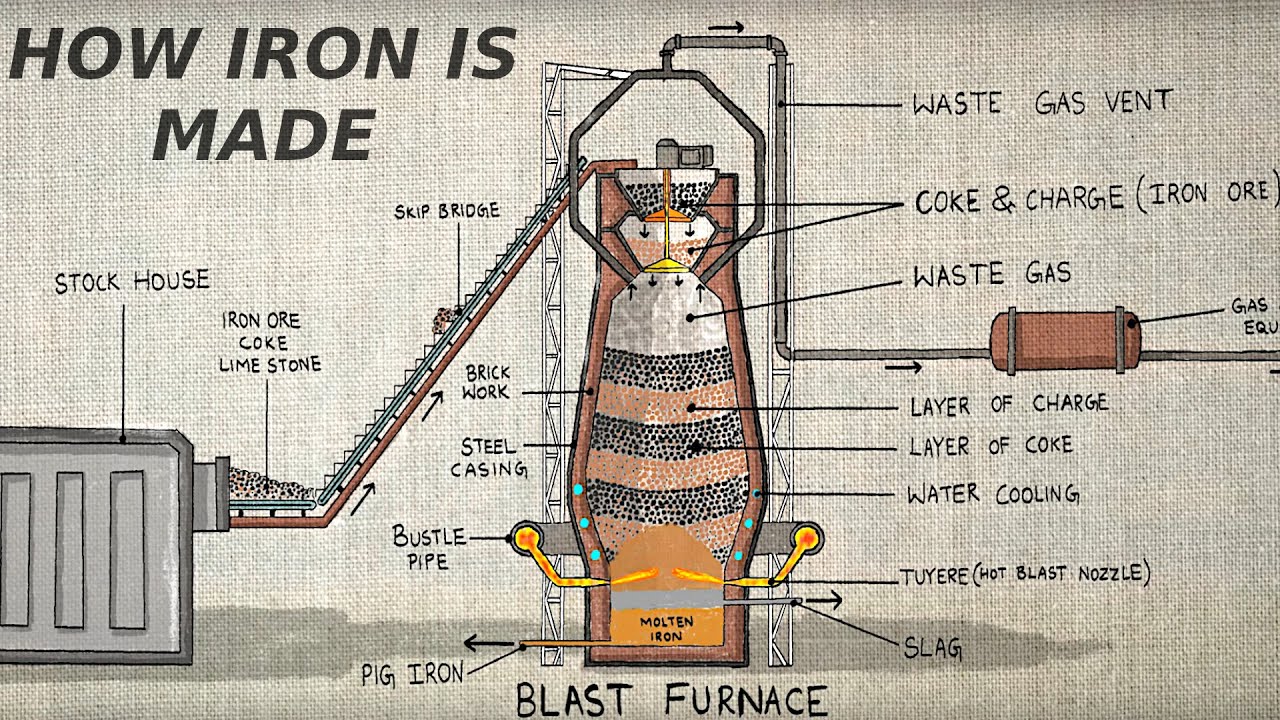
Managing blast furnace slag - its chemical and physical features - Metallurgical waste management
Summary
TLDRThis video explores the concept of blast furnace slag, a waste byproduct of iron extraction, which is sold for profit despite its classification as waste. It delves into the chemical composition of the slag, including silica, calcium oxide, and aluminum oxide, and discusses its environmental implications, particularly the potential for heavy metal leaching. The video also highlights how blast furnace slag can be utilized in various applications, such as construction, cement production, and agriculture, while emphasizing the need for effective management strategies due to the increasing volume of steel production worldwide.
Takeaways
- 😀 BFS (Blast Furnace Slag) is a waste product generated during iron extraction in a blast furnace, but is sold profitably despite being considered waste.
- 😀 Although BFS is sold for profit, it must still be carefully managed due to potential environmental risks, particularly heavy metal leaching.
- 😀 The production of iron and steel is projected to rise globally, leading to an increase in the volume of BFS, necessitating better waste management strategies.
- 😀 The chemical composition of BFS primarily includes silica, calcium oxide, and aluminum oxide, which are non-hazardous in certain forms, but can pose environmental risks if leached.
- 😀 BFS is sometimes categorized as non-hazardous, but the potential for leaching heavy metals in some forms means it cannot always be treated as safe.
- 😀 The heavy metal ions that may leach from BFS can contaminate water bodies and harm the surrounding ecosystem, making proper management essential.
- 😀 There are established test methods to measure the potential for BFS to leach harmful substances, ensuring safer disposal and utilization.
- 😀 Blast Furnace Slag is typically acid-neutralizing in nature, meaning it can help balance acidic conditions when used in certain environments.
- 😀 BFS has different mechanical properties depending on how it is cooled, which influences its potential applications in various industries.
- 😀 Several international associations exist to improve BFS management and develop sustainable practices, with the possibility of new organizations emerging in other regions.
- 😀 Despite BFS having industrial uses, such as in construction, its environmental impact and the need for sustainable management practices remain significant concerns.
Q & A
What is blast furnace slag (BFS) and how is it generated?
-Blast furnace slag (BFS) is a byproduct of the process used to extract iron from its ore in a blast furnace. It is produced when impurities like silica, calcium oxide, and aluminum oxide are separated from the iron during the smelting process.
Why is blast furnace slag sold for profit despite being a waste product?
-Blast furnace slag is sold for profit because it has potential industrial uses, including in construction and cement production. Its properties, such as being an acid-neutralizing agent, make it valuable despite being a byproduct of iron and steel production.
What is the primary chemical composition of blast furnace slag?
-The primary chemical components of blast furnace slag include silica (SiO2), calcium oxide (CaO), and aluminum oxide (Al2O3). These components can vary depending on the iron ore used, but these three elements are typically the main constituents.
How does the increasing demand for iron and steel affect the amount of BFS produced?
-As the global demand for iron and steel rises, the amount of BFS produced also increases. Since iron and steel consumption are projected to continue growing, the quantity of BFS generated in the future will likely exceed current levels.
What are the potential environmental risks of blast furnace slag?
-The environmental risk associated with BFS lies in the possibility of leaching heavy metal ions into water bodies. If BFS is not managed properly, these harmful metals could contaminate the surrounding environment and harm ecosystems.
What is the difference between non-hazardous and hazardous blast furnace slag?
-Non-hazardous BFS is considered safe for the environment, typically due to the chemical composition of the slag. However, some BFS can be hazardous, especially if it contains high levels of heavy metals, which can leach into the environment and cause pollution.
How does blast furnace slag help neutralize acidic environments?
-Blast furnace slag is an acid-neutralizing agent due to its high calcium content. It can counteract acidity in the environment, effectively raising the pH when used in certain applications, such as in soil or water treatment.
Why is it important to understand the chemical composition of BFS when managing it?
-Understanding the chemical composition of BFS is crucial for determining how to manage it safely and effectively. It helps assess the slag’s potential for leaching harmful substances, its neutralizing properties, and its suitability for different industrial uses.
What are some of the potential industrial applications of BFS?
-Blast furnace slag can be used in various industries, including as a cement additive, in road construction, and as a component in soil conditioning. Its acid-neutralizing properties and granulated form make it a valuable resource in these areas.
What future steps are planned for the management of blast furnace slag?
-Future sessions will explore more efficient management techniques for BFS, focusing on its profitable use based on its chemical composition and mechanical properties. This will include finding innovative applications and ensuring its environmental safety.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)