BUMI DAN ANTARIKSA PART 2 | Bentuk Bumi | Lapisan Bumi
Summary
TLDRIn this educational video, the host, Ibu Nurul, explains the shape and layers of the Earth. She presents evidence supporting Earth’s round shape, such as the disappearance of ships at sea, lunar eclipses, and views from high altitudes. The video also covers the Earth's internal structure, including the crust, mantle, and core, as well as the atmosphere, hydrosphere, and biosphere. By breaking down complex scientific concepts in a simple and engaging way, the video helps viewers understand Earth's physical properties and their importance for life on the planet.
Takeaways
- 😀 Earth's shape is round but slightly flattened at the poles, making it an oblate spheroid.
- 😀 Evidence for Earth's round shape includes ships disappearing over the horizon as they move farther away.
- 😀 A lunar eclipse provides further proof of Earth's round shape, as Earth's shadow creates a circular outline on the moon.
- 😀 The view from higher altitudes supports the Earth's round shape, as the horizon becomes wider and more expansive.
- 😀 Earth is the third planet from the Sun in our solar system, located between Venus and Mars.
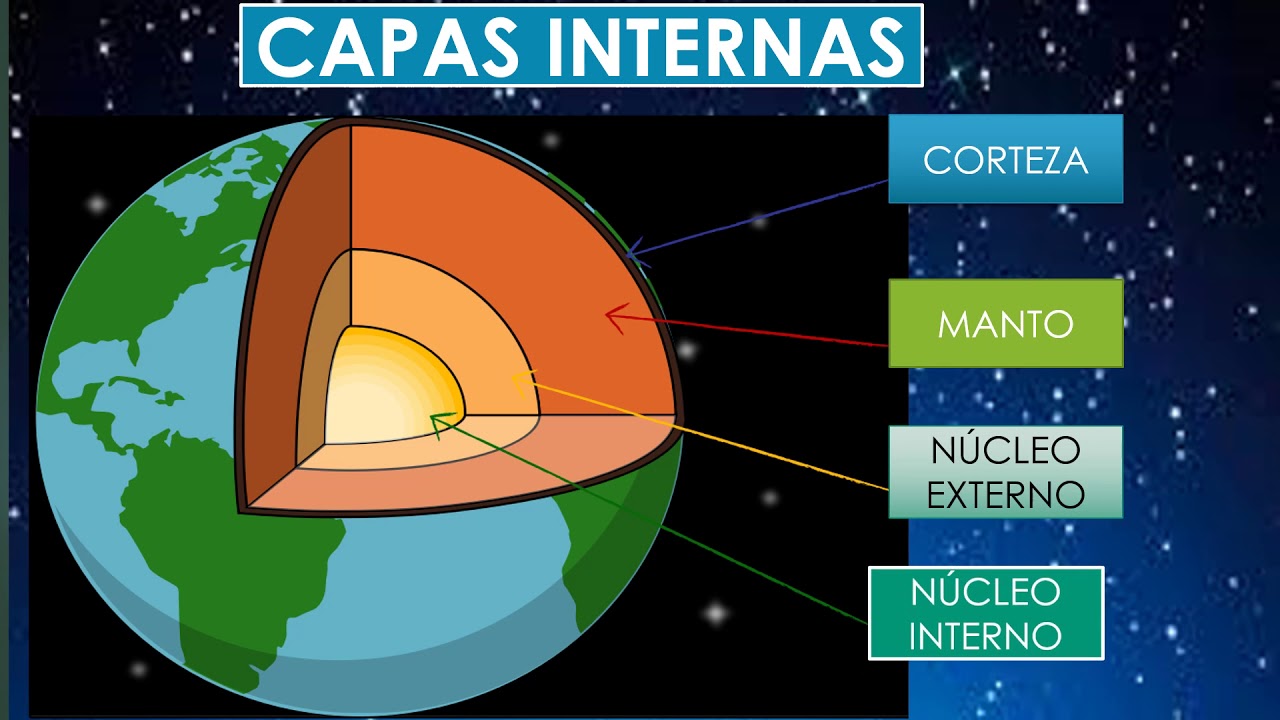
- 😀 The Earth's crust is divided into two types: continental crust (granitic) and oceanic crust (basaltic), with different thicknesses.
- 😀 The mantle lies beneath the crust and contains mineral-rich layers like the lithosphere, asthenosphere, and mesosphere.
- 😀 The Earth's core is divided into two parts: the outer core, which is liquid and made of iron and nickel, and the inner core, which is solid and also composed of iron and nickel.
- 😀 Earth's atmosphere is a layer of gases surrounding the planet, playing a crucial role in supporting life and regulating temperature.
- 😀 The hydrosphere refers to all water on Earth, including oceans, rivers, lakes, and ice, covering about 71% of the planet's surface.
Q & A
What was discussed in the previous lesson about Earth and space?
-In the previous lesson, the topics covered were gravity in the universe, types of gravity, and why objects fall toward the Earth due to gravity. The lesson also included Newton's laws of motion.
What is the main focus of today's lesson?
-Today's lesson focuses on the shape of the Earth and its layers, including the Earth's crust, mantle, and core.
What evidence supports the idea that the Earth is round?
-The evidence includes the observation that ships gradually disappear from view when sailing away from a harbor, the appearance of a red-orange moon during a lunar eclipse, and the changing view from different heights in a building.
How does the Earth's rotation affect its shape?
-The Earth's rotation causes it to slightly bulge at the equator and flatten at the poles, making its shape an oblate spheroid.
What are the differences between oceanic and continental crust?
-The oceanic crust is thinner, about 5-10 km thick, and made up of basalt, while the continental crust is thicker, ranging from 20-70 km, and composed mainly of granite.
What is the lithosphere, and what does it consist of?
-The lithosphere is the outer layer of the Earth, made up of the Earth's crust and part of the mantle. It forms tectonic plates that move and cause geological phenomena like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
What are the three layers of the Earth's mantle?
-The Earth's mantle consists of three layers: the lithosphere, which is rigid; the asthenosphere, which is semi-fluid; and the mesosphere, which is more rigid and extends deeper into the Earth.
What is the difference between the inner and outer core of the Earth?
-The outer core is liquid and composed mainly of iron and nickel, with temperatures around 2200°C, while the inner core is solid, made of iron and nickel, and has a temperature of about 4500°C.
What are the four main layers of the Earth based on composition?
-The four main layers based on composition are the atmosphere (air), hydrosphere (water), lithosphere (rock), and biosphere (life).
What is the biosphere, and how is it related to Earth's ecosystems?
-The biosphere is the largest system of life on Earth, consisting of all ecosystems. It includes all living organisms and their interactions with the environment, forming a cohesive system of life on the planet.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Struktur Bumi dan Perkembangannya

BAB 5 - Lapisan Bumi | IPA SMP/MTs Kelas 7 Semester 2

IPA kelas 7 : Struktur/Lapisan Bumi (Atmosfer)

CHAPTER 6: EARTH'S STRUCTURE AND ITS DEVELOPMENT | Part 1: Earth's Structure and Plate Tectonics ...

Video Pembelajaran Matahari Terbit dan Terbenam
VIDEO DE LAS CAPAS EXTERNAS E INTERNAS DE LA TIERRA. AUTORA VICTORIA GUAMÁN.
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
