Penjelasan Lengkap Struktur Lapisan Bumi dan Karakteristiknya
Summary
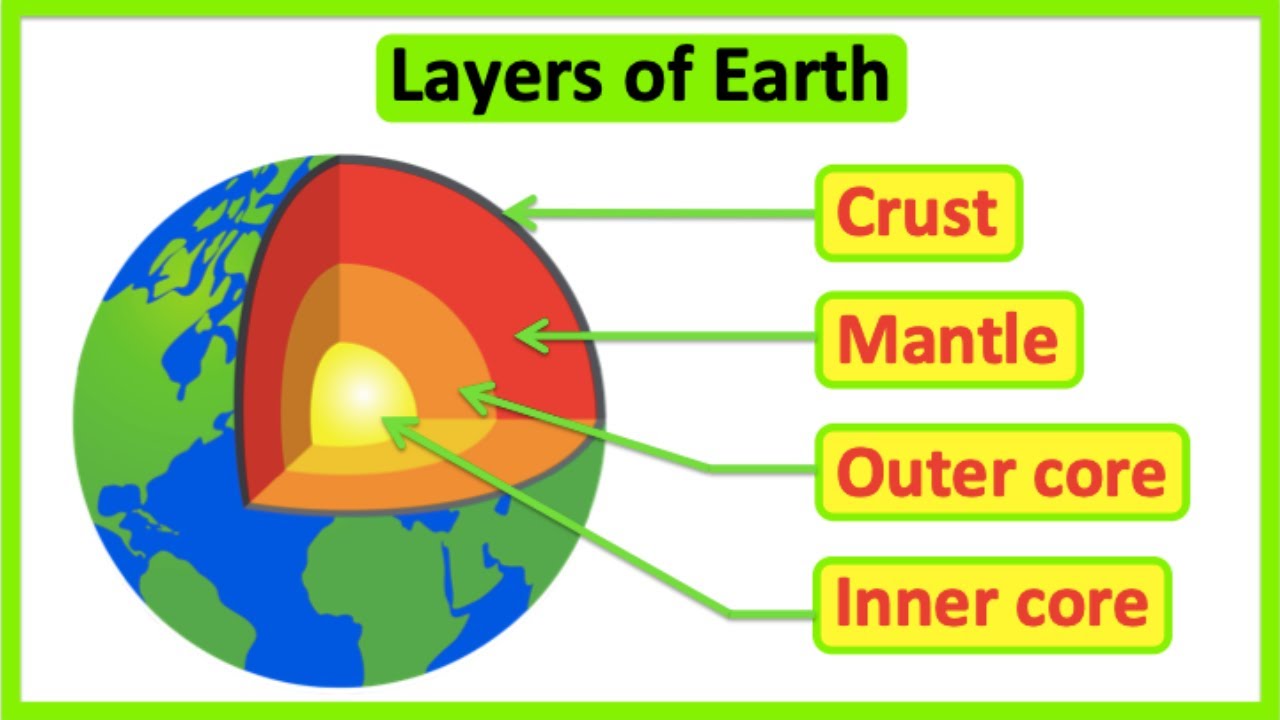
TLDRThis video explains the Earth's structure, breaking it down into four main layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core. The crust is where life exists and is divided into continental and oceanic crusts. Beneath it lies the mantle, the thickest layer, responsible for protecting the core. The core is composed of the outer liquid core and the extremely hot inner core. The video also discusses geological processes like tectonism, volcanism, and seismic activity that shape the Earth's surface. It concludes with an invitation to subscribe and stay tuned for more educational content from the channel.
Takeaways
- 😀 Earth is the only planet in our solar system suitable for living beings due to its atmosphere and water.
- 🌍 Earth consists of multiple layers: the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
- 🌋 The Earth's crust is the outermost layer, made up of continental and oceanic crust.
- 🌐 Continental crust is thicker (30-70 km) than oceanic crust (6-11 km).
- 💥 The Earth's crust experiences endogenic processes, which cause surface changes like earthquakes and volcanic activity.
- ⛏️ Endogenic processes include tectonism, volcanism, and seismic activity.
- 🌡️ Tectonism involves horizontal and vertical movements of Earth's layers, causing fractures and faults.
- 🔥 Volcanism is the process of magma moving from Earth's interior to the surface.
- 🌍 The mantle is the thickest layer of Earth, approximately 2,900 km deep, and protects the core.
- 🔥 The mantle is divided into the outer and inner mantle, with varying temperatures and material compositions.
- 🌡️ The outer core is a liquid layer with temperatures ranging from 4,000 to 5,000 Kelvin, while the inner core, the hottest part of Earth, reaches up to 5,500 Kelvin.
Q & A
What is the Earth's atmosphere's primary function?
-The Earth's atmosphere primarily protects life on Earth by shielding us from harmful solar radiation, making the temperature suitable for living organisms.
What are the four main layers of the Earth?
-The four main layers of the Earth are the crust, mantle, outer core, and inner core.
What is the Earth's crust, and how thick is it?
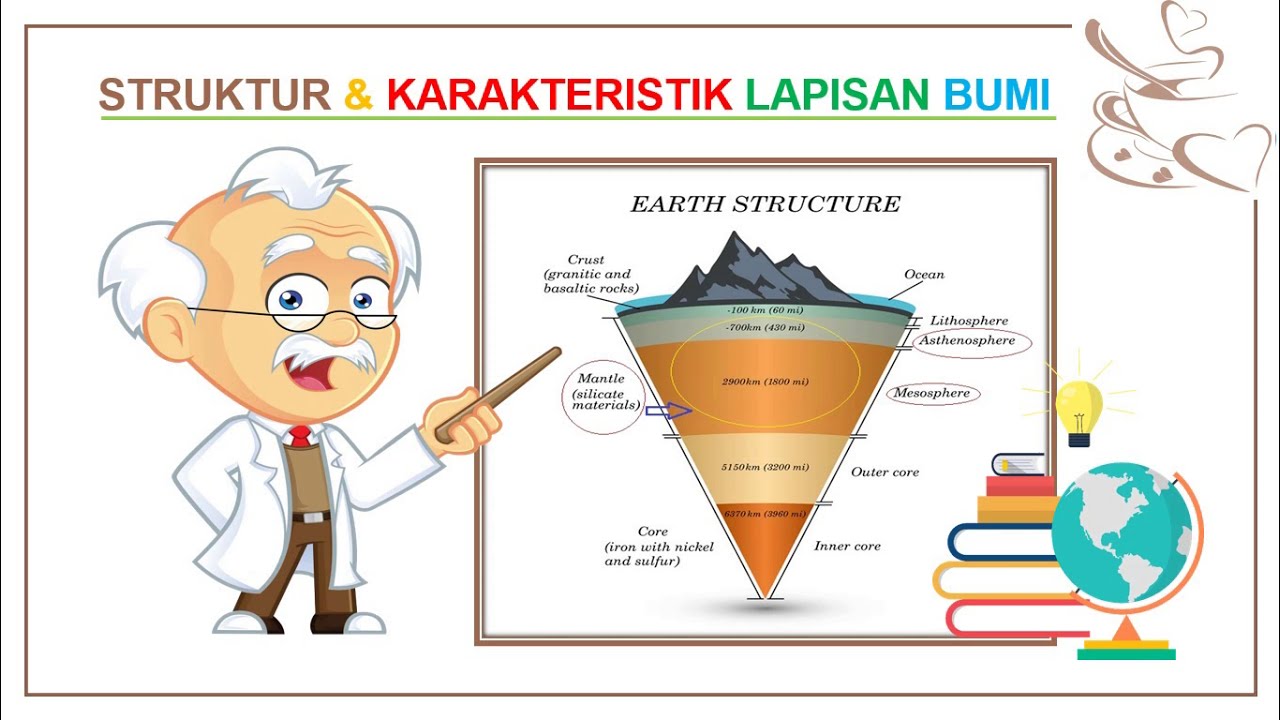
-The Earth's crust is the outermost layer of the Earth and is the thinnest compared to the other layers. It varies in thickness from 6 to 70 kilometers, with continental crust being thicker than oceanic crust.
What are the two types of Earth's crust?
-The two types of Earth's crust are the continental crust, which is found on land, and the oceanic crust, which is found under the oceans.
What is the cause of movements in the Earth's crust?
-Movements in the Earth's crust are caused by endogenic processes, which are driven by energy from within the Earth, resulting in surface changes such as mountains and hills.
What are the three types of endogenic processes?
-The three types of endogenic processes are tectonism (movement of Earth's layers), volcanism (the eruption of magma from the Earth's interior), and seismic activity (earthquakes).
What is tectonism, and how does it affect the Earth?
-Tectonism refers to the horizontal and vertical movement of Earth's layers, which can cause cracks, faults, and the formation of geological features like mountains and valleys.
How does volcanism occur?
-Volcanism occurs when magma from beneath the Earth's crust reaches the surface, causing volcanic eruptions that release molten rock, gas, and ash.
What is the difference between the Earth's outer and inner mantle?
-The outer mantle is located between 10 and 300 kilometers below the Earth's surface and contains mostly solidified metals. In contrast, the inner mantle, found between 300 and 2900 kilometers beneath the surface, consists of hotter, liquid metals.
How hot is the Earth's core, and what is it made of?
-The Earth's core is extremely hot, with temperatures ranging from 5000°C in the outer core to 5500°C in the inner core. The core is composed primarily of metal alloys, such as iron and nickel.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantVoir Plus de Vidéos Connexes
Layers of the Earth | Structure of the Earth | Educational Science Lesson

The Moving Layers of Earth and Plate Tectonics

Materi Dinamika Litosfer (Lapisan Bumi) : Materi Geografi SMA dan SIMAK UI | Part 1

Mexus education
STRUKTUR DAN KARAKTERISTIK LAPISAN BUMI

Layers of the Earth 🌎 | Crust, Mantle, Outer Core, Inner Core | Educational Science Lesson & Quiz
5.0 / 5 (0 votes)
