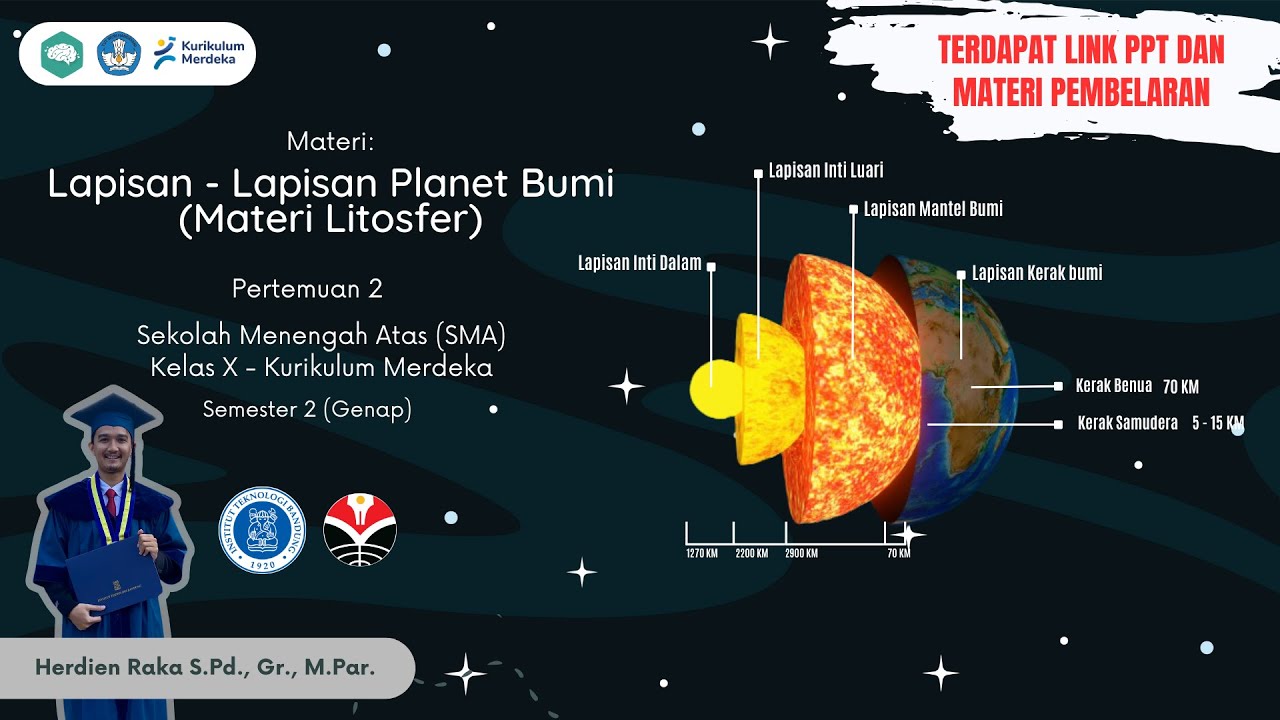
KARAKTERISTIK LAPISAN-LAPISAN BUMI
Summary
TLDRIn this geography class, students explore the Earth's lithosphere and its impact on human life. The lesson covers the characteristics and structure of Earth's layers, including the lithosphere, asthenosphere, and the inner and outer core. Key concepts like plate tectonics, volcanic activity, and erosion are discussed. Students also learn about the different types of rocks—igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic—and the rock cycle. The lesson emphasizes the importance of Earth's crust, its mineral composition, and its role in shaping the planet's surface, fostering a deeper understanding of Earth's dynamic processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 The Earth’s lithosphere is the outermost layer, made up of solid rock that forms the Earth's crust.
- 😀 Lithosphere comes from the Greek words 'lithos' meaning stone and 'sphere' meaning layer, and it is composed of rigid tectonic plates.
- 😀 The Earth's lithosphere is divided into two parts: the 'Sial' (continental crust) and 'Sima' (oceanic crust), each with different characteristics.
- 😀 The Earth's layers include the core (Barisfer), the mantle (Astenosfer), and the outer crust (Litosfer).
- 😀 The lithosphere is not uniform in thickness; the continental crust is thicker than the oceanic crust.
- 😀 The lithosphere interacts with the astenosphere, a softer layer beneath it, and moves via tectonic activity.
- 😀 Earth’s crust is made up of various minerals, forming three types of rocks: igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic.
- 😀 Plate tectonics and dynamic processes like volcanism, earthquakes, and erosion occur within the lithosphere.
- 😀 The Earth’s core (Barisfer) is primarily composed of iron and nickel, with the inner core being solid and the outer core liquid.
- 😀 Rocks and minerals found in the Earth's crust are essential for various uses, with many being extracted through mining.
- 😀 The rock cycle explains how rocks change from one form to another through processes like cooling, weathering, sedimentation, and metamorphosis.
Q & A
What is the lithosphere?
-The lithosphere is the outermost layer of the Earth, primarily composed of solid rock. It is derived from the Greek words 'lithos' meaning rock, and 'sphere' meaning layer.
What are the three main layers of the Earth?
-The three main layers of the Earth are the core (barysphere), asthenosphere, and lithosphere.
What is the difference between the inner core and the outer core?
-The inner core is solid and composed mainly of iron and nickel, while the outer core is liquid and also composed of iron and nickel.
How does the asthenosphere differ from the lithosphere?
-The asthenosphere is a semi-fluid, high-temperature layer of the Earth's mantle located beneath the lithosphere, which is rigid and solid. The lithosphere floats on the asthenosphere.
What is the importance of the Earth's crust?
-The Earth's crust, made up of minerals, is essential because it provides the surface for life, contains valuable minerals, and plays a key role in the Earth's geological processes, such as plate tectonics.
What are the two types of Earth's crust?
-The Earth's crust is divided into two types: the continental crust (kerak benua), which is thicker and primarily composed of granite, and the oceanic crust (kerak samudra), which is thinner and mainly made up of basalt.
What are the main geological processes that occur in the lithosphere?
-The main geological processes in the lithosphere include tectonism (movement of tectonic plates), volcanism (volcanic activity), seismic activity (earthquakes), and exogenous forces such as erosion and weathering.
What is the rock cycle?
-The rock cycle is the continuous process by which rocks are transformed from one type to another through geological processes, such as cooling, erosion, sedimentation, and metamorphism.
What are the three main types of rocks?
-The three main types of rocks are igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks. Igneous rocks form from cooled magma, sedimentary rocks form from compressed sediments, and metamorphic rocks form from high pressure and temperature.
Can you explain the difference between igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks?
-Igneous rocks form from cooling magma, like granite and basalt. Sedimentary rocks are created from the compaction of sediments, such as sandstone. Metamorphic rocks form from existing rocks undergoing changes due to pressure and temperature, such as marble from limestone.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)