Risk | How to Use Risk Matrix Step by Step Risk rating Calculation | Risk Assessment
Summary
TLDRThis video explains how to assess and prioritize risks in a workplace setting using a Risk Matrix. The scenario involves a worker falling from an unstable ladder while hanging a banner at a cinema. The video demonstrates the use of a risk matrix to evaluate the likelihood and severity of injuries for two methods: using a dangerous ladder versus a safer mobile scaffolding. The ladder use is deemed unacceptable due to a high risk score, while the scaffolding presents an acceptable risk. The video emphasizes the importance of using proper equipment and safety practices to prevent workplace accidents.
Takeaways
- 😀 The worker suffered injuries after falling from an unstable step ladder while hanging a banner in a cinema.
- 😀 The lack of proper training and supervision contributed to the accident, as none of the workers were trained in first aid.
- 😀 The step ladder was identified as unstable and had a history of causing accidents, yet the team leader forced the worker to use it despite their fear of heights.
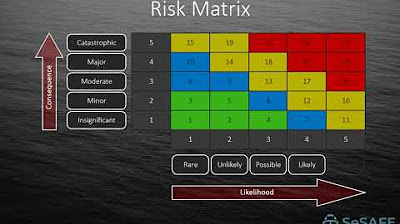
- 😀 A risk matrix is used to assess and prioritize hazards by evaluating their likelihood and severity to calculate risk levels.
- 😀 The risk of using the step ladder for the banner hanging activity was deemed 'unacceptable' due to high likelihood and severity of injury, with a risk level of 9.
- 😀 The risk matrix categorizes risk levels into three zones: acceptable (1-2), tolerable (3-4), and unacceptable (6-9).
- 😀 When calculating the risk level for using the unstable step ladder, the likelihood and severity were both rated at 3, resulting in a high-risk level.
- 😀 To ensure a safer alternative, mobile scaffolding was suggested, reducing the risk to an acceptable level with a risk score of 1.
- 😀 The likelihood of injury when using mobile scaffolding was rated as 'very unlikely,' and the severity of injury was considered 'minor.'
- 😀 The risk matrix helps visually represent risk levels, guiding decisions to choose safer methods for tasks like banner hanging.
- 😀 The overall conclusion is that mobile scaffolding presents an acceptable risk level, while the step ladder posed an unacceptable risk for the banner hanging activity.
Q & A
What was the cause of the worker's injury in the scenario described?
-The worker was found unconscious after falling from an old and unstable step ladder while hanging a banner. The injuries included a broken leg, concussions, and minor injuries.
Why was the worker forced to use the step ladder despite their fear of heights?
-The team leader at the time insisted the young worker use the unstable step ladder despite their fear of heights, which led to the worker's accident.
What was the risk level calculated for using the step ladder in the banner-hanging activity?
-The risk level was calculated to be 9, which falls in the 'unacceptable' category based on the likelihood of injury (very likely) and the severity of injury (major).
How does the risk matrix help in evaluating the danger of a particular activity?
-The risk matrix uses two factors—likelihood of an injury occurring and the severity of the potential injury. By multiplying these factors, it provides a risk score that helps categorize the overall risk level, guiding decisions on whether the activity is safe.
What was the risk level for using mobile scaffolding instead of the step ladder?
-Using mobile scaffolding resulted in a risk level of 1, which falls in the 'acceptable' category due to the low likelihood of injury (very unlikely) and minor severity of potential injury.
What are the key factors to assess when evaluating the likelihood of injury for an activity?
-Key factors include the stability of the equipment being used (like the ladder or scaffolding), the height involved, and the experience or training level of the worker.
How are the severity and likelihood ratings determined in the risk matrix?
-Severity is determined based on the potential outcomes of an injury, such as whether it would result in a minor or major injury, hospitalization, or death. Likelihood is based on factors like the stability of the equipment and the experience of the worker.
Why is the use of the step ladder for hanging banners considered unsafe?
-The step ladder was old, unstable, and had a history of causing accidents. Additionally, the worker had no appropriate training and was forced to use it despite being fearful of heights.
What alternative method was proposed to reduce the risk during the banner-hanging activity?
-Mobile scaffolding was proposed as a safer alternative to the step ladder. It is more stable, and its use resulted in an acceptable risk level.
How does the 'unacceptable' risk category in the risk matrix impact decision-making?
-An 'unacceptable' risk level indicates that the activity is too dangerous and should not be performed. It forces a re-evaluation and suggests the need for safer alternatives to mitigate the risk.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

3. Video Pembelajaran - Penyusunan Risk Register

ANÁLISIS DE RIESGOS - Cómo hacer un análisis de riesgos🧩 como lo pide ISO 9001:2015👍🏻👍🏻

Assessing Risks in the Chemistry Laboratory | ACS College Safety Video #3
Risk Matrix

5 Steps To Risk Assessment

Hazard Identification & Risk Assessment (HIRA) | HIRA In Details || HSE STUDY GUIDE
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
