Math Antics - Perimeter
Summary
TLDRIn this video, Math Antics introduces the concept of perimeter, explaining it as the distance or length around a shape. The lesson covers how to calculate the perimeter of polygons by adding the lengths of their sides, with practical examples such as triangles, rectangles, and regular polygons. Viewers learn the importance of units when measuring perimeter and how to handle shapes with missing side lengths using logical deduction. The video reinforces that perimeter applies to 2D shapes but is always measured in 1D units. Overall, it offers clear, accessible steps for calculating perimeter, encouraging practice to master the concept.
Takeaways
- 😀 Perimeter is the total distance (or length) around a geometric shape.
- 😀 Perimeter is a 1-dimensional quantity, measured in units of length such as centimeters, inches, or miles.
- 😀 The perimeter of a shape is the shortest possible distance around its edges, not the longest or any other path.
- 😀 To calculate perimeter, add up the lengths of all sides of a polygon.
- 😀 When measuring perimeter, always remember to include the units (e.g., cm, meters, inches).
- 😀 The perimeter of a polygon with equal sides (a regular polygon) can be calculated by multiplying the side length by the number of sides.
- 😀 For irregular polygons where some sides are missing, use known side lengths to deduce the unknowns and then calculate the perimeter.
- 😀 Example 1: A triangle's perimeter is calculated by adding the lengths of its three sides (e.g., 3 cm + 4 cm + 5 cm = 12 cm).
- 😀 Example 2: A rectangle's perimeter is found by adding the lengths of all four sides (e.g., 5 m + 5 m + 10 m + 10 m = 30 m).
- 😀 A regular polygon's perimeter can be easily calculated by multiplying the side length by the number of sides (e.g., 6 sides x 4 cm = 24 cm).
- 😀 Practice is key to getting good at math, especially with concepts like perimeter, which require you to add or multiply side lengths.
Q & A
What is the definition of perimeter?
-Perimeter is the total distance around the edge of a shape. It is a 1-dimensional measurement expressed in units of length such as centimeters, inches, or miles.
Why is it important to include units when calculating perimeter?
-Units are essential because they specify the measurement scale of the perimeter, making the result meaningful and clear. For example, a perimeter of 12 could refer to 12 cm, 12 inches, or 12 meters, depending on the units used.
How is the perimeter of a polygon with straight sides calculated?
-The perimeter of a polygon with straight sides is calculated by adding the lengths of all its sides together.
How do you calculate the perimeter of a regular polygon?
-For a regular polygon, where all sides are of equal length, the perimeter can be calculated by multiplying the length of one side by the number of sides.
What is an example of finding the perimeter of a triangle?
-For a triangle with side lengths of 3 cm, 4 cm, and 5 cm, the perimeter is calculated by adding the sides: 3 + 4 + 5 = 12 cm.
How do you calculate the perimeter of a rectangle?
-To find the perimeter of a rectangle, add the lengths of all four sides. For example, if two sides are 5 meters and two sides are 10 meters, the perimeter is 5 + 5 + 10 + 10 = 30 meters.
What is a regular polygon?
-A regular polygon is a shape with all sides of equal length and all angles equal. An example would be a square or an equilateral triangle.
How do you calculate the perimeter of an irregular polygon when some side lengths are missing?
-For an irregular polygon with missing side lengths, use the lengths you do know to deduce the missing ones. After determining all the side lengths, add them together to find the perimeter.
Why does the perimeter of a regular polygon use multiplication?
-Multiplication is used for regular polygons because all sides are of equal length, so instead of adding each side individually, you can multiply the number of sides by the length of one side.
What should you do if you encounter a problem with missing side lengths when calculating perimeter?
-If side lengths are missing, use the known sides to figure out the unknown lengths. For example, combine known vertical or horizontal lengths to deduce the missing sides and then add them to calculate the perimeter.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes

Perimeter and area: the basics | Perimeter, area, and volume | Geometry | Khan Academy
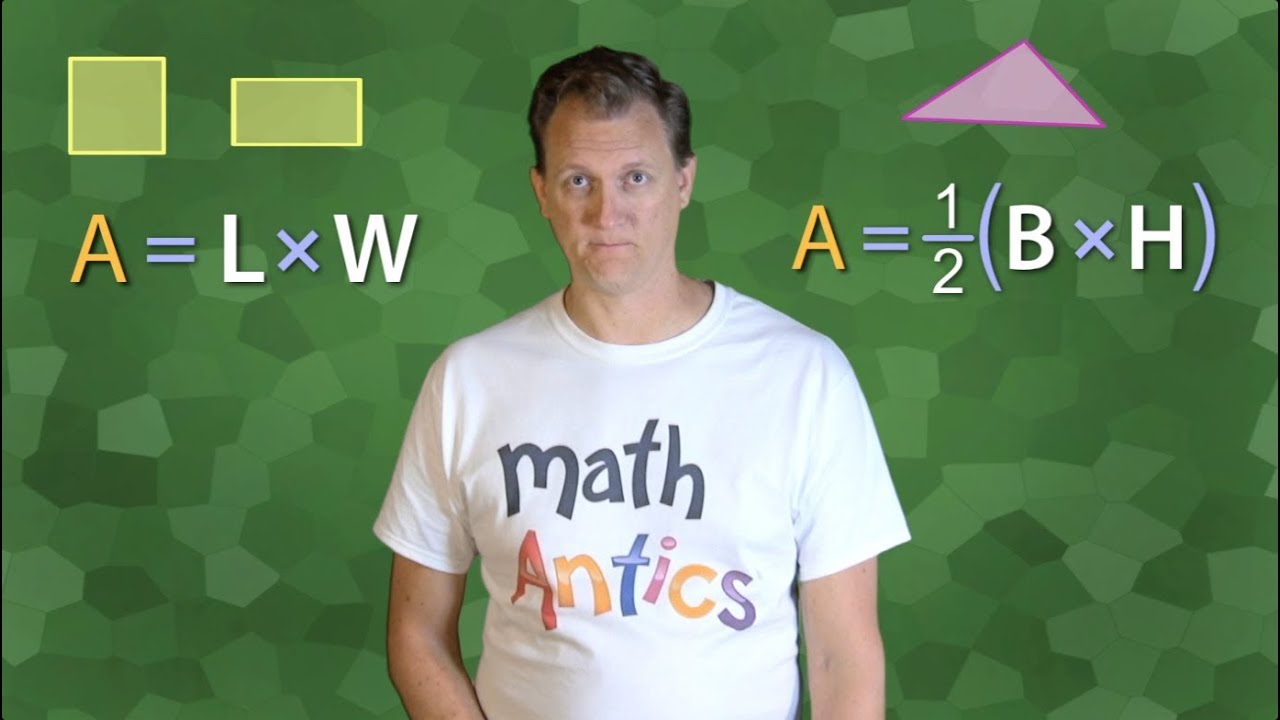
Math Antics - Area
Area and Perimeter Grade 9: Square, rhombus, parallelogram, rectangle
Area & Perimeter in the Coordinate Plane | Geometry | Eat Pi

Math Antics - Intro to the Metric System

Math Antics - Basic Probability
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
