O Monge e a Ervilha - A vida de Gregor Mendel
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the life and groundbreaking discoveries of Gregor Mendel, a monk from Moravia, who unlocked the mystery of heredity. Born into a poor family, Mendel's early struggles led him to a monastery, where his passion for science flourished. He conducted pivotal experiments with peas, uncovering the principles of genetic inheritance that defied the popular theory of blending traits. His work, though initially ignored, later revolutionized biology. Mendel's discoveries laid the foundation for modern genetics, and his contributions were finally recognized after his death, changing our understanding of life on Earth forever.
Takeaways
- 😀 Gregor Mendel, the father of genetics, solved the mystery of heredity in the 19th century.
- 😀 Mendel was born in 1822 in a poor family in what is now the Czech Republic, and had a delicate health as a child.
- 😀 Despite his health struggles, Mendel pursued his scientific ambitions and entered a monastery, where he could focus on education and research.
- 😀 At the time, the prevailing theory of inheritance was the 'blending' theory, which suggested offspring were a mix of both parents' characteristics.
- 😀 Mendel's curiosity led him to study plant genetics, specifically pea plants, and how traits are passed from one generation to the next.
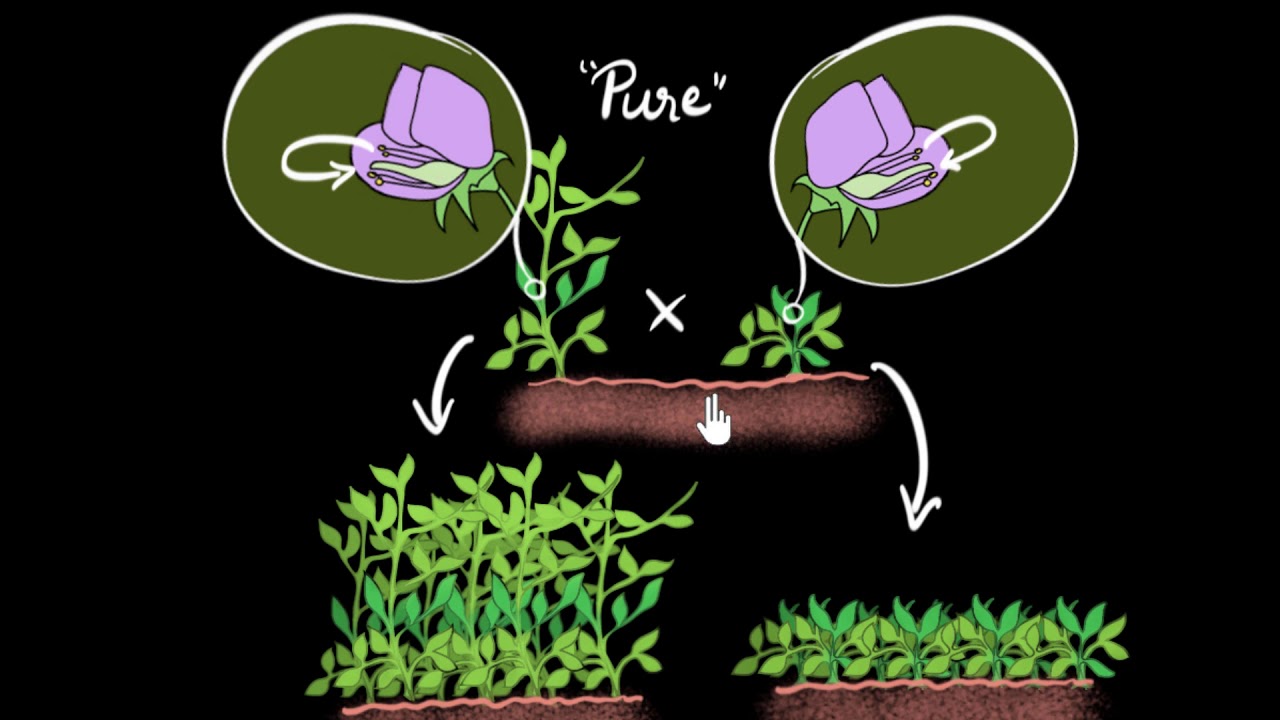
- 😀 Mendel conducted controlled breeding experiments with pea plants, studying traits such as smooth versus wrinkled peas.
- 😀 Contrary to the blending theory, Mendel discovered that traits do not blend but are inherited as discrete units (genes).
- 😀 Mendel's experiments revealed that certain traits are dominant and others are recessive, a concept that became the foundation of modern genetics.
- 😀 Mendel's research was not recognized during his lifetime, but it laid the groundwork for future genetic discoveries, including the work of Darwin and others.
- 😀 Mendel's approach to studying genetics was influenced by his background in mathematics and physics, allowing him to apply statistical methods to his experiments.
Q & A
What mystery did Gregor Mendel solve?
-Gregor Mendel solved the mystery of heredity by discovering the basic laws of inheritance, which explained how characteristics are passed from one generation to the next.
How did Mendel's early life influence his scientific work?
-Mendel's early life, marked by poverty and a fragile health condition, led him to pursue a stable life in a monastery. His early curiosity about life and nature eventually directed him toward scientific studies, particularly in botany and genetics.
What was the prevailing theory of inheritance before Mendel's experiments?
-Before Mendel's experiments, the prevailing theory of inheritance was the 'blending theory,' which proposed that offspring were a blend of the traits of their parents, similar to mixing fluids together.
What is significant about Mendel's use of peas in his experiments?
-Mendel's use of peas was significant because their characteristics, such as smooth or wrinkled seeds, were easy to observe and count, and the plants were easy to crossbreed, making them ideal for studying inheritance patterns.
How did Mendel prove that the blending theory of inheritance was incorrect?
-Mendel proved the blending theory incorrect by showing that traits could disappear in one generation and reappear in later generations. For example, the wrinkled seed trait reappeared in the second generation, demonstrating the existence of dominant and recessive traits.
What was Mendel's key discovery regarding inheritance?
-Mendel discovered the fundamental laws of inheritance, including the concepts of dominant and recessive traits, and how traits are passed through distinct particles (now known as genes), which combine in predictable ways during reproduction.
How did Mendel conduct his experiments on pea plants?
-Mendel conducted his experiments by crossbreeding pea plants with different traits, such as smooth and wrinkled seeds, and then analyzing the traits in the offspring, meticulously counting and categorizing the results.
What did Mendel's experiments reveal about dominant and recessive traits?
-Mendel's experiments revealed that some traits are dominant, meaning they appear in offspring even when only one parent contributes the gene, while recessive traits only appear when both parents contribute the recessive gene.
Why did Mendel's 1865 lecture on his findings fail to make an impact?
-Mendel's 1865 lecture failed to make an impact because the scientific community did not understand the mathematical and statistical concepts he presented. The audience expected a discussion on plants, but instead received a complex lecture on genetics that was not widely accepted at the time.
What was the reaction to Mendel's work after his death?
-After Mendel's death, his work was largely ignored until 16 years later when scientists in England and the Netherlands rediscovered his findings. His theories on genetics eventually became foundational in the field of biology.
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video

Genética Mendeliana
Mendel's experiment (monohybrid cross) | Heredity & Evolution | Biology | Khan Academy

Mendel e a Ervilha - Os Seis Experimentos que Mudaram o Mundo

The history of genetics

História de GREGOR MENDEL - GENÉTICA

How Mendel's pea plants helped us understand genetics - Hortensia Jiménez Díaz
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)