duration concept explained
Summary
TLDRThis video script explains the key elements involved in analyzing musical duration, covering time signatures, ostinatos, tempo, accents, note lengths, beats, and phrasing. It emphasizes the importance of distinguishing between isometric and multimetric time signatures, identifying repeated rhythmic patterns, and using correct Italian terms to describe tempo. The script also discusses the role of accents, syncopation, and the use of call-and-response in phrasing. A focus is placed on providing clear and specific musical terminology to analyze these aspects and how to describe tempo changes, note lengths, and beat patterns for a more insightful musical understanding.
Takeaways
- 😀 Time signature analysis is crucial; determine if the time signature is isometric (constant) or multimetric (changes).
- 😀 For simple time, remember the common signatures: 2/4 (March), 3/4 (Waltz), and 4/4 (Common Time). Compound time uses signatures like 6/8, 9/8, and 12/8, which have a bouncy feel.
- 😀 Always explain the time signature by specifying the beats per measure and the type of beats used (e.g., 2 crotchet beats per bar for 2/4).
- 😀 Identifying repeated rhythmic or melodic patterns is important for analyzing ostinato, which can include percussion or repeated melody lines.
- 😀 Accurately describe the tempo using correct Italian terms such as 'Allegro' (fast) or 'Adagio' (slow). Avoid simply saying 'fast' or 'slow'.
- 😀 Note any changes in tempo, such as accelerando (getting faster), ritardando (slowing down), or rallentando (gradually slowing).
- 😀 Pay attention to accents and syncopation: syncopation occurs when rhythms emphasize the off-beat, and a backbeat focuses on beats 2 and 4 in pop/rock music.
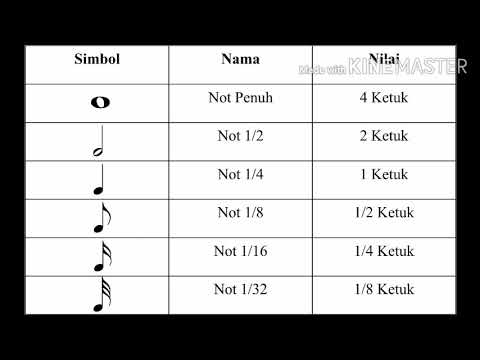
- 😀 Look at the length of notes and describe whether they are mostly long or short. Also, note any changes in note length between sections, using terms like staccato (short) and legato (smooth).
- 😀 Identify which instruments perform the beat. Common instruments include drums, bass guitars, and tubas, depending on the ensemble.
- 😀 Phrasing is important—count how many bars make up each phrase and describe whether the phrasing is balanced (symmetrical) or unbalanced (asymmetrical). If call and response is used, mention the length of each part.
Q & A
What is 'Total BP' in the context of musical duration?
-'Total BP' refers to the breakdown of musical duration concepts, including Time Signature, Ostinato, Tempo, Accents, Length of Notes, and Beat and Phrasing. It's a framework used to analyze how time and rhythm are structured in a piece of music.
What is the difference between isometric and multimetric time signatures?
-An isometric time signature means the time signature remains constant throughout the piece, while a multimetric time signature changes at least once during the piece, even if it's just temporarily.
What are some examples of Simple Time signatures, and what do they represent?
-Examples of Simple Time signatures include 2/4, 3/4, and 4/4. 2/4 is typically a march (Simple duple), 3/4 is a waltz (Simple triple), and 4/4 is the most common time signature (Simple quadruple), used in many musical genres.
What is the 'compound time' and how does it feel compared to simple time?
-Compound time includes time signatures like 3/8, 6/8, 9/8, and 12/8. These time signatures tend to have a bouncy feel because the beats are subdivided into smaller, irregular units, unlike the evenly spaced beats of simple time.
How can you identify ostinato in music?
-Ostinato refers to repeated rhythmic patterns, often performed by percussion instruments such as drums, bongos, maracas, etc. You can identify it by listening for rhythmic patterns that repeat consistently throughout a section of music.
What are some key Italian terms to describe tempo, and what do they mean?
-Key Italian tempo terms include 'Lento' (slow), 'Allegro' (fast), and 'Grave' (very slow). These terms help describe the overall speed of the music with more precision than just saying 'fast' or 'slow.'
What is 'accelerando' and how is it used in music?
-'Accelerando' refers to a gradual increase in tempo. It is used to signal that the music should gradually get faster, providing a sense of building momentum or energy.
How do accents work in music, and what is an example of how they affect rhythm?
-Accents in music emphasize certain notes over others. For example, in most pop and rock music, the emphasis is placed on beats 2 and 4 (the backbeat), while classical music typically emphasizes beats 1 and 3.
What is the difference between legato and staccato notes?
-Legato refers to smooth, connected notes with no breaks between them, while staccato refers to short, detached notes, often with a distinct pause between them.
What does it mean when the beat in a piece of music is described as 'definite' or 'indefinite'?
-A 'definite' beat means the rhythm and tempo are clearly structured and easy to follow, while an 'indefinite' beat, common in some 20th-century music, may lack a clear rhythm or tempo, making it difficult to determine the exact beat.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)