Gateways to Other Network
Summary
TLDRThis video lesson explains key networking concepts such as Gateways and Network Address Translation (NAT). It covers the importance of the default gateway, which allows hosts to communicate across networks, and how routers act as a gateway between internal networks and external ones like the internet. The video also highlights the role of DHCP in automatically assigning IP addresses to hosts and discusses how NAT translates private IPv4 addresses to public ones for internet access. It concludes by emphasizing the router's role in maintaining network security and enabling internet connectivity for internal devices.
Takeaways
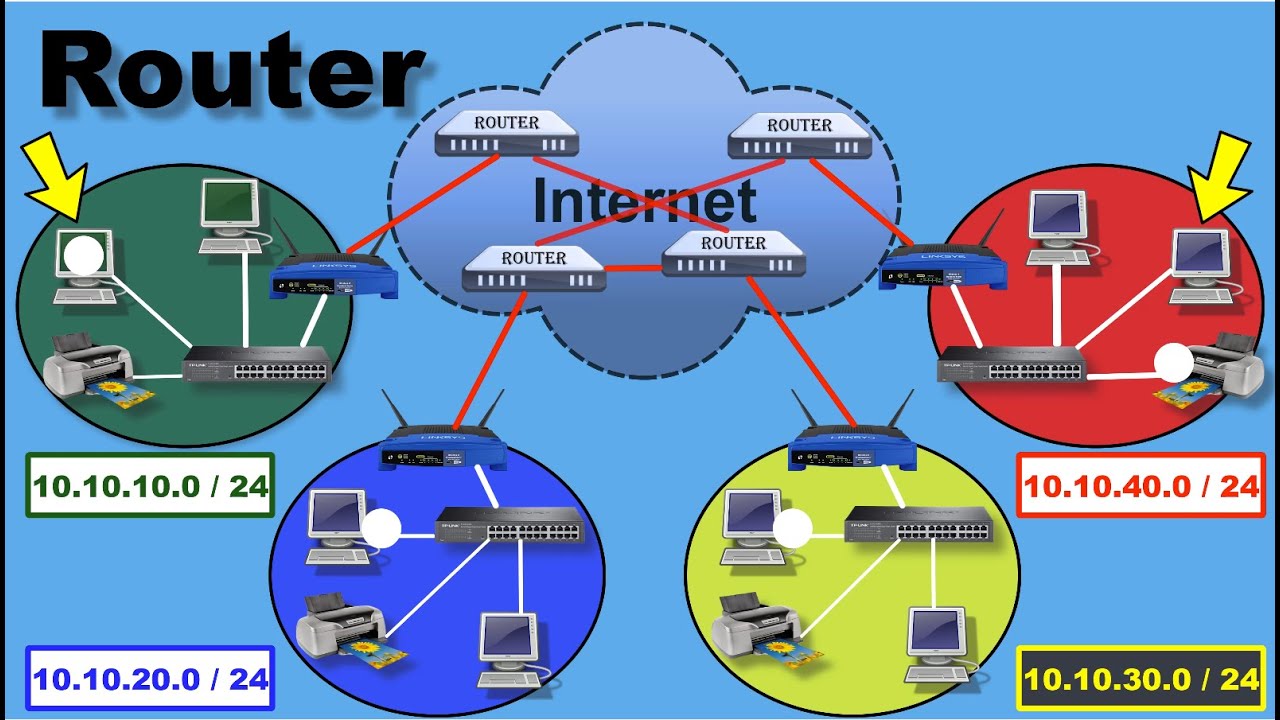
- 😀 Every host in a network must use a router as a gateway to communicate with other networks.
- 😀 A router’s interface connects to different networks, with each interface having an IPv4 address that identifies the local network.
- 😀 Hosts in a network must know the IPv4 address of the router interface that connects them to the network, known as the default gateway.
- 😀 The default gateway can be configured statically on a host or dynamically received via DHCP.
- 😀 A wireless router often acts as a DHCP server for local hosts, automatically assigning the correct IPv4 address to devices in the local network.
- 😀 Local networks usually use private IP addresses, while public, routable IP addresses are assigned to the router’s external interface by the ISP.
- 😀 The router serves as a boundary between the internal network (local) and the external network (internet).
- 😀 When a wireless router is connected to an ISP, it acts as a DHCP client to obtain the correct external IPv4 address for the internet interface.
- 😀 NAT (Network Address Translation) is used to convert private IP addresses to public IP addresses for packets sent from the local network to the internet.
- 😀 NAT also allows multiple internal IPv4 addresses to be mapped to a single public IP address, which enables internet access for devices in the local network.
Q & A
What is the purpose of a gateway in a network?
-A gateway allows hosts in one network to communicate with hosts in another network. Each host in a network needs to know the IPv4 address of the router's interface connected to its network to route messages to other networks.
What is the role of the default gateway address?
-The default gateway address is the IPv4 address of the router's interface that is used by hosts to forward packets to other networks. It can be configured statically or dynamically via DHCP.
How does DHCP work with a router?
-When a router is configured as a DHCP server, it automatically assigns the correct IPv4 address of its interface as the default gateway to hosts in the local network. It also provides other network information, such as subnet masks.
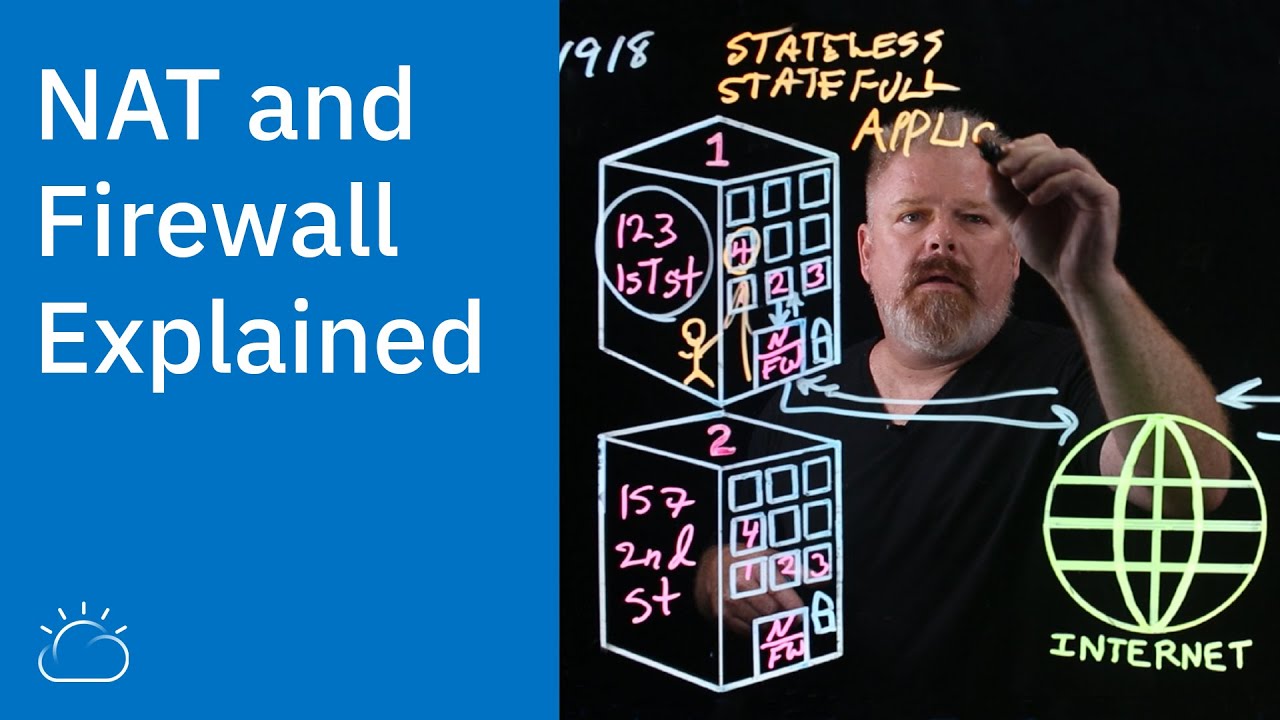
What is NAT (Network Address Translation) and how does it function?
-NAT is the process of translating private or local IPv4 addresses into public, routable IPv4 addresses. This is used to allow internal network devices to communicate with external networks like the internet.
How does a router act as a boundary between networks?
-A router functions as a boundary between different networks, such as the internal network (local network) and the external network (internet). It handles the translation of IP addresses and routing of traffic between these networks.
What is the difference between internal and external networks in the context of a router?
-The internal network refers to the local network behind the router, while the external network refers to the broader internet or external networks that the router connects to via the ISP.
What is the typical function of a wireless router's DHCP server?
-A wireless router's DHCP server provides IP addresses, subnet masks, and the default gateway address to all local hosts connected to the router, whether by Ethernet or wireless connection.
Why is NAT important for network security?
-NAT helps improve network security by keeping internal network addresses private and inaccessible from the outside internet. Only the router's public IP address is exposed to the external network.
What happens when a router receives a public IP address from an ISP?
-When a router receives a public IP address from an ISP, it enables the router to send and receive data packets on the internet. The router can then translate between private internal addresses and the public IP address for communication.
How does NAT handle incoming packets?
-For incoming packets, NAT allows the router to translate multiple internal private IP addresses into the same public IP address. Only packets destined for external networks need to be translated, with the router replacing the internal source IP with its own public IP address.
Outlines

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantMindmap

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantKeywords

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantHighlights

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenantTranscripts

Cette section est réservée aux utilisateurs payants. Améliorez votre compte pour accéder à cette section.
Améliorer maintenant5.0 / 5 (0 votes)