Apa itu INFLASI dan DEFLASI?
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the concepts of inflation and deflation, two key factors influencing a nation's economy. Inflation refers to the general rise in prices, often driven by increased money supply, production costs, or demand-supply imbalances. In contrast, deflation is the continuous decrease in prices, often caused by reduced money circulation or excess supply. The video also explores their causes and their impacts on purchasing power, business revenue, wages, and employment. Viewers are encouraged to engage with the channel by subscribing and leaving feedback.
Takeaways
- 😀 Inflation refers to the general rise in prices of goods and services over time, often leading to a decrease in purchasing power.
- 😀 Deflation is the opposite of inflation, characterized by a general decline in prices and can result in economic downturns.
- 😀 Inflation can be caused by an increase in the money supply, which leads to a rise in demand while the supply of goods remains the same.
- 😀 Rising production costs, such as higher raw material prices, can lead to inflation by pushing businesses to raise prices to maintain profit margins.
- 😀 Increased demand coupled with limited supply of goods and services can cause inflation, particularly when there is a significant mismatch.
- 😀 A limited supply of goods, often caused by rapid population growth or production inefficiencies, can also lead to inflation.
- 😀 Deflation can occur when there is a reduction in the money supply, often due to higher savings rates or reduced consumer spending.
- 😀 An oversupply of goods in the market, typically from producers misjudging demand, can contribute to deflation as prices fall to clear excess stock.
- 😀 A lack of demand for certain goods, especially when products are not well received by consumers, can result in deflationary pressure on the economy.
- 😀 Inflation reduces purchasing power, meaning that people can buy less with the same amount of money, which impacts the economy at large.
Q & A
What is the definition of inflation?
-Inflation is the general increase in the price of goods and services over a period of time, leading to a decrease in the purchasing power of money.
How does inflation differ from deflation?
-Inflation is the rise in the general price level of goods and services, while deflation is the continuous decrease in prices over a short period, both having opposing effects on the economy.
What causes inflation in an economy?
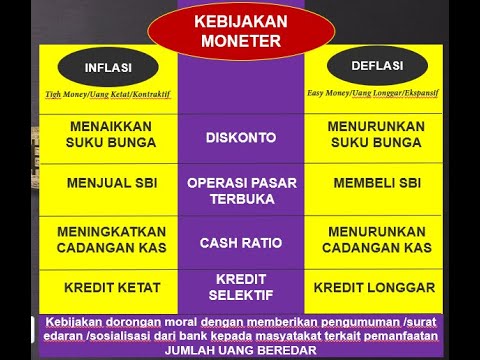
-Several factors cause inflation, including an increase in the money supply, rising production costs, higher demand for goods and services, and limited availability of goods.
How does the amount of money in circulation impact inflation?
-If the amount of money circulating in the economy exceeds the supply of goods and services, it can lead to inflation as demand outpaces supply, pushing prices higher.
What is the effect of rising production costs on inflation?
-Rising production costs, such as higher prices for raw materials or wages, can increase the cost of goods and services, contributing to inflation.
Why does an increase in demand for goods and services cause inflation?
-When demand exceeds supply for goods or services, prices tend to rise as producers try to meet the higher demand, resulting in inflation.
What are the consequences of deflation on an economy?
-Deflation can lead to reduced business revenues, lower wages, job cuts, and a decrease in consumer spending, which can further slow down the economy.
How does the amount of money in circulation contribute to deflation?
-Deflation can occur when there is less money in circulation, as people may prefer to save money rather than spend it, leading to reduced demand and falling prices.
What is the impact of deflation on businesses and wages?
-Deflation can lead to reduced business revenues as prices drop, which may force businesses to cut wages and reduce their workforce to maintain profitability.
What are the key differences in the effects of inflation and deflation on the economy?
-Inflation erodes purchasing power and encourages spending and investment, while deflation reduces prices but can lead to lower business profits, reduced consumer spending, and economic stagnation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Why can’t prices just stay the same?

Winners and losers from inflation and deflation | AP Macroeconomics | Khan Academy

Fenomena Deflasi di Sulawesi Selatan Februari 2025
KEBIJAKAN MONETER

Fiscal and Monetary Policy|Meaning-Scope and Methodology|JKSSB Finance Accounts Assistant|Economics

Apa Jadinya Jika Inflasi Negatif? (Penjelasan Deflasi Ekonomi)
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
