Mitosis | Cells | MCAT | Khan Academy
Summary
TLDRThis video explains the process of mitosis, starting with the cell's preparation during interphase and leading to the division into two daughter cells. It covers key phases such as prophase, where chromosomes condense, metaphase, where chromosomes align, anaphase, where sister chromatids are pulled apart, and telophase, where the cell begins to split. The video also touches on the role of centrosomes, microtubules, and centrioles in organizing cell division. Finally, cytokinesis occurs, completing the process of cell division, resulting in two cells, each with a full set of genetic material, ready to begin the cycle again.
Takeaways
- 😀 Mitosis is the process by which a single nucleus divides into two nuclei, each with identical genetic information.
- 😀 Interphase is the phase before mitosis, where the cell grows and DNA replicates.
- 😀 The cell’s centrosomes play a key role in organizing microtubules, which help pull chromosomes apart during mitosis.
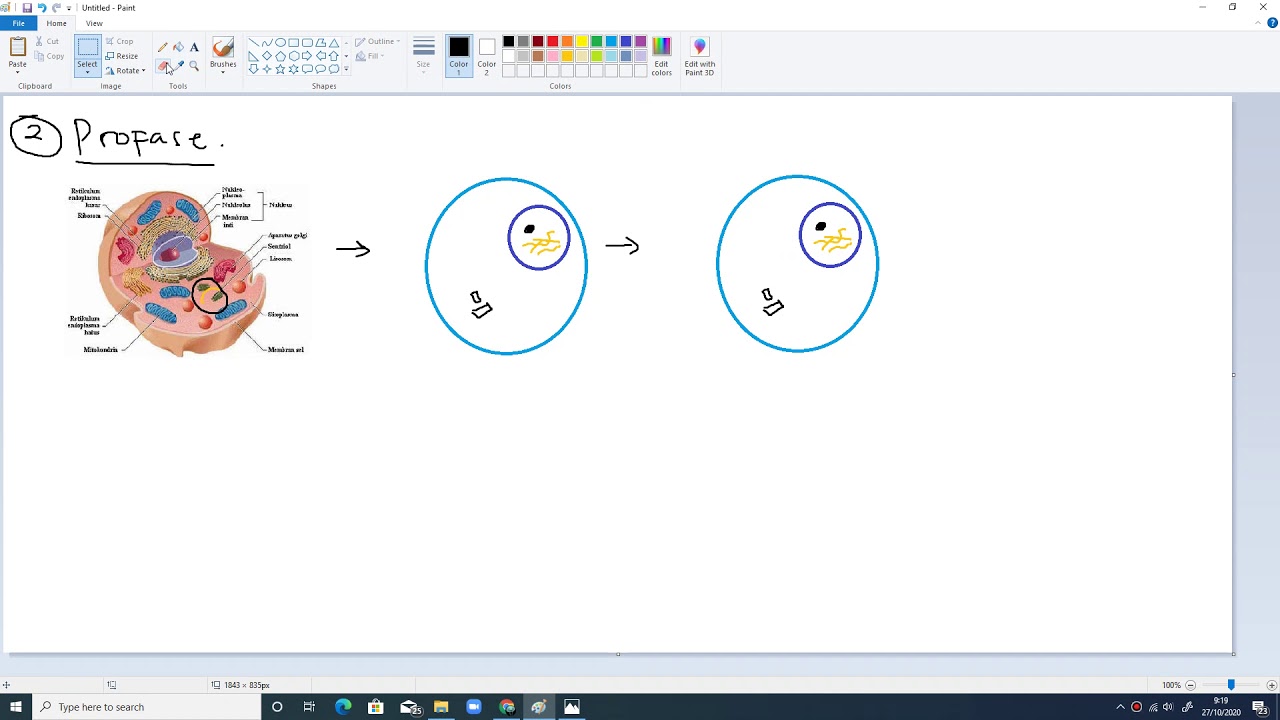
- 😀 Prophase marks the beginning of mitosis, where chromosomes condense and the nuclear membrane starts to disappear.
- 😀 During metaphase, chromosomes align at the center of the cell, and microtubules attach to the centromeres.
- 😀 In anaphase, sister chromatids are pulled to opposite sides of the cell, and they are now considered individual chromosomes.
- 😀 Telophase involves the reformation of nuclear envelopes around the two sets of chromosomes and the unwinding of the chromosomes back into chromatin.
- 😀 Cytokinesis is the final step of cell division, where the cytoplasm is divided and the cell splits into two separate daughter cells.
- 😀 The process of mitosis is orchestrated by a complex network of microtubules, which are coordinated by centrosomes and centrioles.
- 😀 Although the general stages of mitosis are well understood, some aspects of the process, like the exact mechanisms of chromosome movement, are still under research.
- 😀 Despite having no intelligence, the cell division process is highly precise, driven by chemical and thermodynamic reactions triggered by the cell's lifecycle stage.
Q & A
What is the purpose of mitosis?
-The purpose of mitosis is to divide a single nucleus into two identical nuclei, each containing the original genetic information, ensuring that both daughter cells have the same DNA.
What happens during interphase before mitosis begins?
-During interphase, the cell grows, replicates its DNA, and prepares for cell division. This phase includes three sub-phases: G1 (cell growth), S-phase (DNA replication), and G2 (final preparations for mitosis).
What role do centrosomes play in mitosis?
-Centrosomes organize microtubules, which help in aligning and separating the chromosomes during mitosis. They also move to opposite sides of the cell to facilitate the proper distribution of chromosomes.
What is the difference between chromatin and chromosomes?
-Chromatin is the uncondensed form of DNA, found in the nucleus during interphase. Chromosomes are the condensed, visible form of DNA that appears during mitosis and are made up of two sister chromatids connected at the centromere.
What happens during prophase?
-During prophase, the chromosomes condense and become visible, the nuclear membrane begins to break down, and the centrosomes start migrating to opposite sides of the cell.
What is metaphase, and what occurs during this phase?
-Metaphase is the stage where the chromosomes line up along the center of the cell. The centrosomes are at opposite ends, and the microtubules connect to the centromeres of the chromosomes to help position them properly.
What is the significance of centromeres in mitosis?
-Centromeres are the regions where two sister chromatids are connected. During mitosis, microtubules attach to the centromeres to help pull the sister chromatids apart during anaphase.
What occurs during anaphase?
-During anaphase, the sister chromatids are separated and pulled to opposite sides of the cell by the microtubules, turning them into independent chromosomes.
How is telophase different from prophase?
-In telophase, the chromosomes begin to unwind back into chromatin, and nuclear membranes start forming around the two sets of chromosomes. This is the reverse of prophase, where the nuclear membrane breaks down and chromosomes condense.
What is cytokinesis, and how does it relate to mitosis?
-Cytokinesis is the process by which the cytoplasm of the cell is divided into two, resulting in two separate daughter cells. It typically occurs alongside telophase and is considered the final step of cell division, following mitosis.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)