Basic Cognitive Concepts (Schema, Assimilation, Accommodation, Equilibration)
Summary
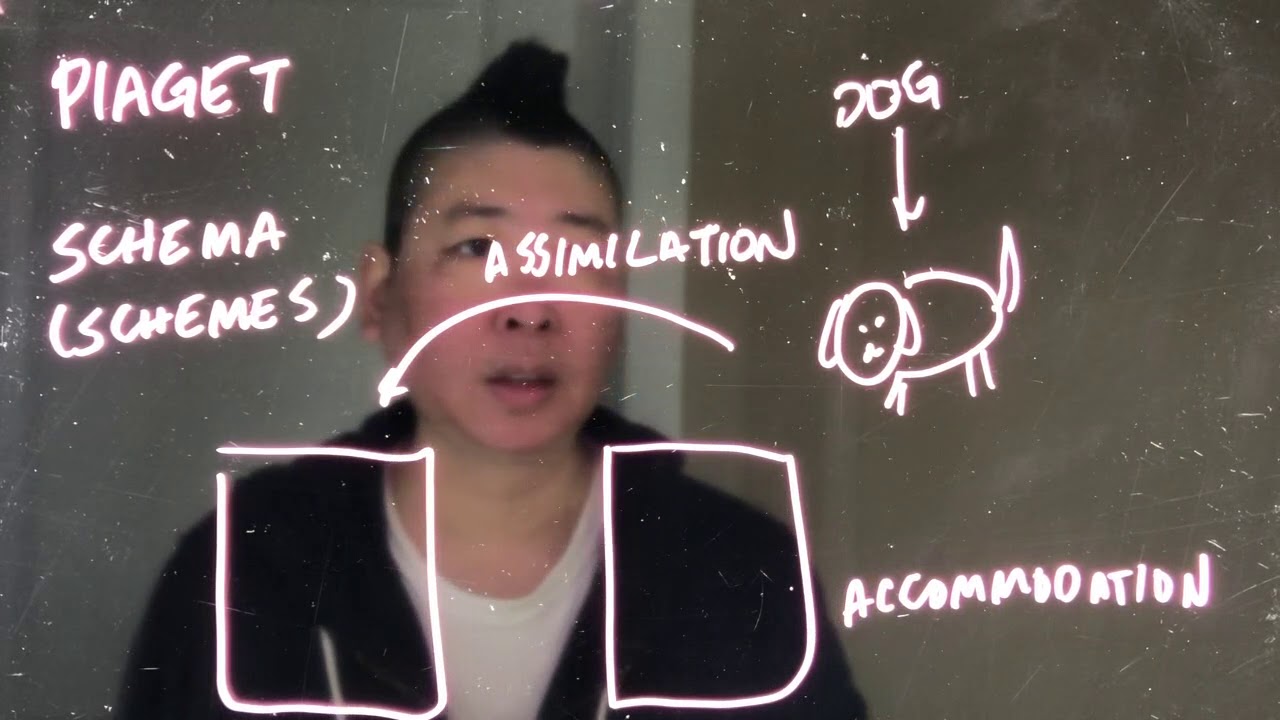
TLDRIn this video, Jay introduces Piaget's cognitive development theory, focusing on key concepts such as schemas, assimilation, accommodation, and equilibration. Piaget's research emphasized how individuals develop cognitive structures to understand and organize their world. The process of assimilation helps incorporate new experiences into existing schemas, while accommodation involves creating new schemas when experiences don't fit. Equilibration refers to the balance between these processes, restoring stability when cognitive disequilibrium occurs. Through these concepts, Piaget explored how children actively construct knowledge and adapt to their environment.
Takeaways
- 😀 Jampa J conducted research for 60 years on cognitive development, observing individuals responding to cognitive tasks.
- 😀 The script introduces key cognitive concepts: schema, assimilation, accommodation, and equilibration.
- 😀 'Schema' refers to the cognitive structures through which individuals understand and organize their experiences.
- 😀 A schema is like a mental filing cabinet, storing information based on personal experiences and understanding.
- 😀 When a child sees a dog for the first time, they create a schema about dogs, including attributes like four legs, a tail, and barking.
- 😀 Assimilation involves incorporating new experiences into existing schemas. For example, a child adds a smaller dog into their existing dog schema.
- 😀 Accommodation is the process of creating a new schema when existing schemas don't fit. A child may create a new schema for a goat after encountering one.
- 😀 Equilibration is the natural drive to understand the world and find order and predictability, balancing assimilation and accommodation.
- 😀 Cognitive disequilibrium occurs when experiences conflict with existing schemas, prompting a need for adjustment.
- 😀 Achieving equilibrium involves adjusting schemas through assimilation and accommodation to reconcile the discrepancy between perception and understanding.
Q & A
What is the main focus of Jean Piaget's research in cognitive development?
-Jean Piaget's research focused on understanding how children develop cognitive abilities and how they adapt their thinking as they encounter new experiences.
What are 'schemas' in Piaget's cognitive development theory?
-Schemas are mental structures or cognitive frameworks that help individuals understand and organize their experiences. They act as mental 'files' in which we store information about the world.
Can you explain the process of assimilation in Piaget's theory?
-Assimilation is the process of incorporating new experiences into an existing schema. For example, if a child sees a new dog, they would fit this new dog into their existing mental schema of what a dog is.
What is accommodation, and when does it occur?
-Accommodation happens when new information cannot be added to an existing schema, and instead, a new schema must be created. For example, when a child sees an animal that looks like a dog but is actually a goat, they must create a new schema for goats.
What role does equilibration play in cognitive development?
-Equilibration is the process by which individuals balance assimilation and accommodation to achieve cognitive stability. When a person encounters a new experience that challenges their existing schemas, they work to restore balance by adjusting their schemas.
How does Piaget describe the development of a child’s understanding of objects in their environment?
-Piaget suggests that as children encounter new objects or experiences, they adapt their understanding through the processes of assimilation and accommodation, continuously refining their mental schemas to better understand the world.
What happens when a child's experience does not match their existing schema?
-When a child's experience doesn't align with their existing schema, they experience cognitive disequilibrium, a state of imbalance. To resolve this, they engage in assimilation and accommodation to restore balance.
How does Piaget’s theory help explain a child's ability to learn about new objects?
-Piaget's theory explains that children actively construct their knowledge by adapting existing schemas or creating new ones as they encounter novel objects or experiences.
What is the example used in the transcript to explain the concept of schema?
-The transcript uses the example of a child encountering a dog for the first time. The child forms a schema that includes the dog's physical features, such as 'four legs, tail, barks,' and stores this information for future encounters with similar animals.
What does Piaget mean by 'cognitive disequilibrium'?
-Cognitive disequilibrium refers to the feeling of imbalance or confusion when a new experience doesn’t fit into an existing schema. This discomfort motivates individuals to reconcile the discrepancy through assimilation and accommodation.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)