Eukaryotic Transcription
Summary
TLDRThis video provides an in-depth exploration of eukaryotic transcription, focusing on the role of RNA polymerase and transcription factors in initiating and elongating mRNA synthesis. It covers the processes involved in transcription initiation, elongation, 5' capping, and termination, highlighting the function of key transcription factors (TF2A, TF2B, TF2D, TF2E, TF2F, TF2H) and enzymes like RNA polymerase II. The video also includes helpful mnemonics for memorizing transcription factors and explains their functions in a simplified and engaging way.
Takeaways
- 😀 Eukaryotic transcription involves RNA polymerase 2, along with transcription factors for proper initiation.
- 😀 Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases, while prokaryotes only have one.
- 😀 Transcription factors are crucial for RNA polymerase 2 binding and initiating transcription, with mnemonics used for easy memorization.
- 😀 TF2D, which contains TBP (TATA-binding protein), binds the TATA box and bends the DNA to facilitate other transcription factors' binding.
- 😀 TF2A stabilizes TF2D's binding to the promoter region during transcription initiation.
- 😀 TF2B helps recruit RNA polymerase 2 to the promoter, crucial for the transcription initiation process.
- 😀 TF2H, a complex with nine subunits, uses ATPase activity to melt the promoter and phosphorylates RNA polymerase 2 for transcription elongation.
- 😀 The dog eats the Apple and plays with the football, helping recall the order and function of transcription factors in eukaryotic transcription.
- 😀 During transcription elongation, elongation factors like TF2S and TF2B are involved in increasing transcription rate and preventing RNA polymerase pausing.
- 😀 mRNA processing includes the formation of a 5' cap, which is critical for translation initiation and mRNA stability.
Q & A
What is the role of RNA polymerase in transcription?
-RNA polymerase is the enzyme responsible for synthesizing RNA during transcription. In eukaryotes, there are three types of RNA polymerases, with RNA polymerase II being primarily responsible for mRNA transcription.
How many RNA polymerase enzymes do eukaryotes have?
-Eukaryotes have three RNA polymerases: RNA polymerase I, II, and III, each involved in different types of RNA synthesis.
What are transcription factors and why are they important?
-Transcription factors are proteins that assist RNA polymerase in initiating transcription. They are critical for binding RNA polymerase to the promoter region and ensuring accurate transcription initiation.
What does the abbreviation 'TF' stand for in transcription factor designations?
-'TF' stands for 'Transcription Factor.' It is followed by a number indicating which RNA polymerase it assists (e.g., TF2 for RNA polymerase II).
How is the 'Tata Box' involved in transcription initiation?
-The Tata Box is a conserved sequence in the promoter region where transcription factors, particularly TF2D, bind to initiate transcription. It helps recruit RNA polymerase II to start mRNA synthesis.
What is the function of TF2D in the transcription process?
-TF2D binds to the Tata Box in the promoter region and bends the DNA to help other transcription factors bind, ultimately assisting in the recruitment of RNA polymerase II.
What role does TF2H play in transcription initiation?
-TF2H is a large complex that acts as a helicase to unwind the DNA and also has kinase activity to phosphorylate the C-terminal domain of RNA polymerase II, promoting transcription elongation.
What is the function of the 5' cap in mRNA processing?
-The 5' cap is added to the nascent mRNA transcript and is important for mRNA stability, nuclear export, and efficient translation initiation.
What happens during the termination of transcription in eukaryotes?
-During termination, the RNA polymerase reaches the end of the gene, where proteins like CSTF and CPSF help in cleaving the mRNA and adding a poly-A tail to the 3' end of the transcript.
How does TF2S help in transcription elongation?
-TF2S helps increase the transcription rate in regions where RNA polymerase slows down, preventing it from pausing and ensuring continuous elongation of the RNA transcript.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

TRANSCRIPTION CHEZ LES EUCARYOTES | ACIDES NUCLEIQUES Partie 3 | Biochimie Facile

Tahapan Transkripsi RNA pada Eukariotik
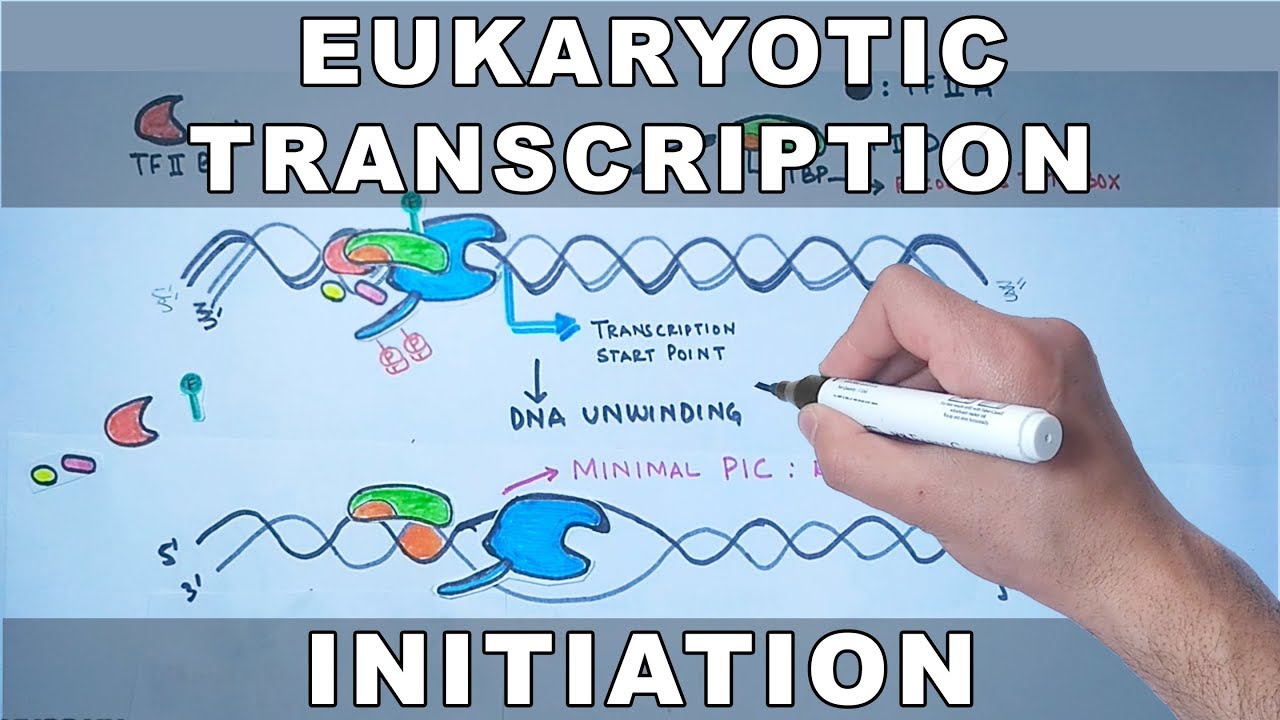
Transcription Initiation in Eukaryotes

[Module 2] Lesson 2: Central Dogma (Part 1)

Transcription and mRNA processing | Biomolecules | MCAT | Khan Academy
Sintesis Protein | Transkripsi
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
