Struktur Bumi dan Perkembangannya
Summary
TLDRThis educational video covers the structure of the Earth, including its four distinct layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. It explains how geological forces shape Earth's landscapes, from mountains to oceans, with a focus on tectonic plate movements. The video introduces key concepts like lithosphere, plate tectonics, and the three types of plate movements: divergent, convergent, and transform. It also explores the causes and effects of geological events like earthquakes and volcanic eruptions, using real-world examples, such as the Himalayas and the Semangko Fault, to illustrate these processes.
Takeaways
- 😀 The lesson focuses on understanding the structure of the Earth and its layers to explain natural phenomena for disaster mitigation.
- 😀 Students will learn to identify the four layers of the Earth, differentiate them, and describe their characteristics.
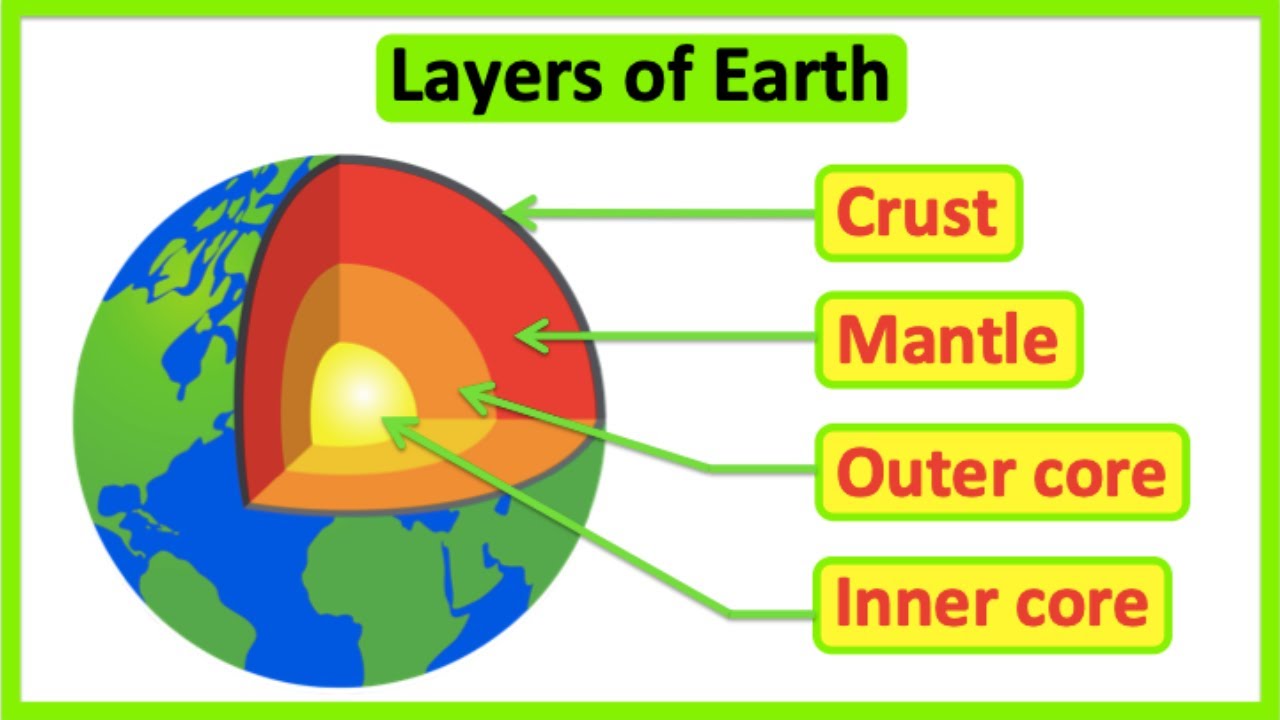
- 😀 The four layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core, each with distinct characteristics and compositions.
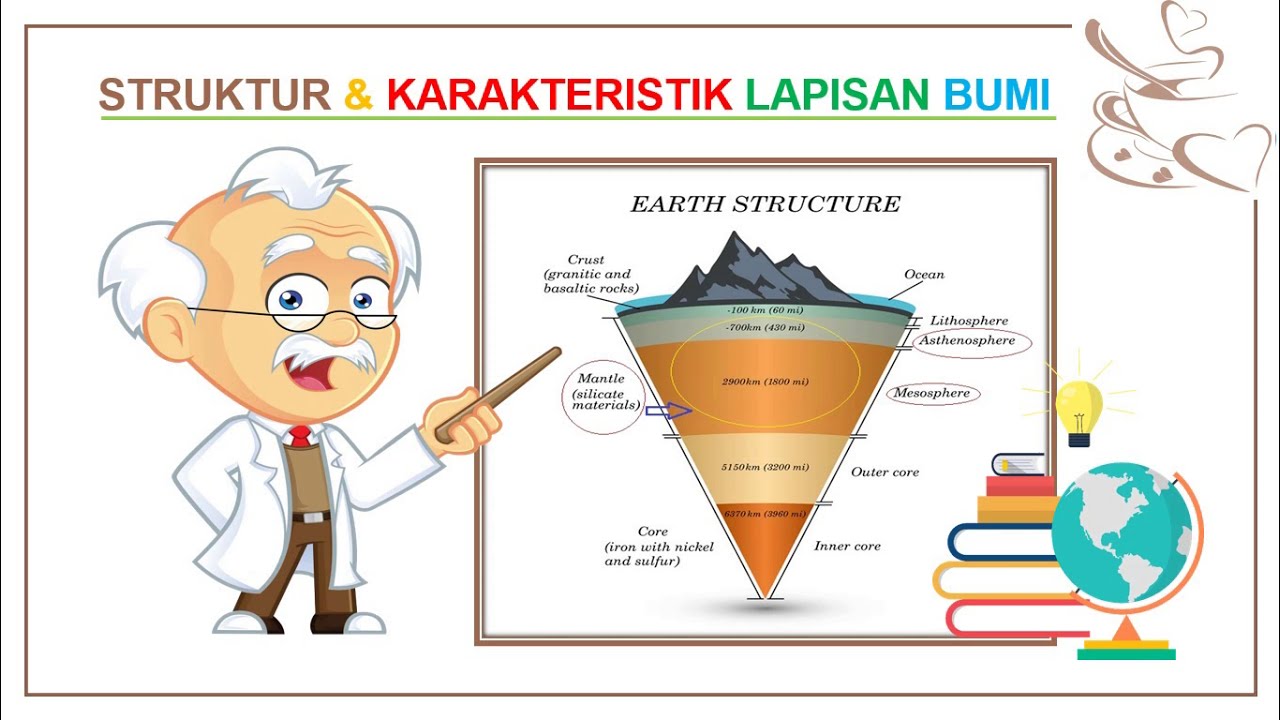
- 😀 The Earth's crust is the thinnest layer, consisting of rocks and minerals, and includes both continental and oceanic crust.
- 😀 The mantle is the thickest layer of the Earth, composed of both a rigid outer part and a semi-fluid inner part that facilitates tectonic movements.
- 😀 The lithosphere is a combination of the crust and the rigid outer part of the mantle, forming the Earth's tectonic plates.
- 😀 The outer core is a liquid layer composed of molten metals, mainly iron and nickel, while the inner core is solid with a higher temperature and pressure.
- 😀 Tectonic plates float on the semi-fluid mantle, and their movements can lead to earthquakes, volcanic activity, and mountain formations.
- 😀 The theory of plate tectonics explains the Earth's surface dynamics, including continental drift and the formation of Pangea in the past.
- 😀 There are three types of tectonic plate movements: divergent (plates move apart), convergent (plates collide), and transform (plates slide past each other), which can result in earthquakes and volcanic eruptions.
Q & A
What is the main objective of learning about the Earth's structure in this lesson?
-The main objective is for students to understand the structure of the Earth's layers and explain natural phenomena in order to assist in disaster mitigation.
How many subtopics are there in this lesson, and what are they?
-There are four subtopics in this lesson: Earth, tectonic plates, earthquakes, and volcanoes.
What are the learning goals for students in this lesson on the Earth's structure?
-The learning goals are for students to identify the four layers of the Earth, distinguish between the different layers, and describe the characteristics of each layer.
What are some examples of landforms in Indonesia mentioned in the lesson?
-Examples of landforms in Indonesia mentioned include the Jayawijaya Mountains, Lake Kelimutu in East Nusa Tenggara, Parang Tritis Beach, and Grojokan Sewo Waterfall.
What are the two types of geological forces discussed in the lesson?
-The two types of geological forces are exogenous forces, which come from outside the Earth (e.g., weathering, erosion, and deposition), and endogenous forces, which originate from within the Earth (e.g., plate movements).
What are the four main layers of the Earth described in the lesson?
-The four main layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
What is the difference between the continental crust and oceanic crust?
-The continental crust is thicker, ranging from 30 to 70 km, and is found on land. The oceanic crust is thinner, ranging from 6 to 11 km, and is located under the oceans.
What is the composition and temperature of the Earth's outer core?
-The Earth's outer core is composed of molten iron and nickel and has a temperature ranging from 3,800°C to 6,000°C. It is the only liquid layer of the Earth.
What does the term 'lithosphere' refer to, and how is it formed?
-The lithosphere refers to the outermost layer of the Earth, which is a combination of the crust and the upper mantle. It is formed through the interaction of the crust and the outer mantle.
What are the three types of tectonic plate movements described in the lesson?
-The three types of tectonic plate movements are divergent (plates moving apart), convergent (plates moving toward each other), and transform (plates sliding past one another).
Outlines

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowMindmap

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowKeywords

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowHighlights

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowTranscripts

This section is available to paid users only. Please upgrade to access this part.
Upgrade NowBrowse More Related Video
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)