Biology Learning - Learn About Excretory System
Summary
TLDRThe human excretory system plays a critical role in maintaining homeostasis by removing excess, harmful, and waste materials from the body. Central to this process are the kidneys, which filter blood and produce urine through a network of nephrons. The system also involves other organs like the skin, lungs, and liver, each contributing to waste elimination. The urinary system, consisting of kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra, ensures the body stays balanced by regulating fluid levels, pH, and the removal of toxins. Understanding this intricate process highlights the importance of the excretory system in overall health.
Takeaways
- 😀 The excretory system is essential for maintaining homeostasis by removing excess, unnecessary, or harmful materials from the body.
- 😀 The primary organs of the human excretory system are the kidneys, which help regulate water, iron, and pH balance in the body.
- 😀 Besides kidneys, the excretory system also includes skin, lungs, and liver, with skin playing a minimal role in waste removal through sweat.
- 😀 In multicellular organisms, excretory systems are necessary since cells are not in direct contact with the external environment to release waste products.
- 😀 Kidneys filter metabolic wastes, toxic substances, and regulate blood volume, interstitial fluids, and optimal pH for chemical reactions.
- 😀 The human urinary system consists of kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder, and urethra, and plays a critical role in waste elimination.
- 😀 Kidneys are bean-shaped structures located at the upper posterior part of the abdominal cavity and are protected by the 11th and 12th ribs.
- 😀 Each kidney contains around 1.2 million functional units called uriniferous tubules, which are composed of nephrons and collecting tubules.
- 😀 The nephron consists of the renal corpuscle (glomerulus and Bowman's capsule) and the renal tubule, which includes the proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule.
- 😀 Micturition is the voluntary process of urine elimination, regulated by parasympathetic stimulation and brain signals, where the external urethral sphincter relaxes to allow voiding of urine.
Q & A
What is the primary function of the excretory system?
-The primary function of the excretory system is to remove excess, unnecessary, or dangerous materials from the body to help maintain homeostasis, regulate chemical balance, and prevent damage to the organism.
Which organs are involved in the human excretory system?
-The main organs involved in the human excretory system are the kidneys, urinary bladder, ureters, and urethra. Other organs like the skin, lungs, and liver also play secondary roles.
How do the kidneys contribute to maintaining homeostasis?
-The kidneys help maintain homeostasis by filtering blood, removing waste products, regulating water and electrolyte balance, and maintaining optimal pH levels required for chemical reactions in the body.
What role does the liver play in the excretory system?
-The liver detoxifies harmful substances, converts ammonia into urea, and releases it into the bloodstream. The urea is then filtered out by the kidneys and excreted in the urine.
How do single-celled organisms eliminate waste without an excretory system?
-Single-celled organisms do not have a specialized excretory system. They release waste products and excess water directly through their body surface into the surrounding medium.
What is the structure and function of the nephron in the kidney?
-The nephron is the functional unit of the kidney, consisting of a renal capsule (Bowman’s capsule and glomerulus) for filtration, and a renal tubule (proximal convoluted tubule, loop of Henle, and distal convoluted tubule) for reabsorption and secretion of substances.
What is the role of the glomerulus in urine formation?
-The glomerulus is a network of capillaries that filters blood, allowing small molecules, such as water and waste products, to pass into the Bowman’s capsule, while retaining larger molecules like proteins and blood cells.
How is urine formed in the kidneys?
-Urine is formed in the kidneys through a process of filtration, reabsorption, and secretion. Blood is filtered in the glomerulus, and essential substances are reabsorbed in the renal tubule, while waste products are secreted into the urine.
What is the function of the loop of Henle in the nephron?
-The loop of Henle plays a key role in concentrating urine. It reabsorbs water from the descending limb and sodium chloride from the ascending limb, which helps in creating an osmotic gradient for water reabsorption.
What is micturition, and how is it controlled?
-Micturition is the process of urination. It is controlled by both voluntary and involuntary systems. When the bladder fills, signals are sent to the brain, which coordinates the relaxation of the external urethral sphincter and contraction of pelvic muscles for urine expulsion.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
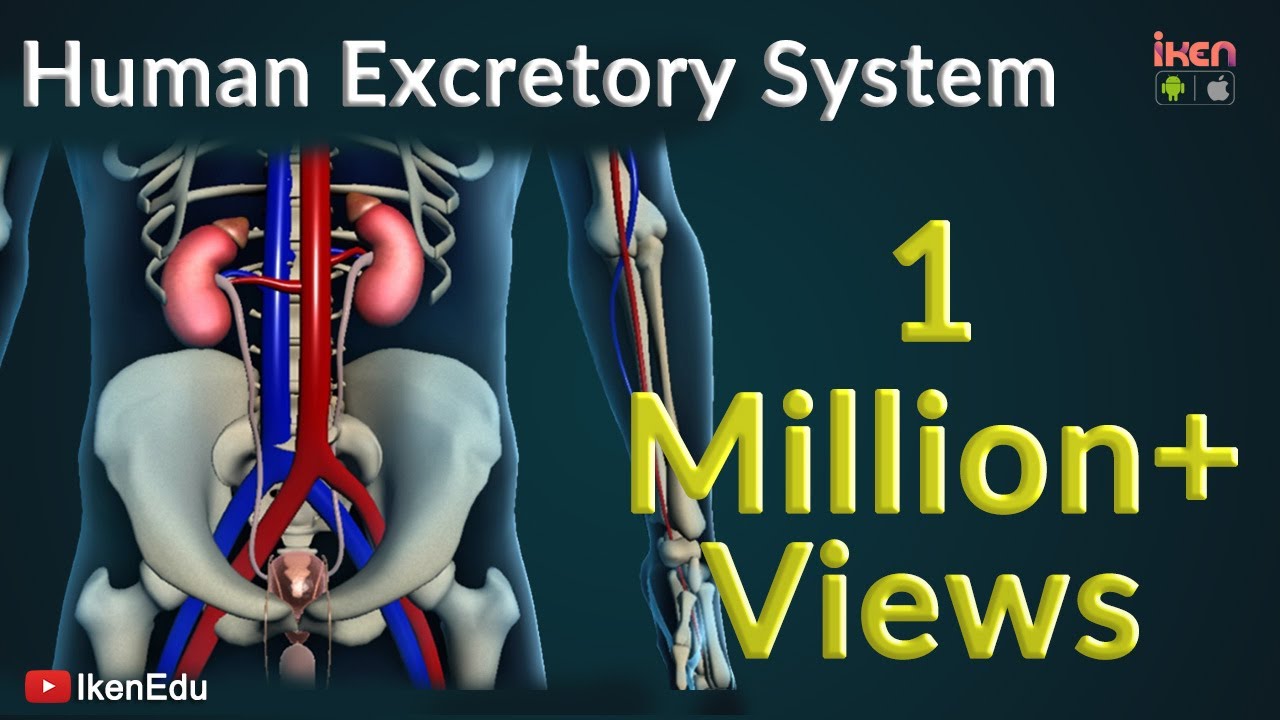
Learn About Human Excretory System | iKen | iKen Edu | iKen App

Biologi Kelas 11: Sistem Ekskresi - Pembuangan Zat Sisa Metabolisme
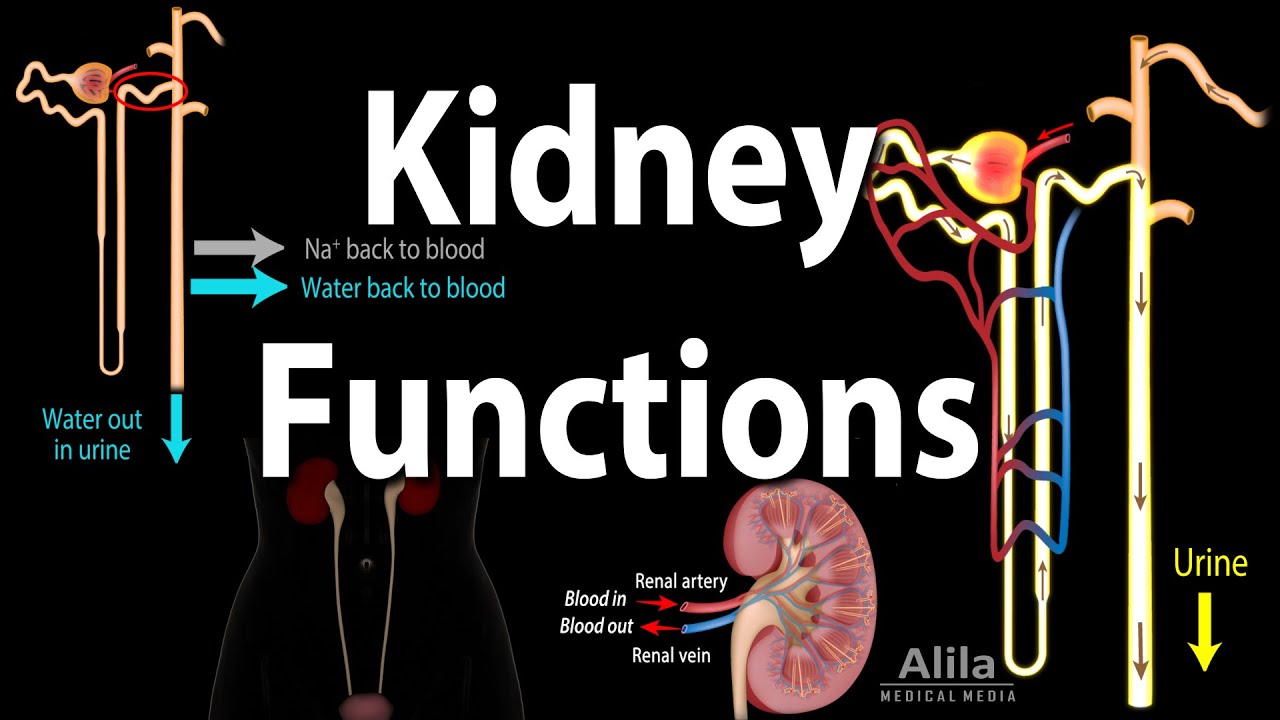
Kidney Homeostatic Functions, Animation
The Lymphatic System | Health | Biology | FuseSchool
SISTEM EKSKRESI PADA MANUSIA : KULIT, PARU-PARU, HATI (PART 2)

How Does the Lymphatic System Work?
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
