science #25
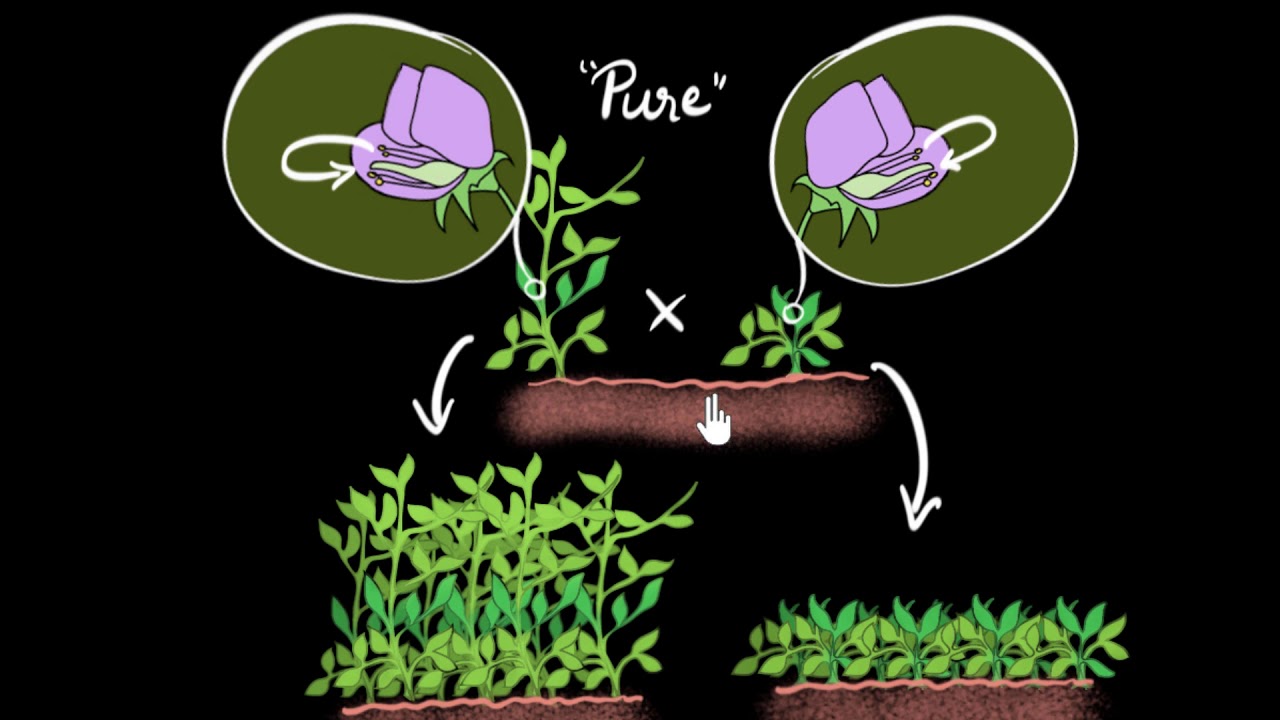
Mendel's experiment (monohybrid cross) | Heredity & Evolution | Biology | Khan Academy
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
